# Stream Data into Kafka
Setup a Kafka, taking Mac OSX for instance:
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/kafka/2.8.0/kafka_2.13-2.8.0.tgz tar -xzf kafka_2.13-2.8.0.tgz cd kafka_2.13-2.8.0 # start Zookeeper ./bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties # start Kafka ./bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.propertiesCopied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Create topics for Kafka:
$ ./bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic testTopic --create Created topic testTopic. .. note:: Kafka topics should be created before creating the kafka rule, or the rule creation would not success.Copied!
2
3
4
5
Create a rule:
Go to EMQX Dashboard (opens new window), select the "rule" tab on the menu to the left.
Select "message.publish", then type in the following SQL:
SELECT * FROM "message.publish"Copied!
2
3
4
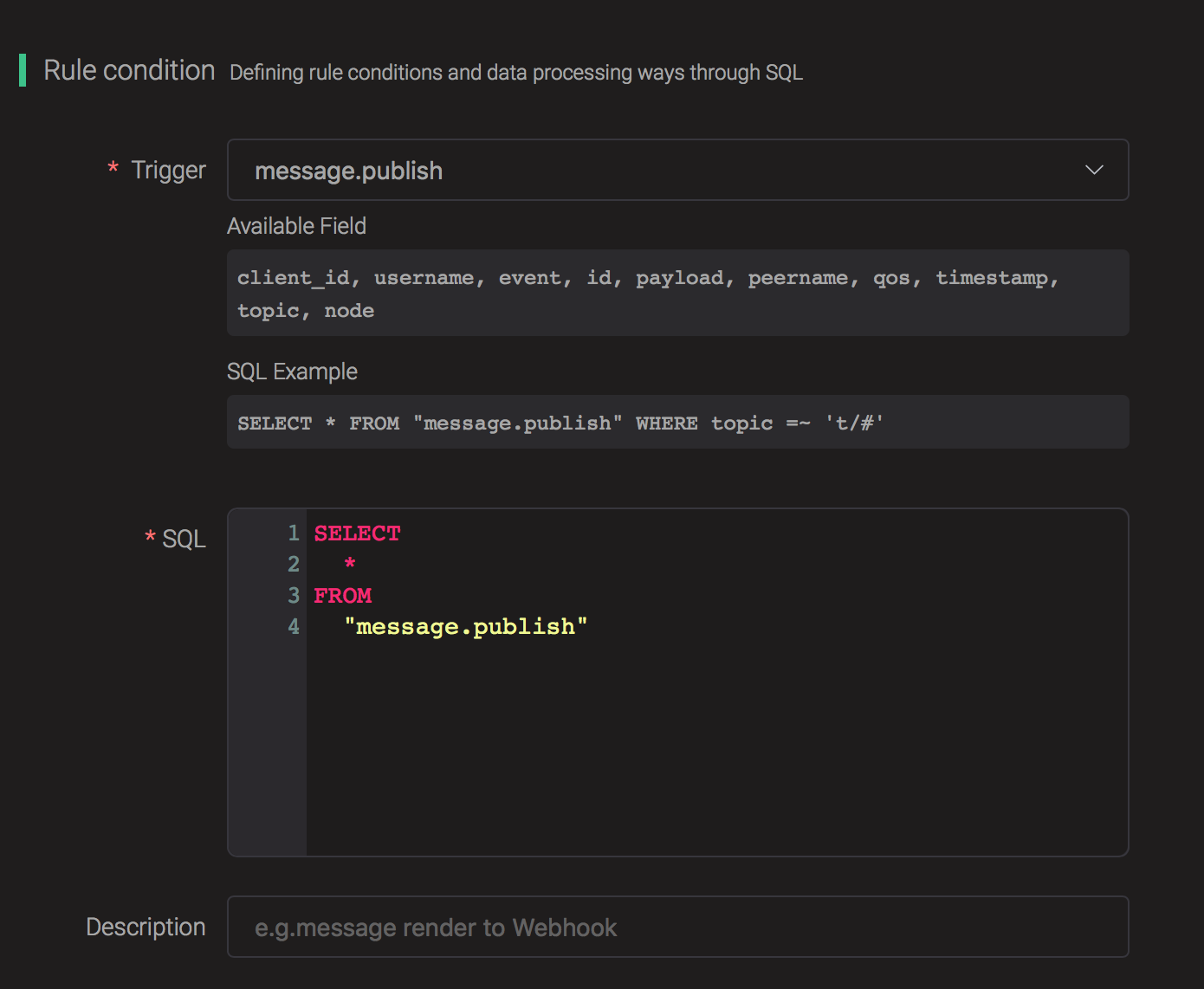
Bind an action:
Click on the "+ Add" button under "Action Handler", and then select "Data bridge to Kafka" in the pop-up dialog window.
