Ingest Data into Microsoft SQL Server
Set up an SQL Server database and set the user name and password to sa/mqtt_public. Take MacOS X as an example:
docker run -e 'ACCEPT_EULA=Y' -e 'SA_PASSWORD=mqtt_public' -p 1433:1433 -d mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2017-latestEnter the SQL Server container and initialize the SQL Server table:
Setting up SQL Server sa password
$ /opt/mssql-tools/bin/sqlcmd -S localhost -U sa -P mqtt_public -d masterCreate the "mqtt" database:
CREATE DATABASE mqtt;
go;Create the t_mqtt_msg table:
USE mqtt;
go;
CREATE TABLE t_mqtt_msg (id int PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1000000001,1) NOT NULL,
msgid VARCHAR(64) NULL,
topic VARCHAR(100) NULL,
qos tinyint NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
payload NVARCHAR(100) NULL,
arrived DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP);
go;Configure odbc driver in Mac:
$ brew install unixodbc freetds
$ vim /usr/local/etc/odbcinst.ini
[ms-sql]
Description = ODBC for FreeTDS
Driver = /usr/local/lib/libtdsodbc.so
Setup = /usr/local/lib/libtdsodbc.so
FileUsage = 1Configure odbc driver in CentOS:
$ yum install unixODBC unixODBC-devel freetds freetds-devel perl-DBD-ODBC perl-local-lib
$ vim /etc/odbcinst.ini
# add as below
[ms-sql]
Description = ODBC for FreeTDS
Driver = /usr/lib64/libtdsodbc.so
Setup = /usr/lib64/libtdsS.so.2
Driver64 = /usr/lib64/libtdsodbc.so
Setup64 = /usr/lib64/libtdsS.so.2
