# Kafka Consumer Group
The Kafka consumer group uses external Kafka as a message queue, which can convert consumer messages from Kafka into MQTT messages and publish them in EMQX.
# Set Up Kafka
TIP
Kafka consumer groups do not support Kafka versions below 0.9.
Before creating resources, you must create Kafka topics in advance, otherwise an error will be prompted.
- Set up the Kafka environment, taking MacOS X as an example:
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/kafka/2.8.0/kafka_2.13-2.8.0.tgz tar -xzf kafka_2.13-2.8.0.tgz cd kafka_2.13-2.8.0 # Start Zookeeper $ ./bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties # Start Kafka $ ./bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.propertiesCopied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
- Create a Kafka topic:
./bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic testTopic --createCopied!
# Create Module
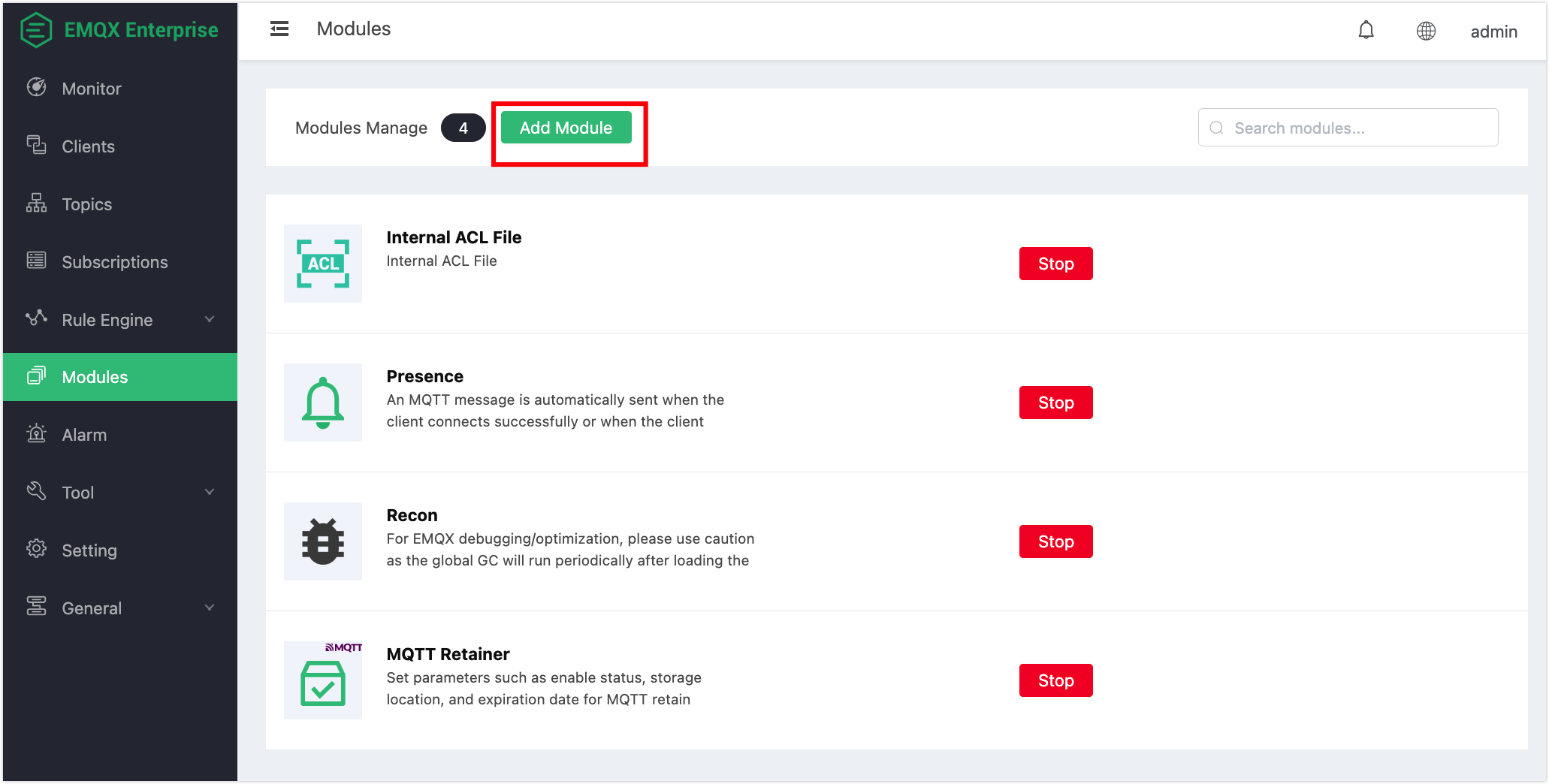
- Open EMQX Dashboard (opens new window), click Modules in the left-navigation menu, and select Add Module.
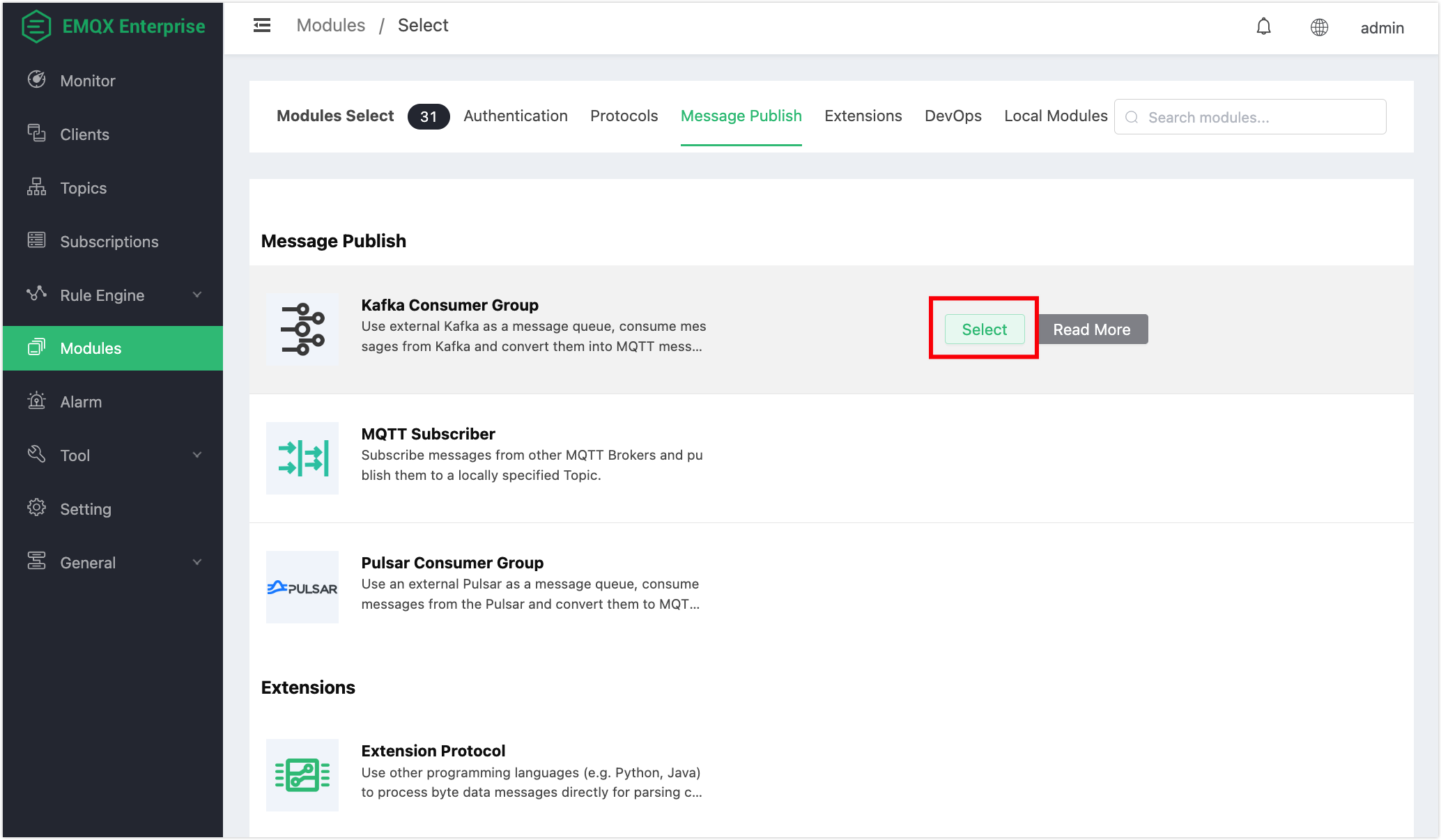
- Under the Message Publish tab, select the Kafka Consumer Group module:
- Configure the parameters:
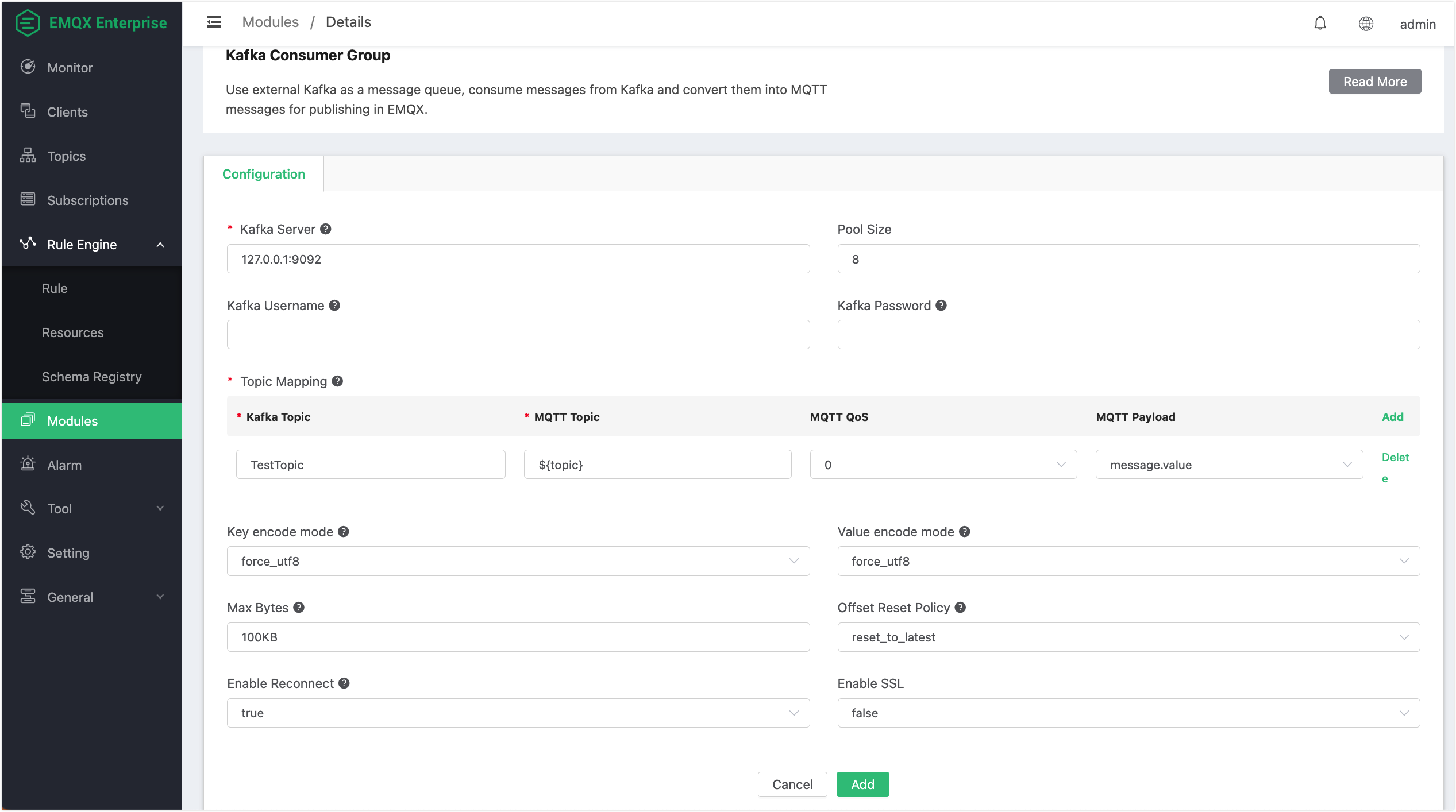
- Kafka Server: Enter the Kafka server address; the default is
127.0.0.1:9092. - Pool Size: Kafka consumer connection pool size.
- Kafka Username and Password: Username and password to connect to the Kafka server.
- Topic Mapping:
Kafka Topic: The topic from which Kafka messages will be forwarded; in this example, you can use the Kafka topic created earlier,
TestTopic.MQTT Topic: The topic of the received MQTT message; you can specify a fixed topic, or dynamically construct the topic from Kafka messages using
${field}template syntax. Currently, the following fields can be used:value: The message content. If the message is in JSON format,${value.field}can be used to extract the value of the specified field.ts_type: The message operation type.ts: The message timestamp in milliseconds, indicating when the message was created.topic: The Kafka Topic where the message is from.offset: The message offset in the Partition, used to uniquely identify a message.key: The message Key.headers: The message headers, which may contain additional metadata.
MQTT QoS: MQTT message quality of service.
MQTT Payload: Optionally, you can use either Kafka
message.valueor the entire message information.
- Key encode mode: Binary key encoding mode, UTF-8, or base64; encoding method for the key in the message. If the key value is non-string or may cause character encoding exceptions, it is recommended to use base64 mode.
- Value encode mode: Binary value encoding mode, UTF-8, or base64; encoding method for the value in the message. If the value is non-string or may cause character encoding exceptions, it is recommended to use base64 mode.
- Max Bytes: Kafka Max Bytes (maximum number of bytes to consume from Kafka at a time).
- Offset Reset Policy: The policy for resetting the offset where Kafaka consumers start to read from a Kafka topic partition. Optional values:
reset_to_latestandreset_by_subscriber. - Enable Reconnect: Whether the Kafka consumer should automatically reconnect.
- Enable SSL: SSL connection parameters.
After clicking Add, the module will be added successfully.
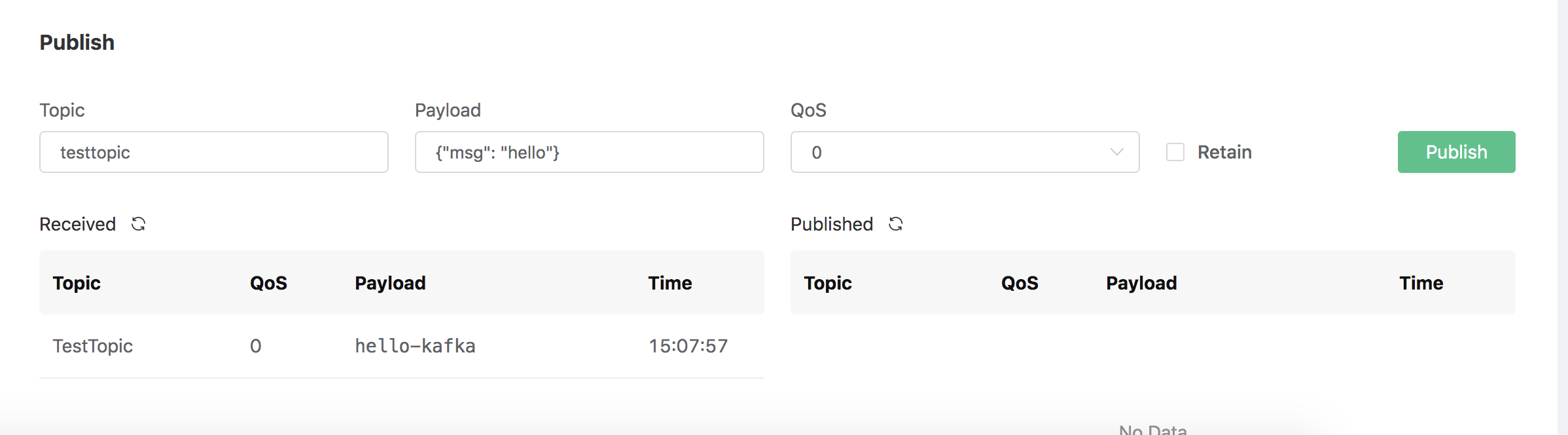
# Test Message Publish
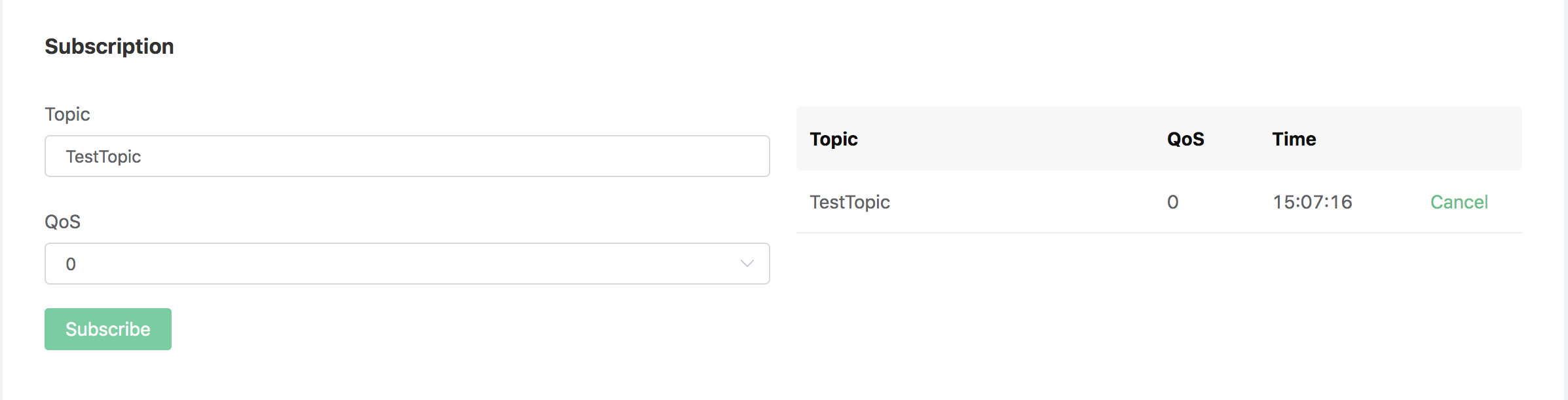
After the resource is created, you can use Dashboard's Websocket tool to subscribe to the MQTT topic "TestTopic":
Use the kafka command line to produce a message:
./bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic TestTopicCopied!
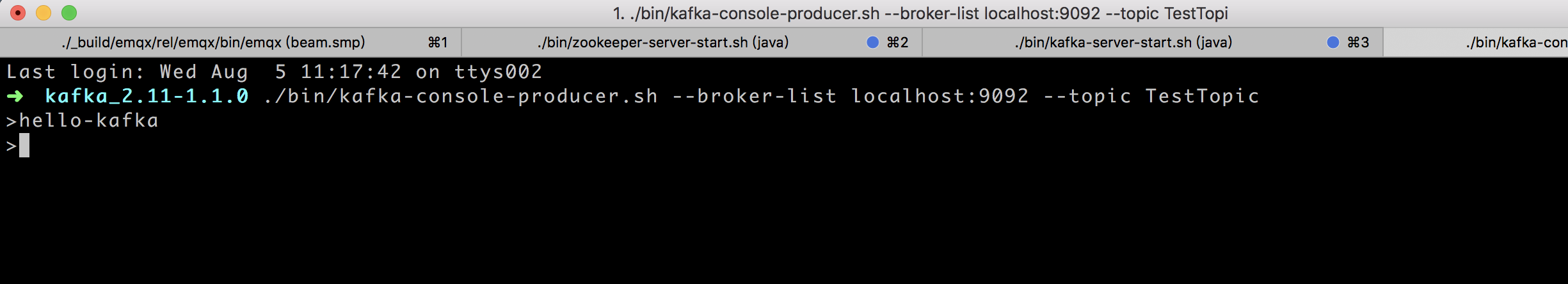
The Websocket tool of Dashboard will receive the message "hello-kafka" produced by Kafka: