Cluster Load Rebalancing (EMQX Enterprise)
Task Target
How to rebalance MQTT connections.
Why Need Load Rebalancing
Cluster load rebalancing is the act of forcibly migrating client connections and sessions from one set of nodes to another. It will automatically calculate the number of connections that need to be migrated to achieve node balance, and then migrate the corresponding number of connections and sessions from high-load nodes to low-load nodes, thereby achieving load balancing between nodes. This operation is usually required to achieve balance after a new join or restart of a node.
The value of rebalancing mainly has the following two points:
- Improve system scalability: Due to the persistent nature of MQTT connections, connections to the original nodes will not automatically migrate to the new nodes when the cluster scales. To address this, you can use the load rebalancing feature to smoothly transfer connections from overloaded nodes to newly-added ones. This process ensures a more balanced distribution of load across the entire cluster and enhances throughput, response speed, and resource utilization rate.
- Reduce O&M costs: For clusters with unevenly distributed loads, where some nodes are overloaded while others remain idle, you can use the load rebalancing feature to automatically adjust the load within the cluster. This helps achieve a more balanced distribution of work and reduces operation and maintenance costs.
For EMQX cluster load rebalancing, please refer to the document: Rebalancing.
TIP
The cluster load rebalancing requirements EMQX Enterprise must be greater than or equal to 4.4.12
How to Use Load Rebalancing
The corresponding CRD of the cluster rebalancing in EMQX Operator is Rebalance, and its example is as follows:
apiVersion: apps.emqx.io/v1beta4
kind: Rebalance
metadata:
name: rebalance-sample
spec:
instanceName: emqx-ee
rebalanceStrategy:
connEvictRate: 10
sessEvictRate: 10
waitTakeover: 10
waitHealthCheck: 10
absConnThreshold: 100
absSessThreshold: 100
relConnThreshold: "1.1"
relSessThreshold: "1.1"For Rebalance configuration, please refer to the document: Rebalance reference.
Test Load Rebalancing
Cluster Load Distribution Before Rebalancing
Before Rebalancing, we built a cluster with unbalanced load. And use Grafana + Prometheus to monitor the load of EMQX cluster:
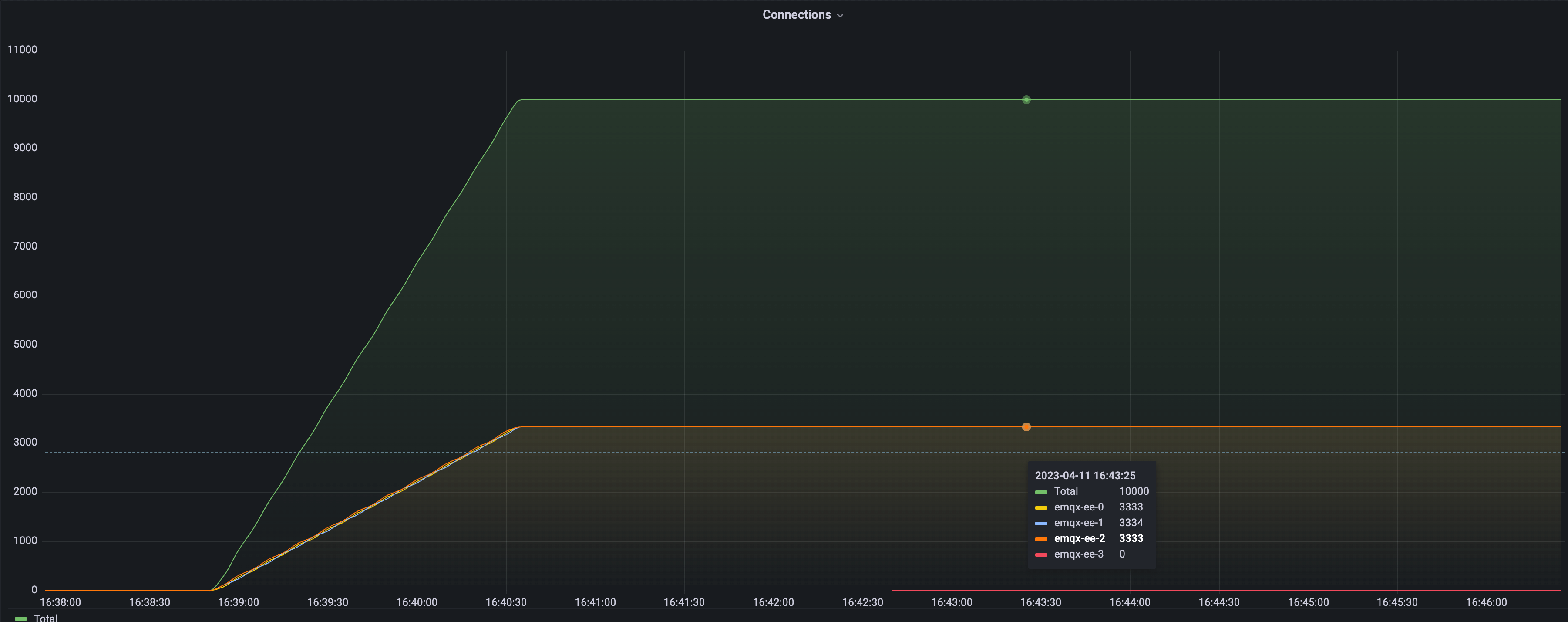
It can be seen from the figure that there are four EMQX nodes in the current cluster, three of which carry 10,000 connections, and the remaining one has 0 connections. Next, we will demonstrate how to perform a rebalancing operation so that the load of the four nodes reaches a balanced state. Next, we will demonstrate how to perform a rebalancing operation so that the load of the four nodes reaches a balanced state.
- Submit the Rebalance task
apiVersion: apps.emqx.io/v1beta4
kind: Rebalance
metadata:
name: rebalance-sample
spec:
instanceName: emqx-ee
rebalanceStrategy:
connEvictRate: 10
sessEvictRate: 10
waitTakeover: 10
waitHealthCheck: 10
absConnThreshold: 100
absSessThreshold: 100
relConnThreshold: "1.1"
relSessThreshold: "1.1"Save the above content as: rebalance.yaml, and execute the following command to submit the Rebalance task:
$ kubectl apply -f rebalance.yaml
rebalance.apps.emqx.io/rebalance-sample createdExecute the following command to view the rebalancing status of the EMQX cluster:
$ kubectl get rebalances rebalance-sample -o json | jq '.status.rebalanceStates'
{
"state": "wait_health_check",
"session_eviction_rate": 10,
"recipients":[
"emqx-ee@emqx-ee-3.emqx-ee-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
],
"node": "emqx-ee@emqx-ee-0.emqx-ee-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"donors":[
"emqx-ee@emqx-ee-0.emqx-ee-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"emqx-ee@emqx-ee-1.emqx-ee-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"emqx-ee@emqx-ee-2.emqx-ee-headless.default.svc.cluster.local"
],
"coordinator_node": "emqx-ee@emqx-ee-0.emqx-ee-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"connection_eviction_rate": 10
}For a detailed description of the rebalanceStates field, please refer to the document: rebalanceStates reference.
Wait for the Rebalance task to complete:
$ kubectl get rebalances rebalance-sample
NAME STATUS AGE
rebalance-sample Completed 62sThere are three states of Rebalance: Processing, Completed, and Failed. Processing indicates that the rebalancing task is in progress, Completed indicates that the rebalancing task has been completed, and Failed indicates that the rebalancing task failed.
Cluster Load Distribution After Rebalancing
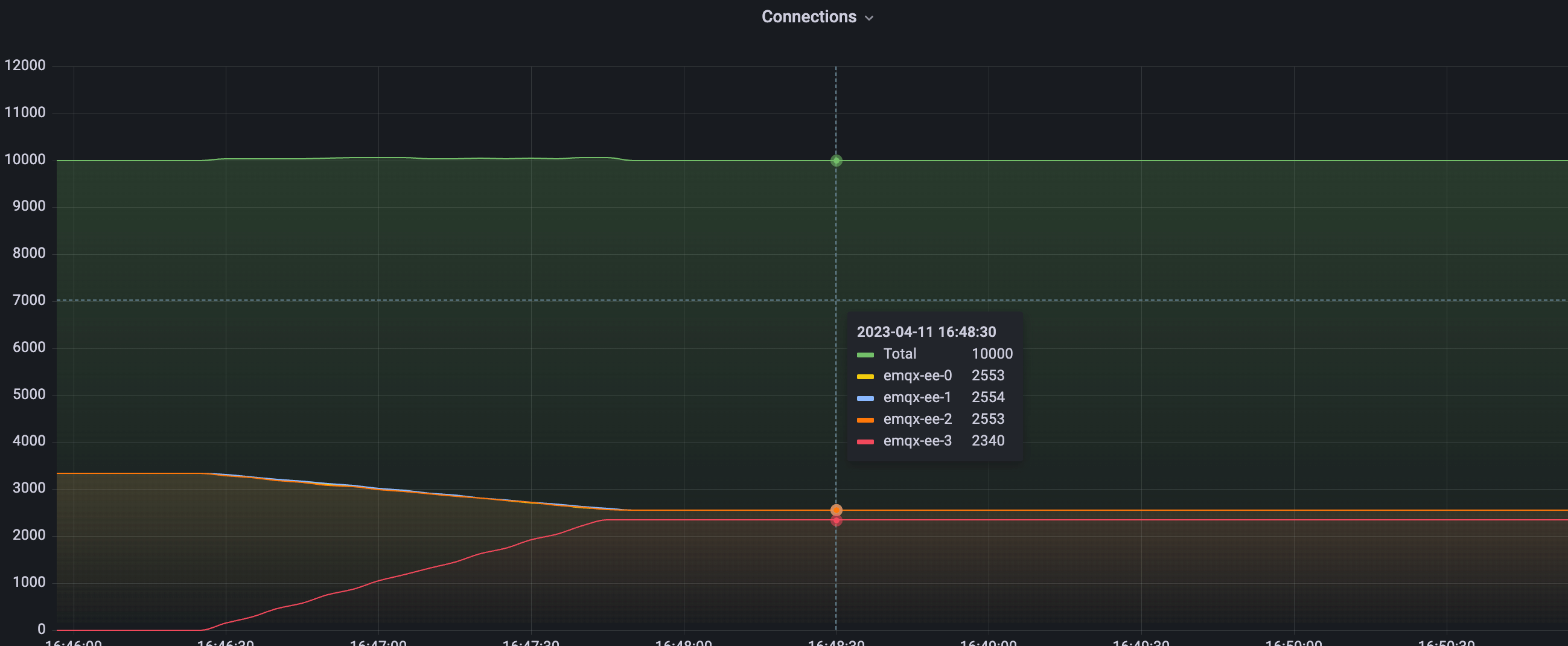
The figure above shows the cluster load after Rebalance is completed. It can be seen from the graph that the entire Rebalance process is very smooth. It can be seen from the data that the total number of connections in the cluster is still 10,000, which is consistent with that before Rebalance. The connections of four nodes has changed, and some connections of three nodes have been migrated to newly expanded nodes. After rebalancing, the loads of the four nodes remain stable, and the connections is close to 2,500 and will not change.
According to the conditions for the cluster to reach balance:
avg(source node connection number) < avg(target node connection number) + abs_conn_threshold
or
avg(source node connection number) < avg(target node connection number) * rel_conn_thresholdSubstituting the configured Rebalance parameters and the number of connections can calculate avg(2553 + 2553+ 2554) < 2340 * 1.1, so the current cluster has reached a balanced state, and the Rebalance task has successfully rebalanced the cluster load.