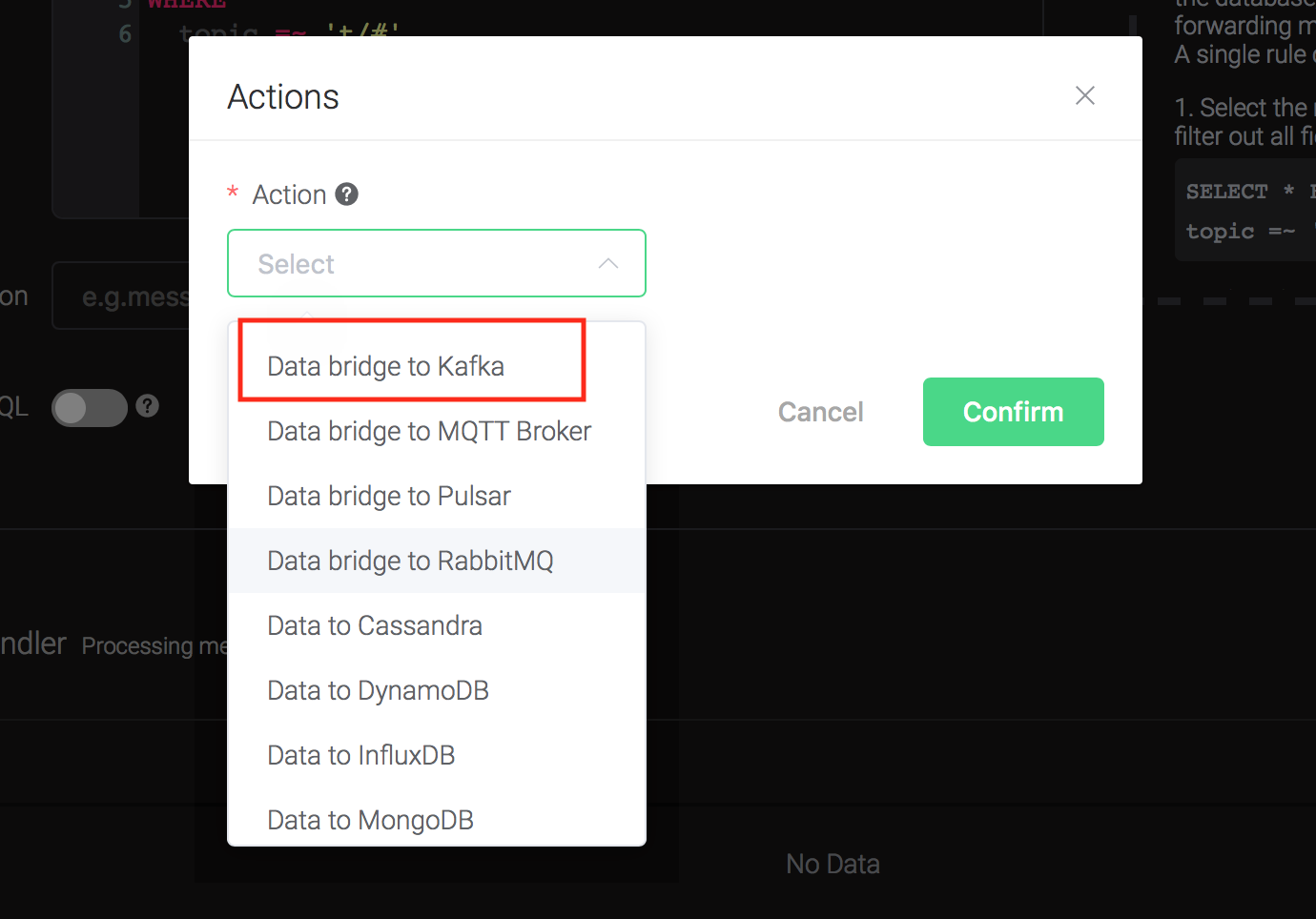
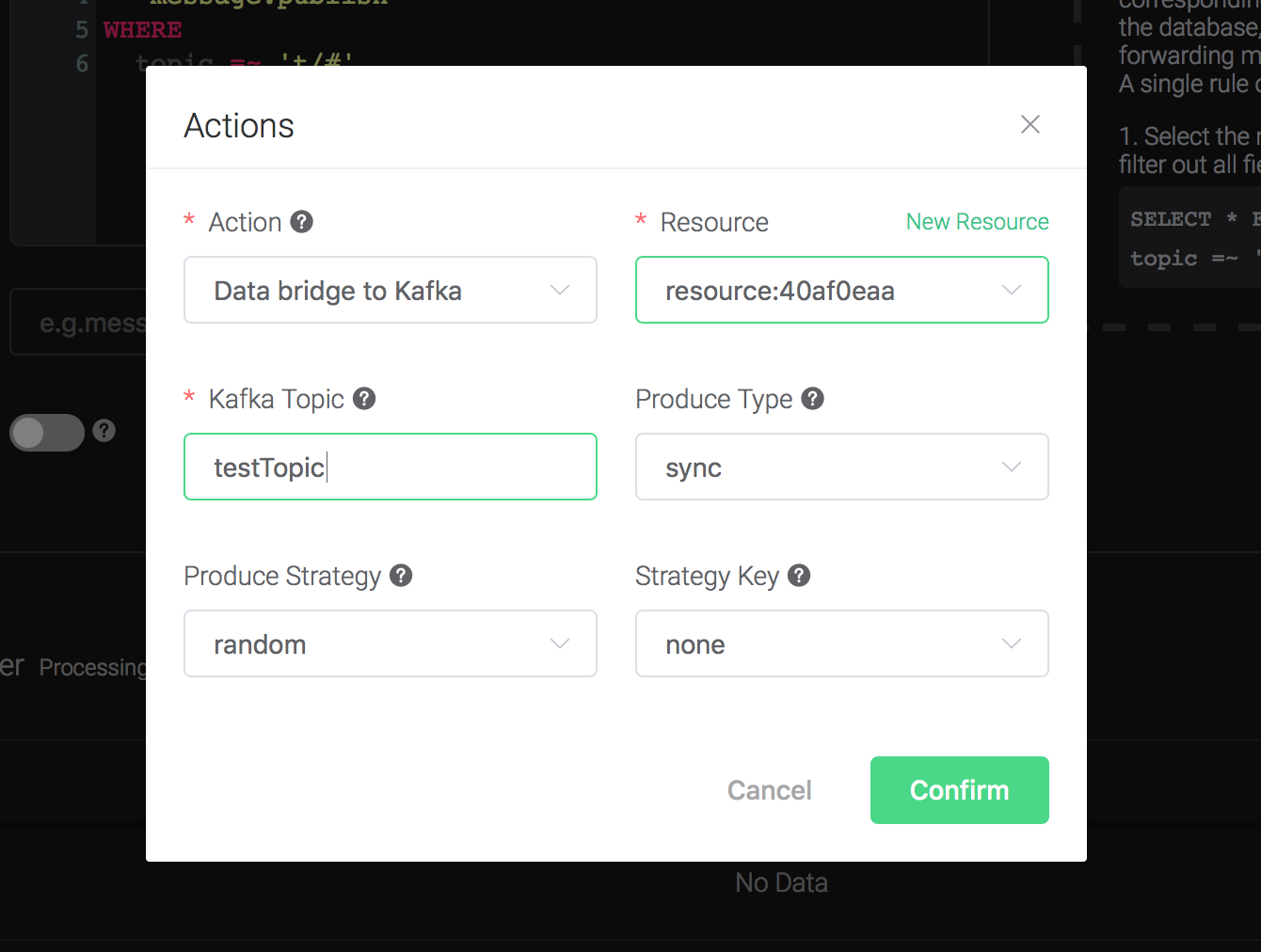
Fill in the parameters required by the action:
Two parameters is required by action "Data to Kafka":
1). Kafka Topic
2). Bind a resource to the action. Since the dropdown list "Resource" is empty for now, we create a new resource by clicking on the "New Resource" to the top right, and then select "Kafka":
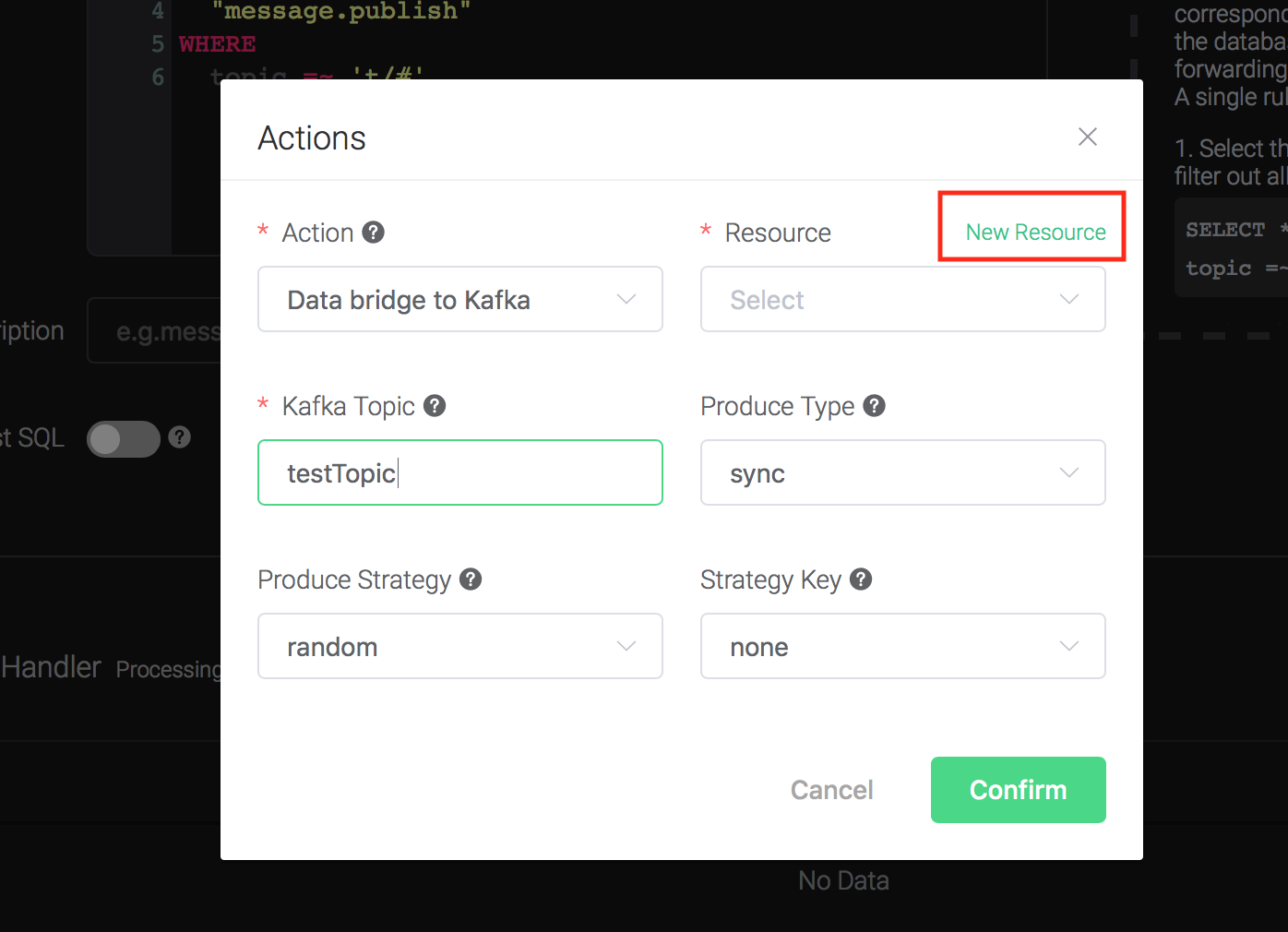
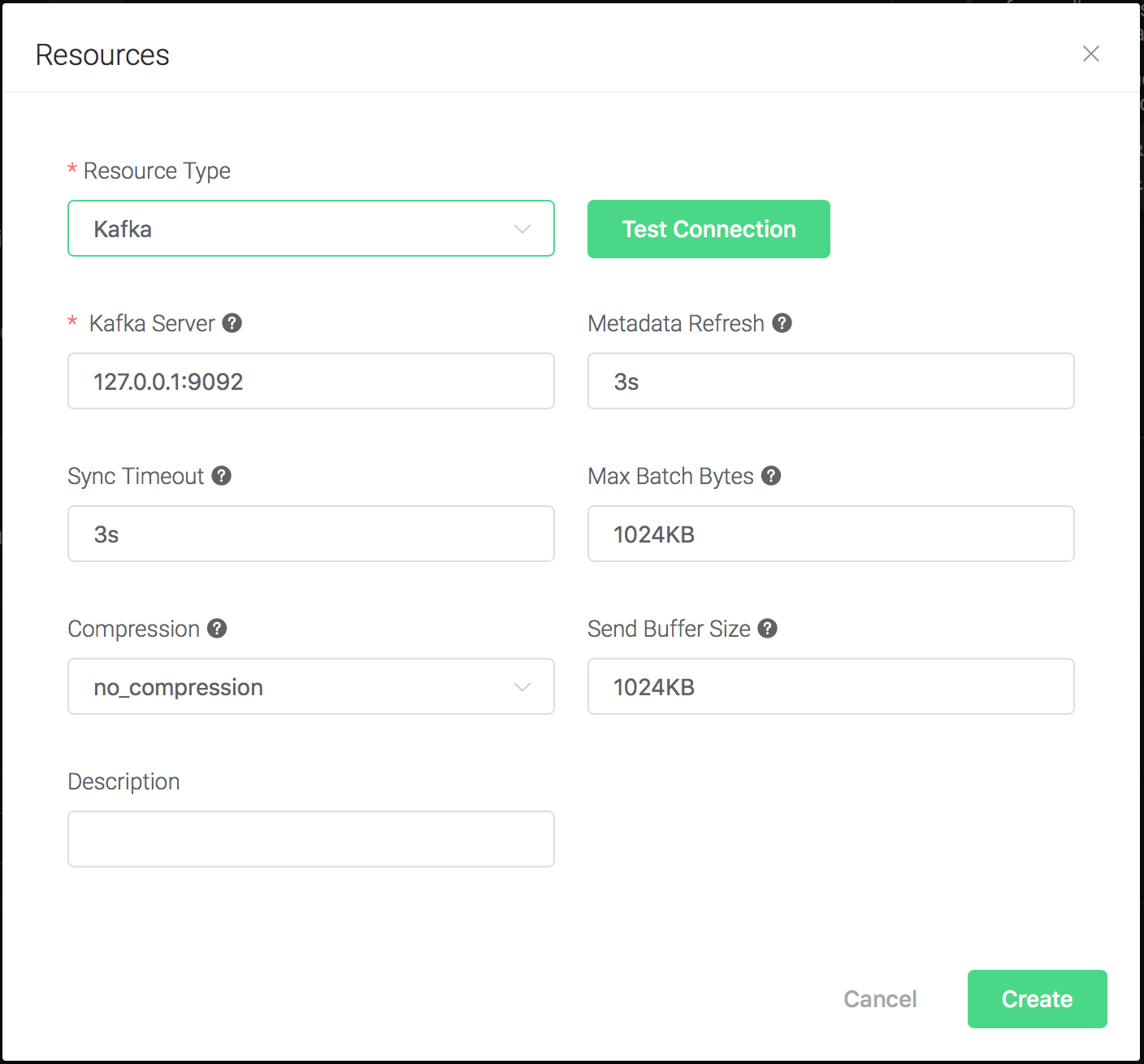
Configure the resource:
Set the "Kafka Server" to "127.0.0.1:9092" (multiple servers should be separated by comma), and keep all other configs as default, and click on the "Testing Connection" button to make sure the connection can be created successfully, and then click on the "Create" button.
Back to the "Actions" dialog, and then click on the "Confirm" button.
Back to the creating rule page, then click on "Create" button. The rule we created will be show in the rule list:
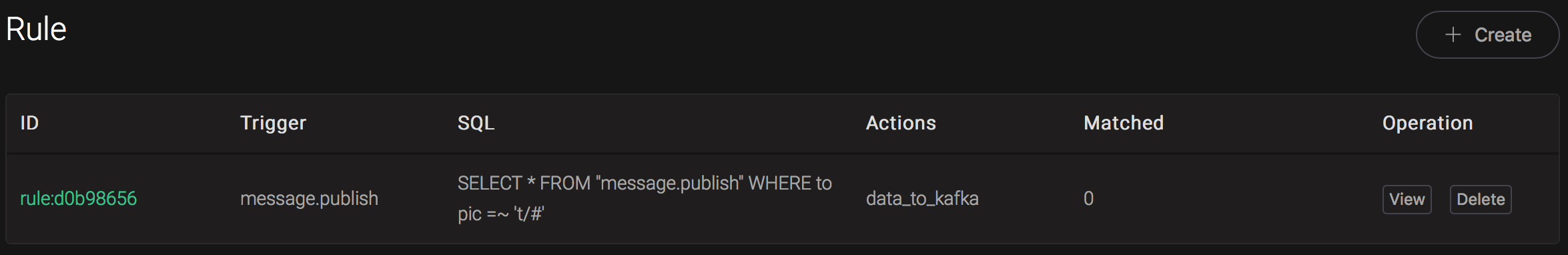
We have finished, testing the rule by sending an MQTT message to emqx:
Topic: "t/1" QoS: 0 Retained: false Payload: "hello"Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
Then inspect Kafka by consume from the topic:
$ ./bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server 127.0.0.1:9092 --topic testTopic --from-beginningCopied!
And from the rule list, verify that the "Matched" column has increased to 1:

# Authentication
This section describes how one can configure a Kafka resource to use an
authentication mechanism. The EMQX Kafka resource supports the following
authentication methods for Kafka: NONE (no authentication needed),
SCRAM_SHA_256, SCRAM_SHA_512, and Kerberos. We refer to the
Kafka documentation (opens new window)
for how to set up Kafka to use these different authentication mechanisms. The
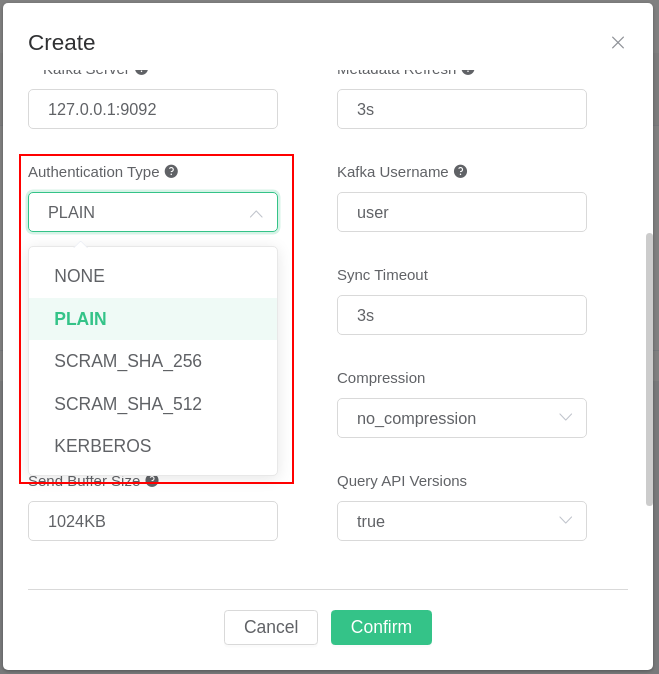
authentication mechanism used can be selected under "Authentication Type" (see
image below). Depending on which authentication type is selected, different
fields will appear.
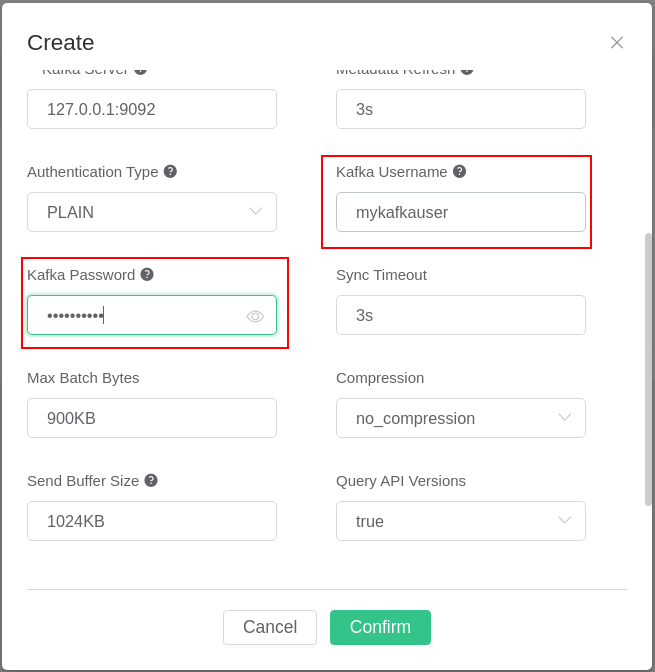
The fields for the authentication methods PLAIN, SCRAM_SHA_256, and SCRAM_SHA_512 are the Kafka username and password (see picture below).
The Kerberos authentication method is slightly more complex to configure. Before the Kafka resource is set up with Kerberos authentication, it is assumed that you have a Kafka instance set up with Kerberos authentication and the Keytab file for a Kerberos principal (a.k.a. user) with rights to access the Kafka instance. We refer to the documentation of Kafka (opens new window) and Kerberos (opens new window) for how to set up Kerberos authentication for Kafka. You might also find the Kafka and Kerberos example from the brod_gssapi project (opens new window) useful. Here is a list of common pitfalls that is worth being aware of before proceeding:
- One must install Kerberos libraries, the SASL library, and the SASL/GSSAPI
Kerberos plugin on the hosts running EMQX for Kerberos authentication to work
correctly. EMQX's official Docker images contain the needed libraries. If you
are building EMQX by yourself, you must ensure that the required libraries
are installed before the build starts. If the build process does not find the
libraries necessary for Kerberos authentication, a warning will be printed
when building, and support for Kerberos authentication will be disabled. On
Centos 7, the following packages need to be installed
libsasl2,libsasl2-dev,krb5-workstation,cyrus-sasl-devel,cyrus-sasl,cyrus-sasl-gssapiandkrb5-server. On Ubuntu 22.04, the following packages need to be installedkrb5-kdc,krb5-admin-server,libkrb5-dev,libsasl2-devandlibsasl2-modules-gssapi-mit. Please refer to EMQX's official Docker files (opens new window) for which packages are required on other platforms. - The Kerberos configuration file
/etc/krb5.confneeds to be in sync between all Kerberos clients and servers. One must copy the/etc/krb5.conffile to all the nodes in a multi-node cluster. Please refer to the Kerberos documentation (opens new window) for how to configure/etc/krb5.conf. - Kerberos is time sensitive, so the hosts running EMQX, the Kerberos Key Distribution Center, and Kafka must have their time synchronized.
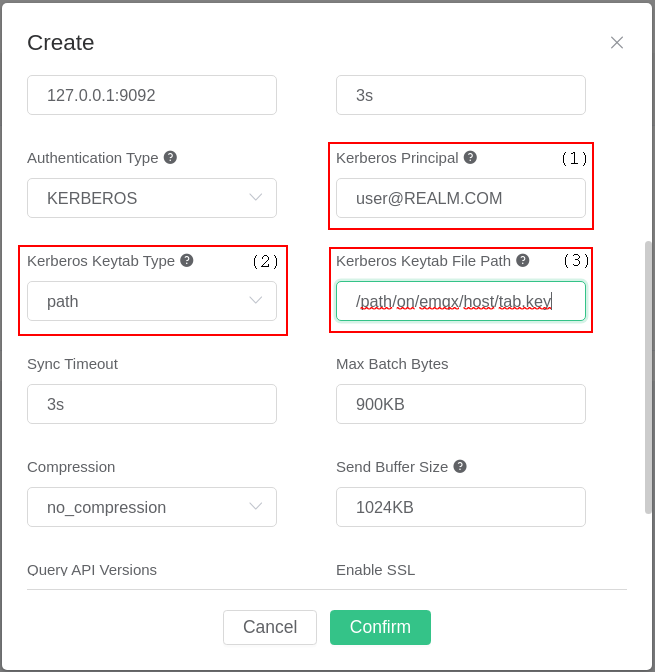
When configuring a Kafka resource with Kerberos authentication, one has to set a Kerberos principal ((1) in the image below) and a corresponding Kerberos Keytab ((2) and (3) in the image below). There are two options for specifying the Keytab file ((2) in the image below). The Keytab can be uploaded to the host directly from the configuration UI, or one can specify a path to the Keytab file on the host. The field marked with (3)'s type changes depending on how one sets the field marked with (2). If a Keytab path is specified and EMQX is set up as a multi-node cluster, one must upload the Keytab file to the specified path on all nodes.
# Kafka Headers
Starting from EMQX Enterprise Version 4.4.15, the Kafka action supports Kafka Headers:
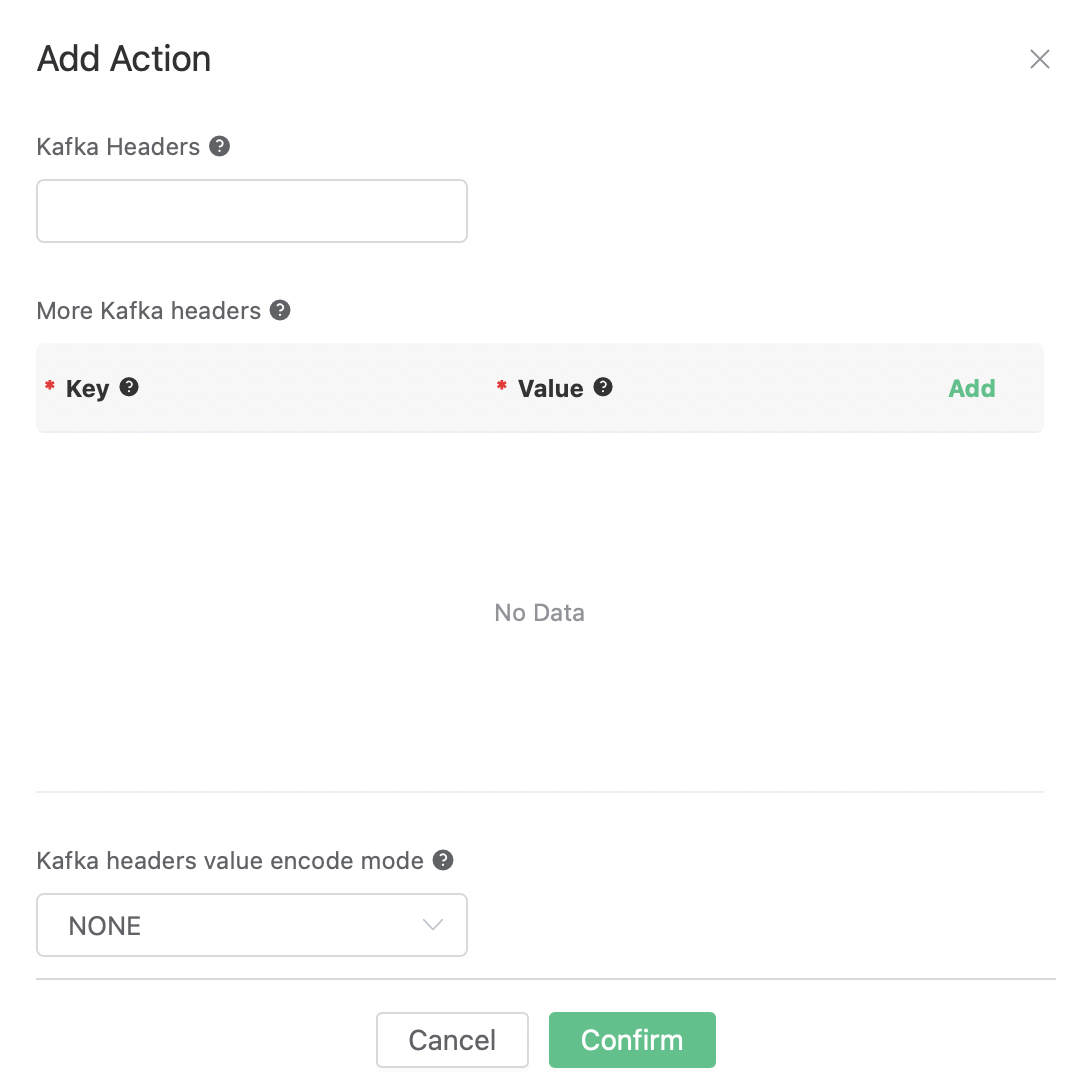
Three fields are added as shown in the figure: Kafka Headers, More Kafka headers, and Kafka headers value encode mode.
# Kafka Headers:
This field is used to directly send a variable output by the rule as Kafka Headers. This field is optional.
For example, we can fill in ${pub_props}, so for the rules that handles MQTT messages, the Kafka action will send all PUBLISH Properties of the MQTT message as Kafka Headers.
# More Kafka headers:
This field provides a method to add one or more Kafka headers in the form of key-value pairs. The key and value can use placeholders in the format of ${var}. This field is optional.
For example, we can add a key-value pair with key clientid and value ${clientid}. When a MQTT client with the client ID foo triggers the action, it will send out a Kafka header clientid: foo.
# Kafka headers value encode mode:
According to the specification (opens new window), the key of Kafka Headers must be in string format(utf8), and its value must be in binary or string format.
So if the specified key in the "Kafka Headers" and "More Kafka Headers" fields is not in string format, or the specified value is not in binary or string format, the Kafka action of EMQX needs to do something before sending the headers out.
There're optional values: NONE or JSON:
NONE: Only headers with a string key and a binary or string value will be sent, all headers with other key and value formats will be discarded.
JSON: Before sending any headers, try to encode the
valueto a JSON string. If the encoding is successful then send it, otherwise discard it. In addition, thekeymust be in string format, otherwise it will be discarded.
