Flow Designer
Flow Designer is a powerful visual tool based on an earlier version of the visual viewing tool, Flows. It adds capabilities for creating and editing, aiming to make the configuration of data processing and integration simpler and more efficient.
Features
Flow Designer is a feature-rich and user-friendly tool that helps users process and integrate data more efficiently, drive business innovation, and improve the visibility and control of data management. Its main features and advantages include:
- Intuitive Visual Interface: Users can easily create, adjust, and customize data processing workflows using intuitive drag-and-drop and connecting features. This means that even users without programming experience can quickly get started and design complex data integration logic.
- Fast Real-time Processing: Flow Designer enables users to establish real-time processing workflows for messages and events within minutes. This helps businesses respond more quickly to emerging data and events, supporting real-time business needs.
- Extensive Integration Capabilities: Supports seamless integration with over 40 types of data systems, offering users flexible data connection and exchange options. Regardless of where your data resides, Flow Designer can help you achieve integration.
- Unified Management and Monitoring: Users can clearly manage the entire data integration process through a unified view, understanding the status and performance of each processing node. This helps in real-time monitoring and tracking of data flows, ensuring high reliability and integrity of data.
- EMQX Data Processing Capabilities: The underlying layer of Flow Designer utilizes Rule SQL and Sink/Source, inheriting EMQX's powerful data processing and performance advantages. Users can freely switch between the UI and SQL editors, providing a simpler, faster experience while retaining the flexibility of SQL editing. This means that users don't need to deeply understand EMQX Rule SQL syntax to leverage its powerful data processing capabilities for business innovation and data-driven decision-making.
In summary, it's an indispensable component in IoT application development, supporting various data processing and fast configuration needs.
Get Started
Flow Designer is located under the Dashboard Data Integration menu. This page includes all data processing flows created by the Rule Engine, Webhook, and Flow Designer.
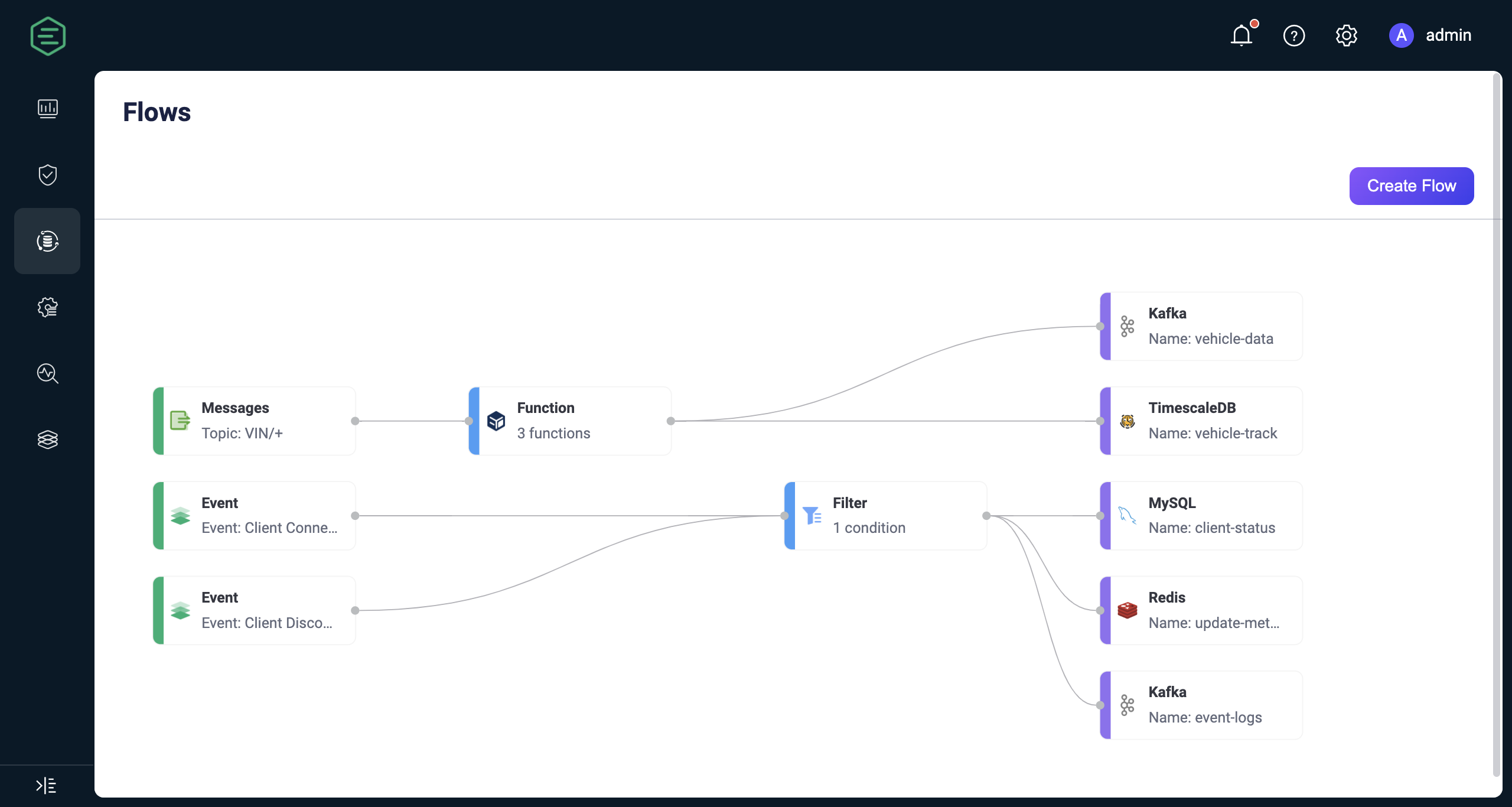
Flow describes the processing workflows for client messages and events, consisting of data sources, data processing and filtering, and data outflow. Clicking the Create button allows you to enter the Flow creation page for visual configuration. You can drag and drop to select the nodes needed for each step and connect them to implement the workflow.
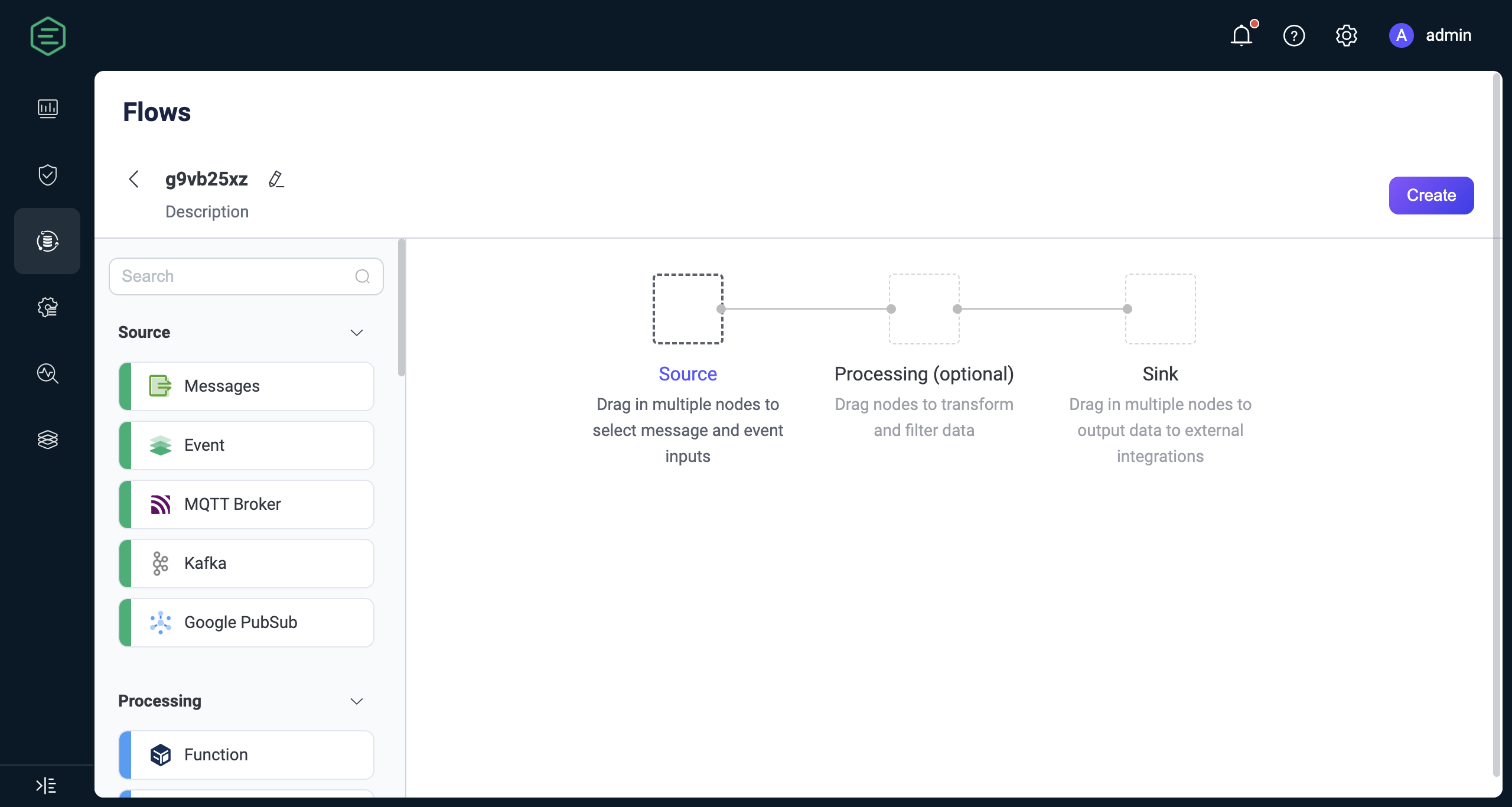
Source
The data input supports messages, events, or messages flowing from external data systems. A Flow must contain at least one Source node, and multiple data input nodes can be supported simultaneously. Currently supported Sources include:
- Messages: Specified through topics and topic wildcards for client-published messages
- Events: Supports all client events within EMQX; refer to Client Events.
- External Data Systems:
Processing
Use function and filter nodes for data processing and filtering. This step is optional, and a Flow can support at most one function and one filter node:
- Functions: Supports all SQL built-in functions of the rule engine.
- Filters: Supports comparison filtering for data fields coming from the Source; supported comparison operations include
>, <, <=, >=, <>, !=, =, =~
In addition to visual form editing, Processing nodes also support switching to expression mode to edit using Rule SQL syntax. Filter nodes can only be connected after functions, meaning data must first be processed and then filtered.
Sink
Outputs the data sources and processing results to specific nodes and external data systems. A Flow must contain at least one Sink node, and supported Sink nodes include:
- Message Republishing: Publishes messages to locally specified MQTT topics.
- Console Output: Prints messages to logs for debugging.
- External Data Systems: Supports over 40 types of data systems, such as MySQL and Kafka; refer to Data Integration.