FileUsage = 1Configure odbc driver in Ubuntu (Take Ubuntu 20.04 as an example, for other versions please refer to the odbc official documentation):
$ apt-get install unixodbc unixodbc-dev tdsodbc freetds-bin freetds-common freetds-dev libdbd-odbc-perl liblocal-lib-perl
$ vim /etc/odbcinst.ini
# add as below
[ms-sql]
Description = ODBC for FreeTDS
Driver = /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/odbc/libtdsodbc.so
Setup = /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/odbc/libtdsS.so
FileUsage = 1Create rules:
Open EMQX Dashboard and select the "Rules" tab on the left.
Fill in the rule SQL:
SELECT * FROM "t/#"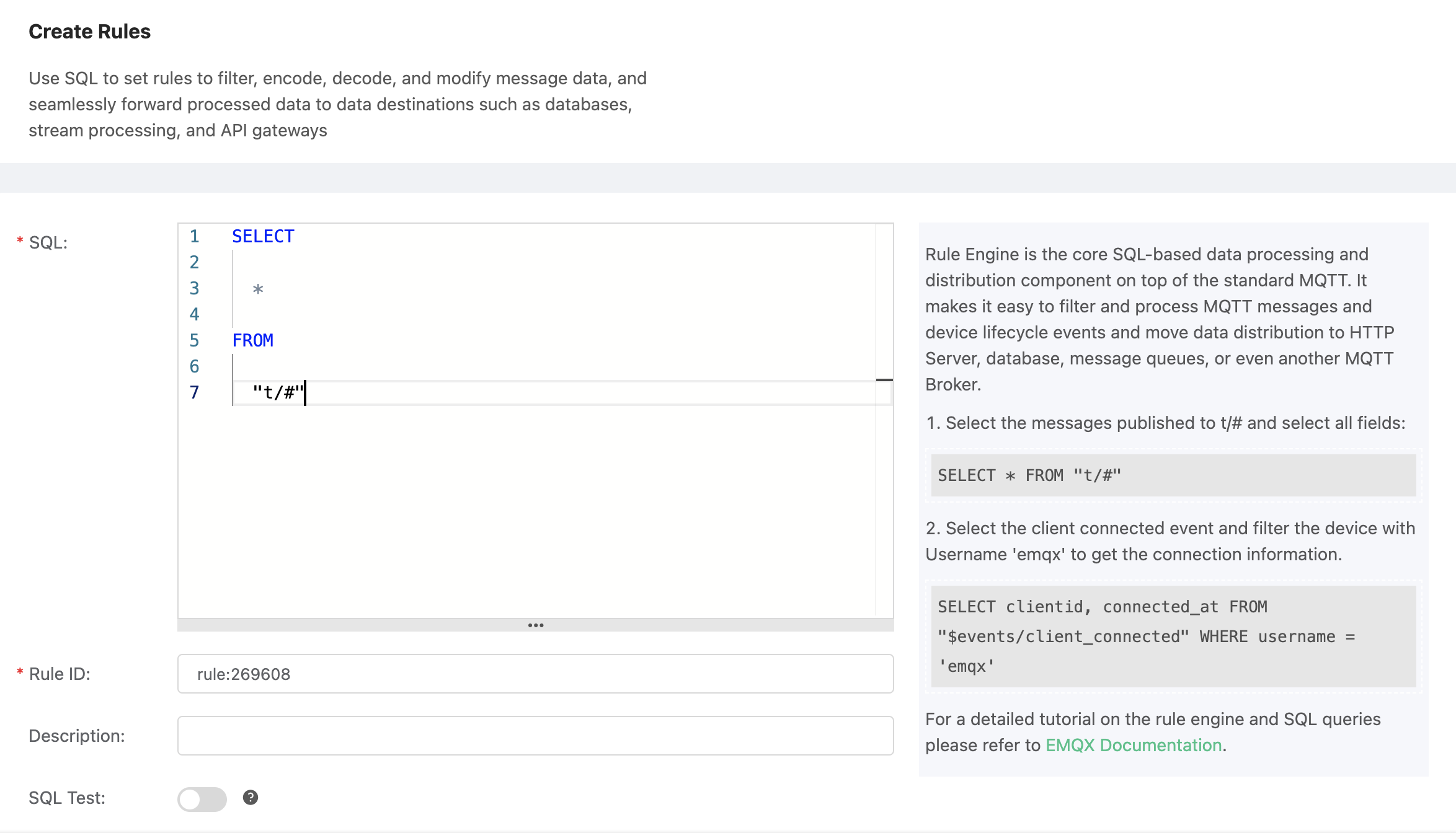
Related actions:
