Ingest MQTT Data into GCP Pub/Sub
Google Cloud Pub/Sub is an asynchronous messaging service designed to achieve extremely high reliability and scalability. EMQX supports seamless integration with Google Cloud Pub/Sub for real-time extraction, processing, and analysis of MQTT data. It can push data to various Google Cloud services such as Cloud Functions, App Engine, Cloud Run, Kubernetes Engine, and Compute Engine. Alternatively, it can also distribute data from Google Cloud to MQTT, helping users rapidly build IoT applications on GCP.
This page provides a comprehensive introduction to the data integration between EMQX and GCP Pub/Sub with practical instructions on creating and validating the data integration.
How It Works
GCP Pub/Sub data integration is an out-of-the-box feature of EMQX designed to help users seamlessly integrate MQTT data streams with Google Cloud and leverage its rich services and capabilities for IoT application development.
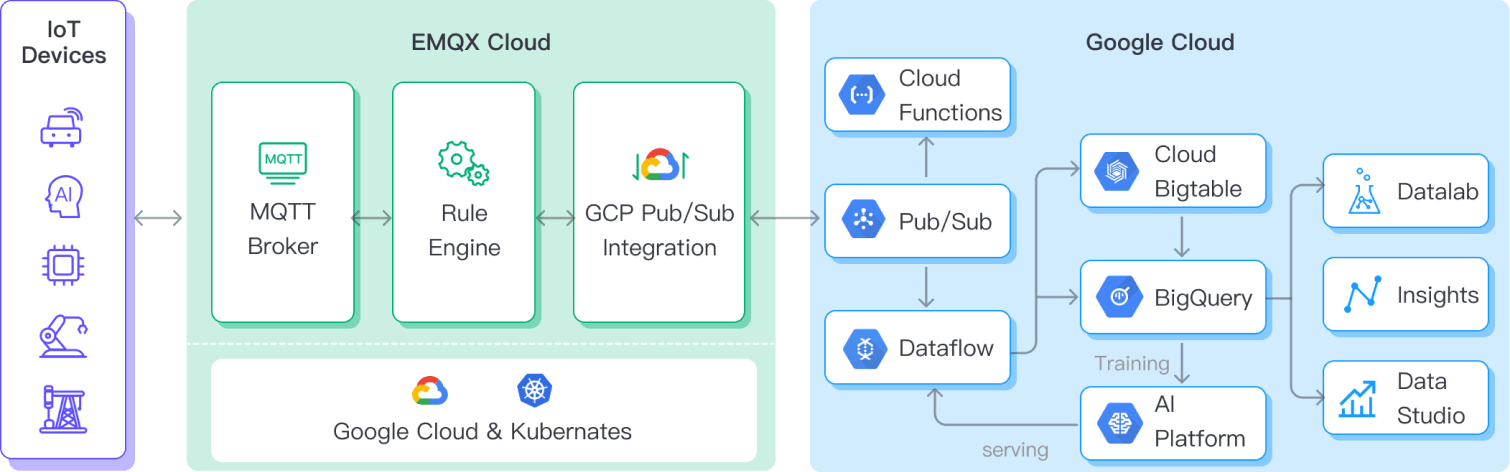
EMQX forwards MQTT data to GCP Pub/Sub through the rule engine and Sink. Taking the example of a GCP Pub/Sub producer role, the complete process is as follows:
- IoT Devices Publish Messages: Devices publish telemetry and status data through specific topics, triggering the rule engine.
- Rule Engine Processes Messages: Using the built-in rule engine, MQTT messages from specific sources are processed based on topic matching. The rule engine matches corresponding rules and processes messages, such as converting data formats, filtering specific information, or enriching messages with contextual information.
- Bridging to GCP Pub/Sub: The rule triggers the action of forwarding messages to GCP Pub/Sub, allowing easy configuration of data properties, ordering keys, and mapping of MQTT topics to GCP Pub/Sub topics. This provides richer context information and order assurance for data integration, enabling flexible IoT data processing.
After MQTT message data is written to GCP Pub/Sub, you can perform flexible application development, such as:
- Real-time Data Processing and Analysis: Utilize powerful Google Cloud data processing and analysis tools like Dataflow, BigQuery, and Pub/Sub's own streaming capabilities to perform real-time processing and analysis of message data, obtaining valuable insights and decision support.
- Event-Driven Functionality: Trigger Google Cloud event handling, such as Cloud Functions and Cloud Run, to achieve dynamic and flexible function triggering and processing.
- Data Storage and Sharing: Transmit message data to Google Cloud storage services like Cloud Storage and Firestore for secure storage and management of large volumes of data. This allows you to share and analyze this data with other Google Cloud services to meet various business needs.
Features and Benefits
The data integration with GCP Pub/Sub offers a range of features and benefits:
- Robust Messaging Service: Both EMQX and GCP Pub/Sub possess high availability and scalability features, ensuring the reliable reception, delivery, and processing of large-scale message streams. They support IoT data sequencing, message quality assurance, and persistence, ensuring the dependable transmission and handling of messages.
- Flexible Rules Engine: With the built-in rules engine, specific source messages and events can be processed based on topic matching. Messages and events can be manipulated, such as data format conversion, filtering out specific information, or enriching messages with context information. Combining this with GCP Pub/Sub allows for further processing and analysis.
- Rich Contextual Information: Through the GCP Pub/Sub data integration, you can add richer contextual information to messages, mapping client attributes to Pub/Sub attributes, sorting keys, and more. This aids in performing more precise analysis and processing in subsequent application development and data handling.
In summary, integrating EMQX and GCP Pub/Sub enables highly reliable, scalable message delivery, along with extensive tools and services for data analysis and integration. This empowers you to build robust IoT applications and implement flexible business logic based on event-driven capabilities.
Before You Start
This section describes the preparations you need to complete before you start to create the GCP Pub/Sub data integration.
Prerequisites
- Knowledge about EMQX data integration rules
- Knowledge about Data Integration
Create Service Account Key in GCP
You need to create a service account and a service account key to use the GCP PubSub service.
Create a Service Account in your GCP account. Ensure that the Service Account has permission to at least publish messages to the topic of interest.
Click the email address for the service account you created. Click the Key tab. In the Add key drop-down list, select Create new key to create a Service Account key for that account and download it in JSON format.
TIP
Store the Service Account key securely for later use.
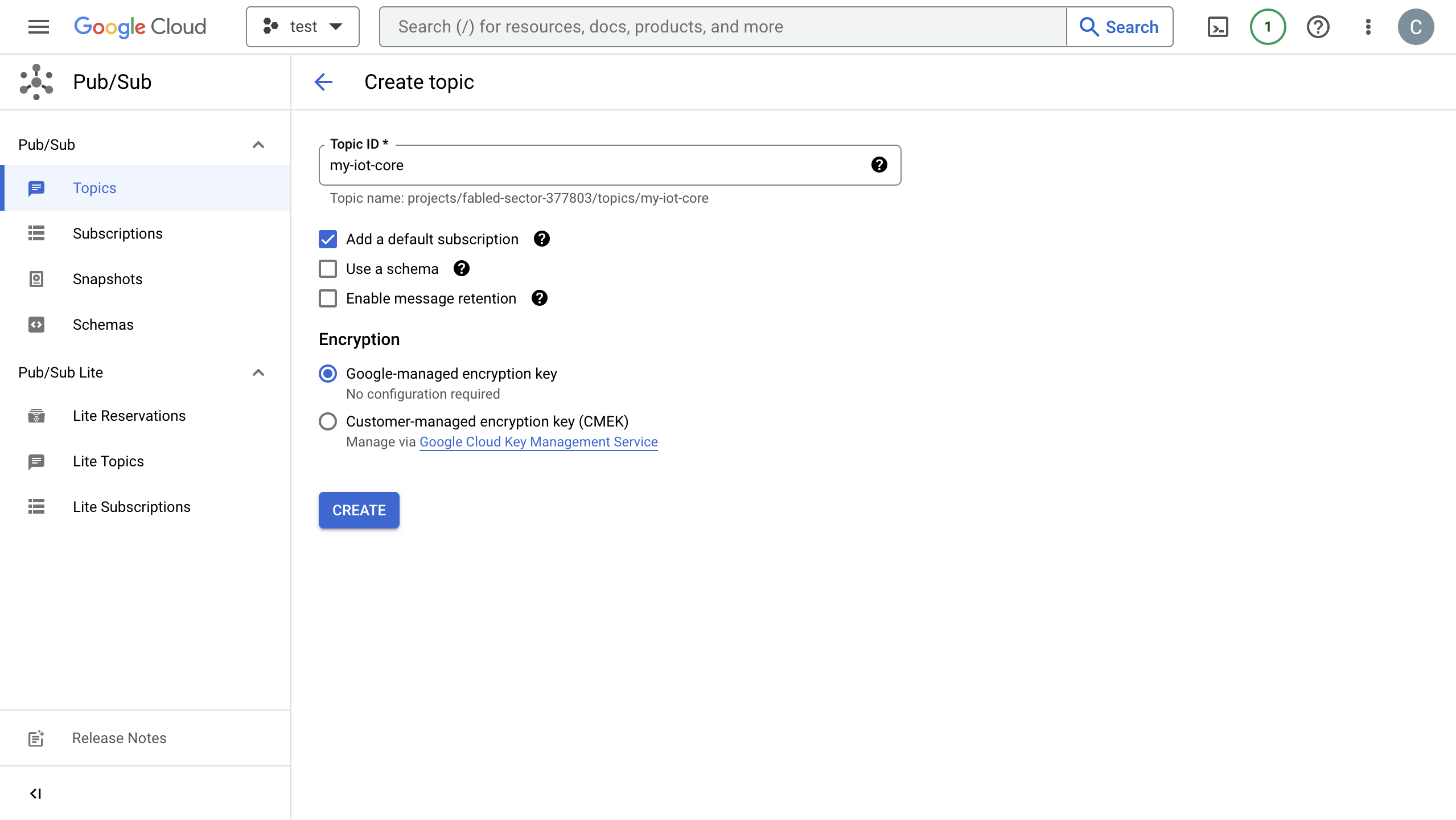
Create and Manage Topics in GCP
Before configuring the GCP Pub/Sub data integration on EMQX, you need to create a topic and be familiar with the basic management operation in GCP.
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Pub/Sub ->Topics page. For detailed instructions, see Create and manage topics.
TIP
The Service Account must have permission to publish that topic.
In the Topic ID field, enter an ID for your topic. Click Create topic.
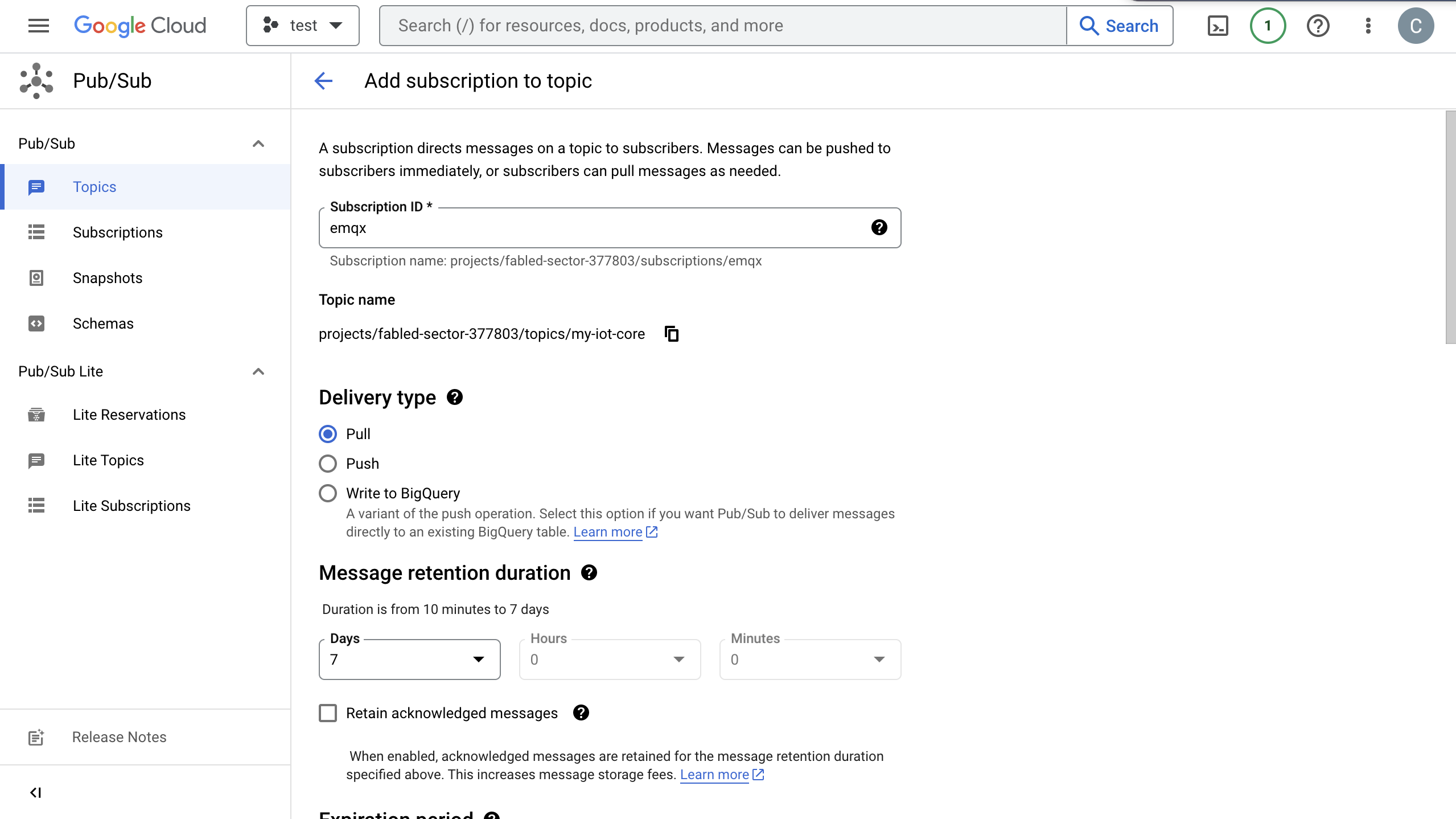
Go to the Subscriptions page. Click the Topic ID in the list. Create a subscription to the topic.
- Select Pull in Delivery type.
- Select
7Days for Message retention duration.
For detailed instructions, see GCP Pub/Sub Subscription.
Click Subscription ID -> Messages -> Pull can view the message sent to the topic.
Create a Rule for Google PubSub Sink
This section demonstrates how to create a rule to specify the data to be saved into GCP PubSub.
Go to EMQX Dashboard, and click Integration -> Rules.
Click Create on the top right corner of the page.
Enter
my_ruleas the rule ID.Set the rules in the SQL Editor. Here if you want to save the MQTT messages under topic
/devices/+/eventsto GCP PubSub, you can use the SQL syntax below.Note: If you want to specify your own SQL syntax, make sure that the
SELECTpart includes all fields required by the payload template in the Sink.sqlSELECT * FROM "/devices/+/events"Note: If you are a beginner user, click SQL Examples and Enable Test to learn and test the SQL rule.
Click the + Add Action button to define an action that will be triggered by the rule. Select
Google PubSubfrom the Type of Action dropdown list so that EMQX will send the data processed by the rule to GCP Pub/Sub.Keep the Action dropdown box with the value
Create Action. Or, you also can select a Google Pub/Sub Sink previously created. In this demonstration, you create a new Sink and add it to the rule.In the Name field, enter a name for the Sink. The name should be a combination of upper/lower case letters and numbers.
In the Bridge Role field, select
ProducerorConsumerfrom the drop-down list according to your business needs and complete the corresponding configurations.- GCP PubSub Topic: Enter the topic ID
my-iot-coreyou created in Create and Manage Topic in GCP. - GCP Service Account Credentials: Upload the Service Account credentials in JSON format you exported in Create Service Account Key in GCP.
- Payload Template: Leave it blank or define a template.
- If left blank, it will encode all visible inputs from the MQTT message using JSON format, such as clientid, topic, payload, etc.
- If using the defined template, placeholders of the form
${variable_name}will be filled with the corresponding value from the MQTT context. For example,${topic}will be replaced withmy/topicif such is the MQTT message topic.
- Attributes Template and Ordering Key Template (optional): Similarly, you can define templates for formatting the attributes and/or ordering key of the outgoing message.
- For Attributes, both keys and values may use placeholders of the form
${variable_name}. Such values will be extracted from the MQTT context. If a key template resolves to an empty string, that key is omitted from the outgoing message to GCP PubSub. - For Ordering Key, placeholders of the form
${variable_name}may be used. If the resolved value is an empty string, theorderingKeyfield will not be set for the GCP PubSub outgoing message.
- For Attributes, both keys and values may use placeholders of the form
- Advanced settings (optional): Choose whether to use sync or async query mode as needed.
- GCP PubSub Topic: Enter the topic ID
Advanced settings (optional): Choose whether to use sync or async query mode as needed. For details, see Features of Sink.
Before clicking Create, you can click Test Connectivity to test that the Connector can connect to the GCP Pub/Sub server.
Click the Add button to complete the Sink configuration. Back on the Create Rule page, you will see the new Sink appear under the Action Outputs tab.
You have now successfully created the rule. You can see the newly created rule on the Integration -> Rules page. Click the Actions(Sink) tab and you can see the new Google PubSub Sink.
You can also click Integration -> Flow Designer to view the topology and you can that the messages under topic /devices/+/events are sent and saved to GCP PubSub after parsing by rule my_rule.
Test the Rule
Use MQTTX to send messages on the topic
/devices/+/events.bashmqttx pub -i emqx_c -t /devices/+/events -m '{ "msg": "hello GCP PubSub" }'Check the running status of the Sink, there should be one new incoming and one new outgoing message.
Go to GCP Pub/Sub -> Subscriptions, click MESSAGES tab. You should see the message.