On the "Response Action" interface, select "Add", and then select "Save Data to SQLServer" in the "Action" drop-down box.
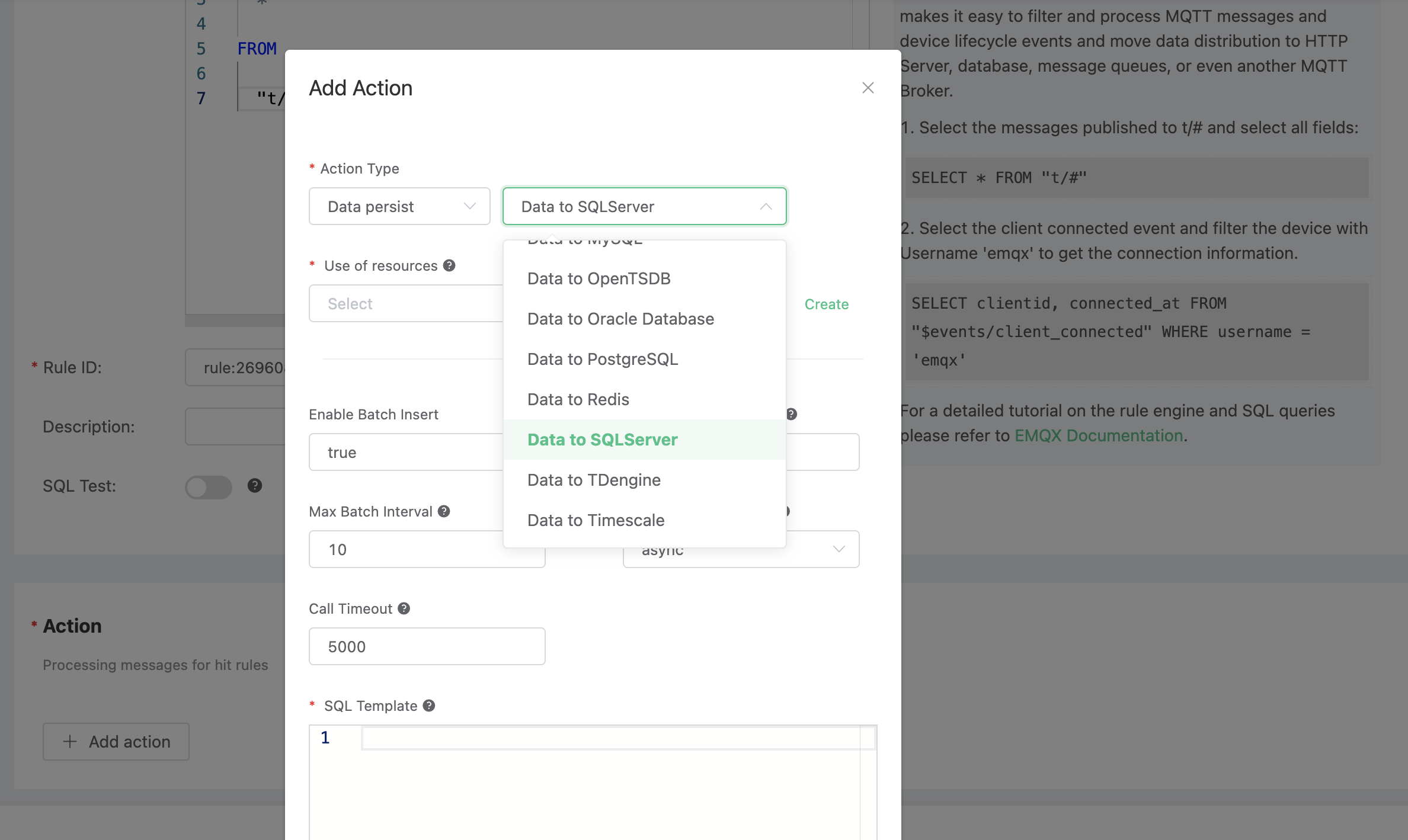
Fill in the action parameters:
The "Save data to SQLServer" action requires two parameters: 1). SQL template. In this example, we insert a piece of data into SQL Server, and the SQL template is:
insert into t_mqtt_msg(msgid, topic, qos, payload) values ('${id}', '${topic}', ${qos}, '${payload}')Before data is inserted into the table, placeholders like ${id} will be replaced by the corresponding values.
If a placeholder variable is undefined, you can use the Insert undefined value as Null option to define the rule engine behavior:
false(default): The rule engine can insert the stringundefinedinto the database.true: Allow the rule engine to insertNULLinto the database when a variable is undefined.
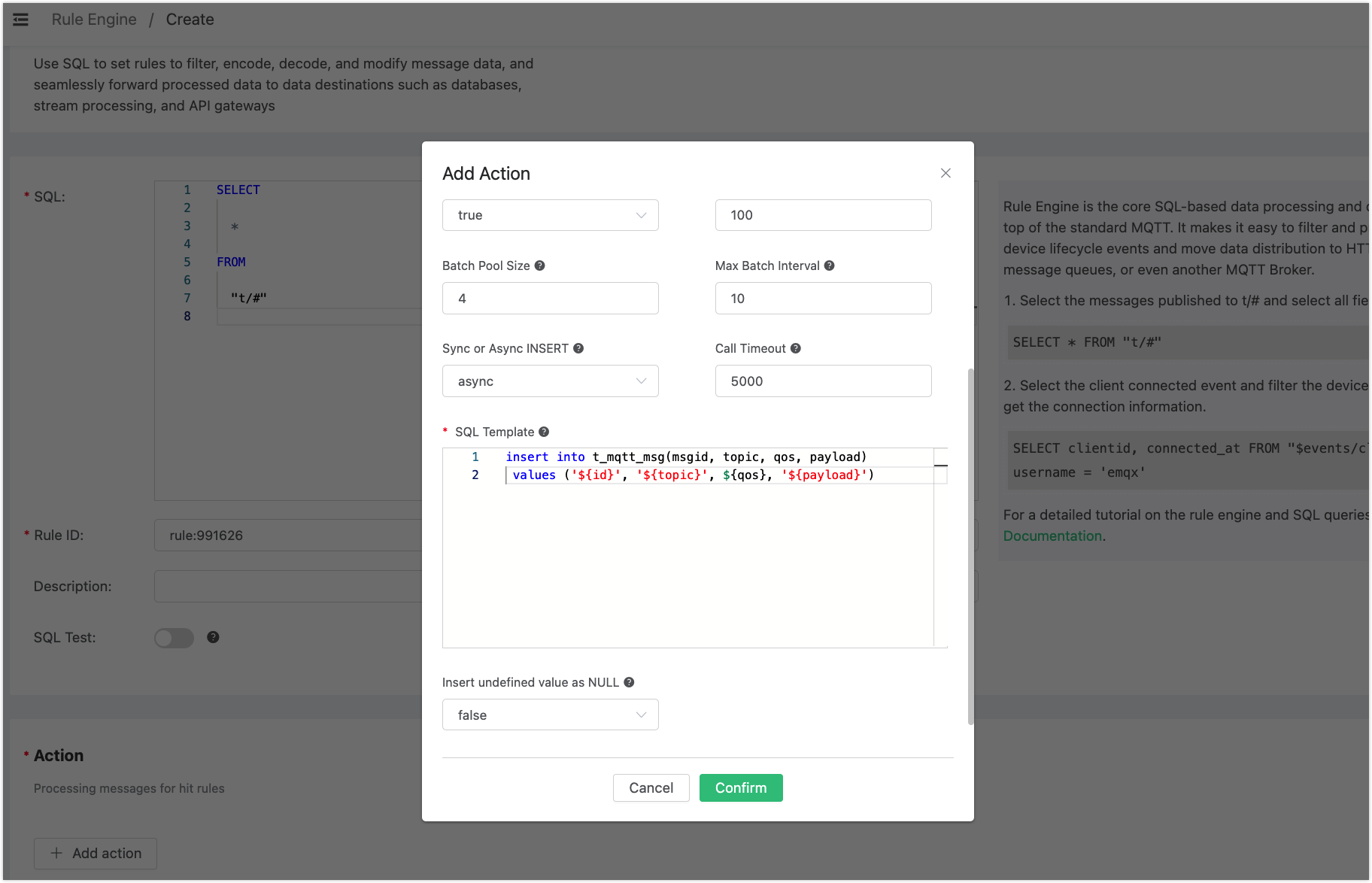
2). The ID of the associated resource. Now the resource drop-down box is empty, and you can click "New Resource" in the upper right corner to create a SQL Server resource. In the popup dialog box, configure as instructed below: input “mqtt” for database name, “sa” for user name, and “mqtt_public” for password.
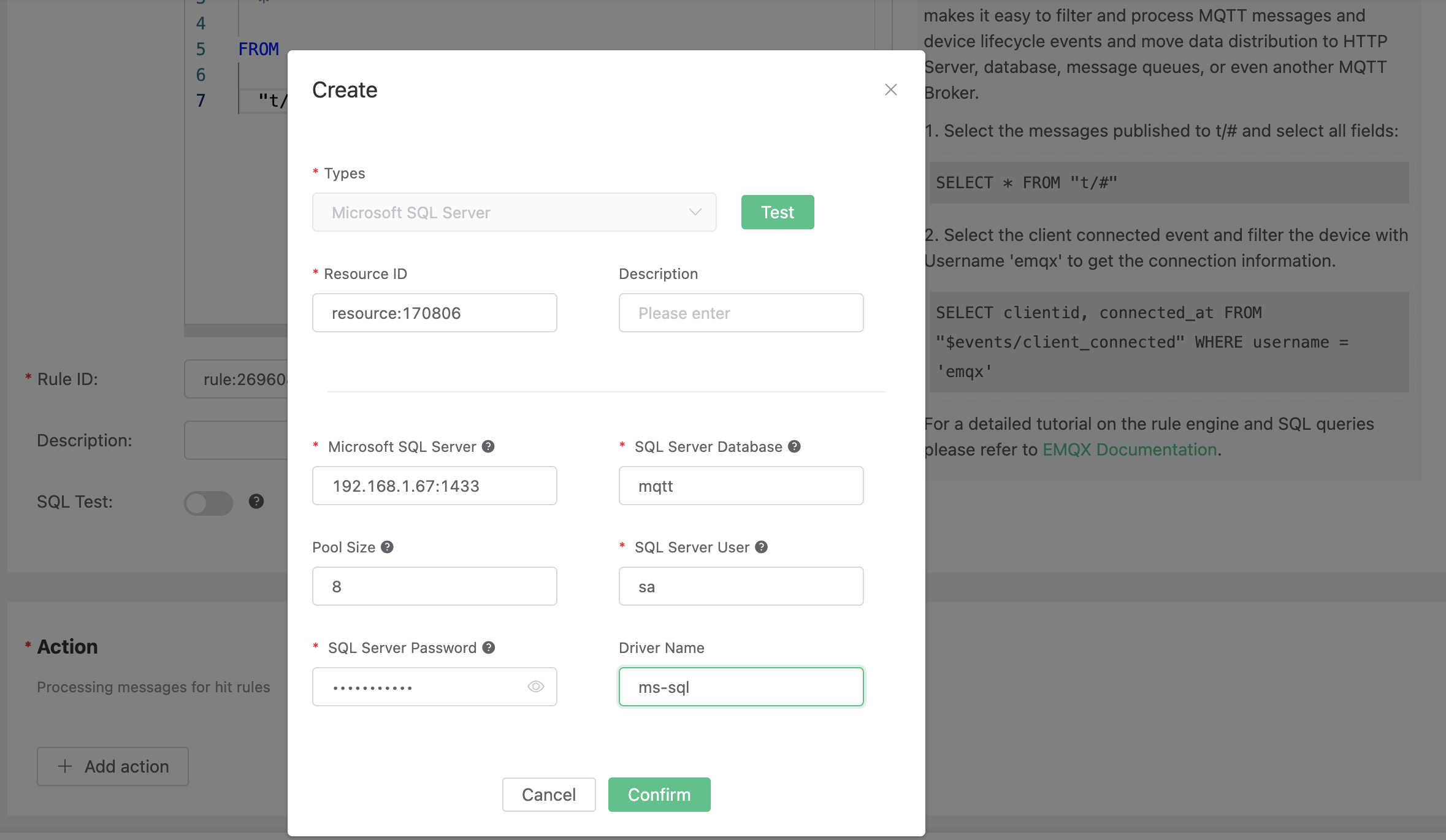
Click the "Confirm" button.
Return to the response action interface and click "OK".
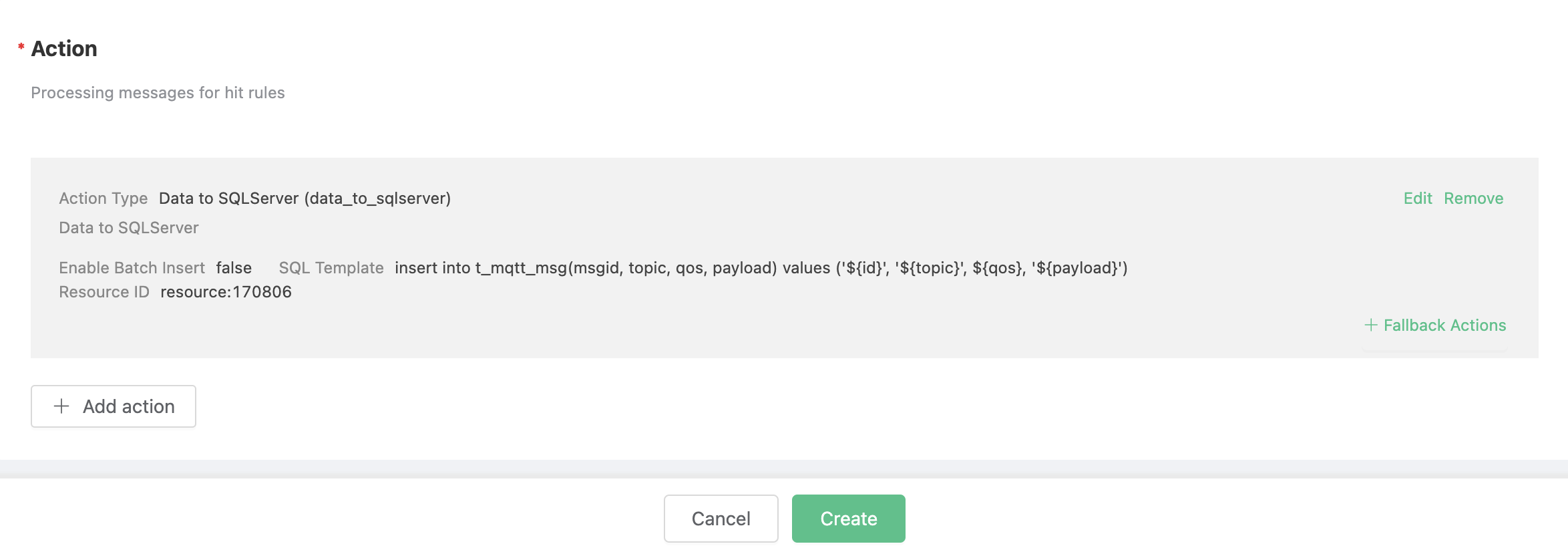
Return to the rule creation interface and click "Create".
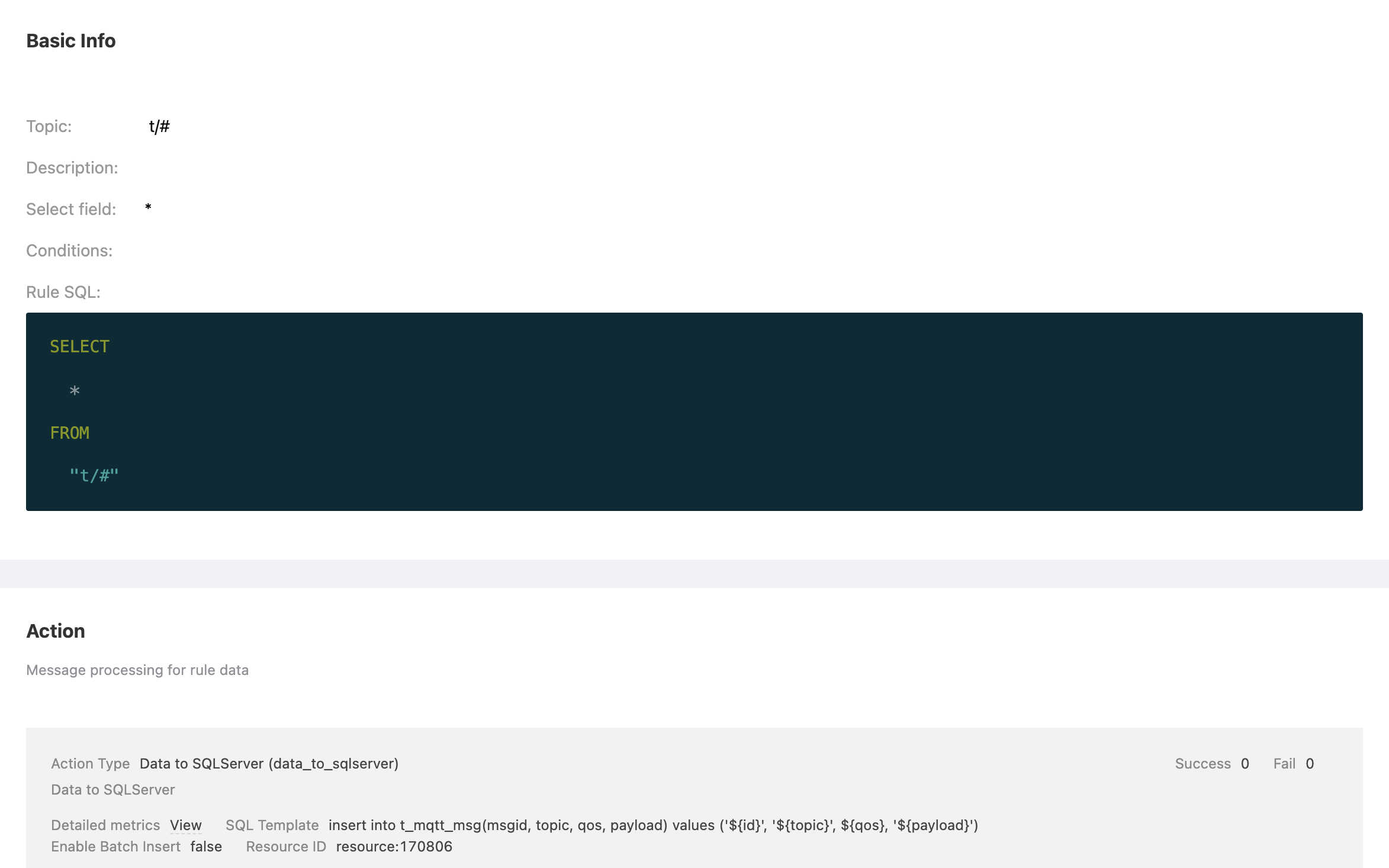
The rule has been created. Now, send a piece of data:
Topic: "t/a"
QoS: 1
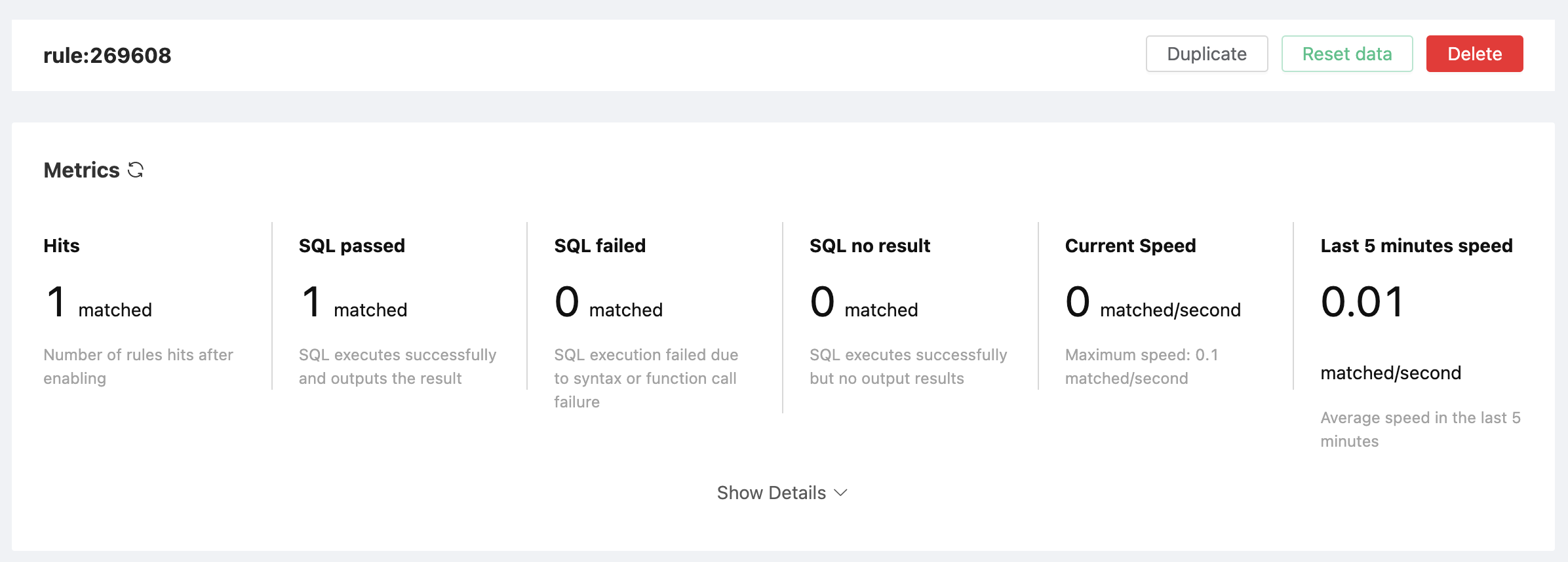
Payload: "hello"In the rule list, click the "View" button or the rule ID connection to preview the rule you just created:
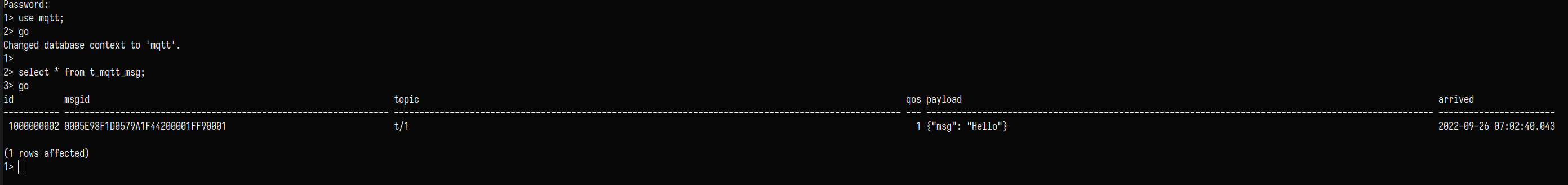
Here we can see that metrics has been increased.
Then check the SQL Server table to see whether the new record is added successfully: