Enhance Message Traceability with EMQX Event Topics and TimescaleDB Integration
The EMQX Cloud's message collection and transmission capability can fully utilize the event topic feature to enable comprehensive end-to-end message monitoring throughout the transmission process. This capability empowers users to generate detailed logs to track messages from their origin at the publisher, through the EMQX Cloud, to their destination at the subscriber. The comprehensive monitoring covers various scenarios, allowing the precise detection of any message delays. Moreover, users can have the flexibility to effortlessly transmit critical monitoring data to an external database or message queue through the EMQX Cloud's data integration function.
This guide demonstrates the setup of an end-to-end message tracing system, with a focus on using the Timescale database as an example. It introduces how to use the EMQX Cloud's data integration with TimescaleDB to observe the latency of MQTT messages throughout the entire transmission process, from the publishing client to the subscribing client.
Prerequisites
The following conditions must be met before the demonstration:
- Client Timezone: EMQX operates in UTC timezone; ensure the client's timezone is set to UTC. Adjust the default timezone of time fields in database tables if necessary.
- Client Time Synchronization: Ensure synchronization of system clocks across all clients.
- Message Timestamps: Configure MQTT clients to include a
publish_attimestamp in each message. - Data Integration: Set up EMQX data integration to capture
$events/message_deliveredand$events/message_ackedevents, recording them in TimescaleDB. - Strategy: To guarantee the reception of
message_acked events, use at least QoS 1 level.
Timestamp Definitions
The following timestamp fields are defined for the demonstration:
- Message Payload Timestamp (
publish_at): The timestamp when the client publishes a message. - EMQX Received Message Timestamp (
publish_received_at): The timestamp when EMQX receives the message. - EMQX Processing Timestamp (
message_delivered): The timestamp when EMQX processes the message and places it into the TCP packet. - Subscriber Client ACK Timestamp (
message_acked): The timestamp when the subscribing client receives the message and sends an acknowledgment (ACK).
Set Up a Timescale Instance
This section demonstrates how to create a Timescale instance and create a table for storing message traces and data monitoring.
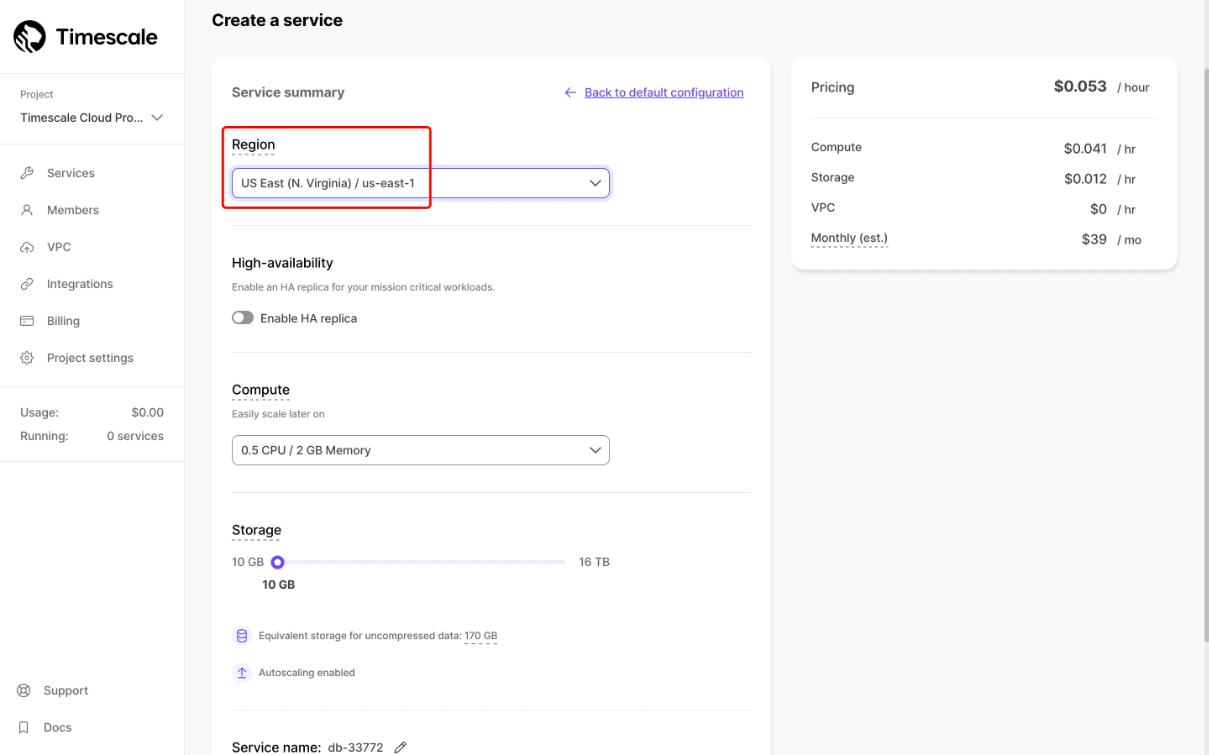
Log in to Timescale Cloud. On the Create a service page, select a region from the Region dropdown list. Click Create service at the bottom of the page.
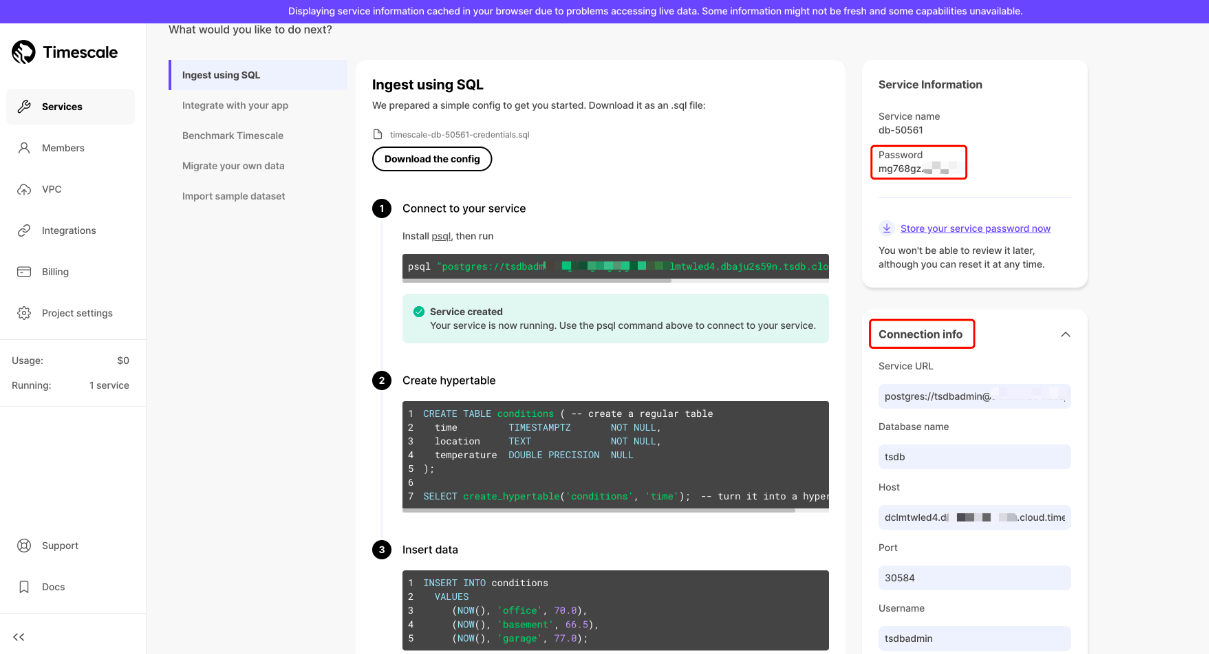
After creating the service, follow the instructions on the page to connect to your service. Store your Username and Password properly.
Use the following SQL statement to create a new table
mqtt_message_tracesfor storing message traces and monitoring data related to MQTT.sqlCREATE TABLE mqtt_message_traces ( event_at TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL, event character varying NOT NULL, msg_id character varying NOT NULL, publish_at bigint, emqx_received_at bigint, emqx_delivered_at bigint, sub_ack_at bigint, pub_clientid character varying, sub_clientid character varying, topic character varying NOT NULL, qos integer NOT NULL, payload text );Turn the
mqtt_message_tracestable into a hypertable by specifying theevent_atcolumn as the time dimension.sqlSELECT create_hypertable( 'mqtt_message_traces', 'event_at', chunk_time_interval => interval '12 hour', if_not_exists => TRUE );Create 3 indexes to optimize query performance:
emqx_mqtt_message_traces_event_idxon theeventcolumn for faster event type lookups.emqx_mqtt_message_traces_msg_id_event_at_idxon themsg_idandevent_atin descending order for querying message-specific events over time.emqx_mqtt_message_traces_pub_clientid_event_at_idxon thepub_clientidandevent_atin descending order for tracking events related to specific publishers over time.
sqlCREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS "emqx_mqtt_message_traces_event_idx" ON mqtt_message_traces ("event"); CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS "emqx_mqtt_message_traces_msg_id_event_at_idx" ON mqtt_message_traces ("msg_id", "event_at" DESC); CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS "emqx_mqtt_message_traces_pub_clientid_event_at_idx" ON mqtt_message_traces ("pub_clientid", "event_at" DESC);
Configure TimescaleDB Data Integration in EMQX Cloud
This section demonstrates how to create a data integration with TimescaleDB for forwarding the message traces from the clients to TimescaleDB.
Sign in to your Cloud Console and navigate to the deployment details page.
Click Data Integration from the left navigation menu. Under Data Persistence, select TimescaleDB.
Fill in the TimescaleDB connection information obtained from creating a Timescale cloud service. Set the Pool Size to
1. Then click Test to test the connection.Under Configured Resources, select the configured TimescaleDB resource. Click New Rule and enter the following rule to match the SQL statement. The
SELECTpart of the rule includes the following fields:id: MQTT message IDclientid: Client IDtopic: MQTT topicqos: Enumeration of message QoS 0, 1, 2event: Event topic of EMQXtimestamp: Event Timestamp (ms)publish_received_at: Time when PUBLISH message reaches Broker (ms)up_timestamp: Time when the pub client reports data (ms)payload: MQTT payload
sqlSELECT timestamp div 1000 as event_at, event, id as msg_id, payload.publish_at as publish_at, publish_received_at as emqx_received_at, clientid as pub_clientid, topic, qos, payload FROM "#"The rule will be triggered when the publishing client sends messages to any topics matching
#.Click on the Next button at the bottom to enter the Action view. Select the TimescaleDB resource and enter the following data to insert into the SQL template.
INSERT INTO mqtt_message_traces(event_at,event,msg_id,publish_at,emqx_received_at,emqx_delivered_at,sub_ack_at,pub_clientid,sub_clientid,topic,qos,payload) VALUES ( to_timestamp(${event_at}), ${event}, ${msg_id}, ${publish_at}, ${emqx_received_at}, NULL, NULL, ${pub_clientid}, NULL, ${topic}, ${qos}, ${payload} );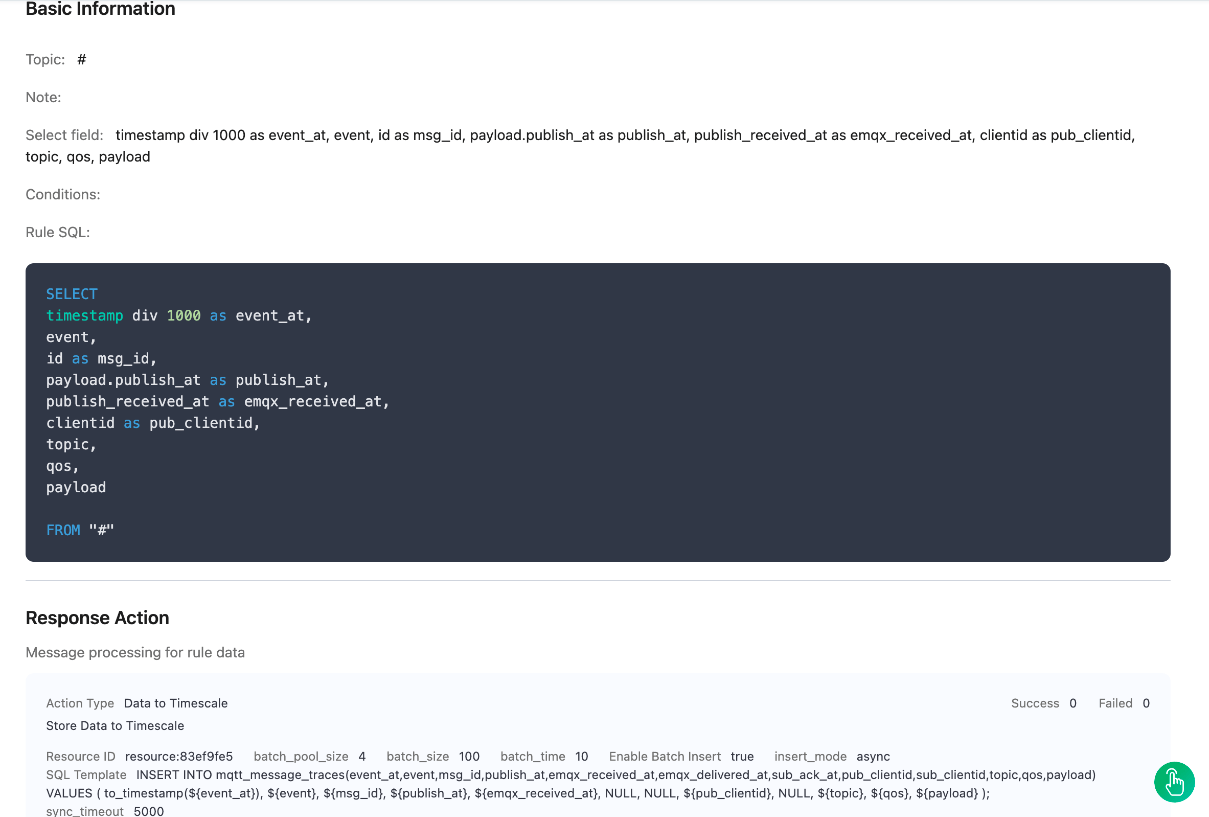
Click Create to complete the creation.
Create the second rule. It must be triggered when a message is delivered by EMQX to a client that subscribes to the topic.
sqlSELECT timestamp div 1000 as event_at, event, id as msg_id, payload.publish_at as publish_at, publish_received_at as emqx_received_at, timestamp as emqx_delivered_at, from_clientid as pub_clientid, clientid as sub_clientid, topic, qos, payload FROM "$events/message_delivered"Click the Next button in the bottom to enter the Action view. Select the TimescaleDB resource and enter the following data to insert into the SQL template.
INSERT INTO mqtt_message_traces(event_at,event,msg_id,publish_at,emqx_received_at,emqx_delivered_at,sub_ack_at,pub_clientid,sub_clientid,topic,qos,payload) VALUES ( to_timestamp(${event_at}), ${event}, ${msg_id}, ${publish_at}, ${emqx_received_at}, ${emqx_delivered_at}, NULL, ${pub_clientid}, ${sub_clientid}, ${topic}, ${qos}, ${payload} );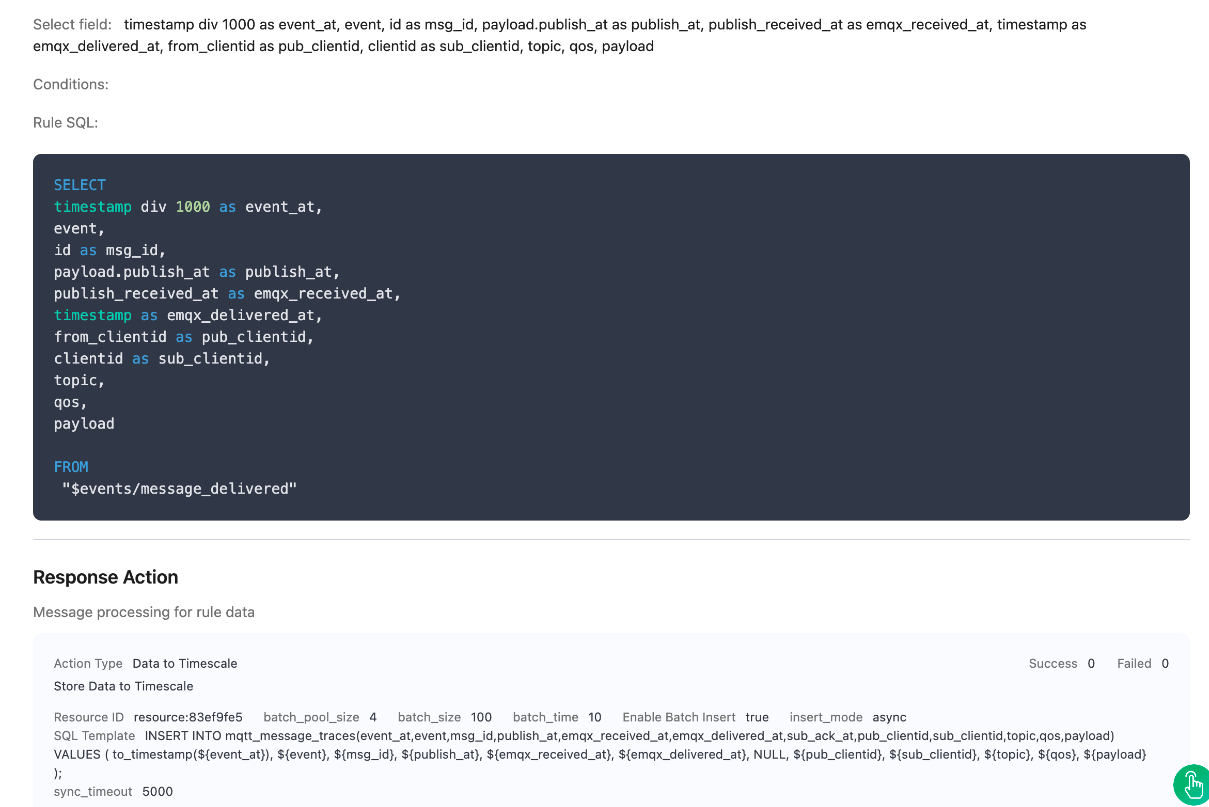
Click the Create button to complete the creation.
Create the third rule. It will be triggered when the message is sent to the client and an acknowledgment is received from the client. The rule will only be triggered when the message QoS is 1 and 2.
sqlSELECT timestamp div 1000 as event_at, event, id as msg_id, payload.publish_at as publish_at, publish_received_at as emqx_received_at, timestamp as sub_ack_at, from_clientid as pub_clientid, clientid as sub_clientid, topic, qos, payload FROM "$events/message_acked"Click the Next button in the bottom to enter the Action view. Select the TimescaleDB resource and enter the following data to insert into the SQL template.
INSERT INTO mqtt_message_traces(event_at,event,msg_id,publish_at,emqx_received_at,emqx_delivered_at,sub_ack_at,pub_clientid,sub_clientid,topic,qos,payload) VALUES ( to_timestamp(${event_at}), ${event}, ${msg_id}, ${publish_at}, ${emqx_received_at}, NULL, ${sub_ack_at}, ${pub_clientid}, ${sub_clientid}, ${topic}, ${qos}, ${payload} );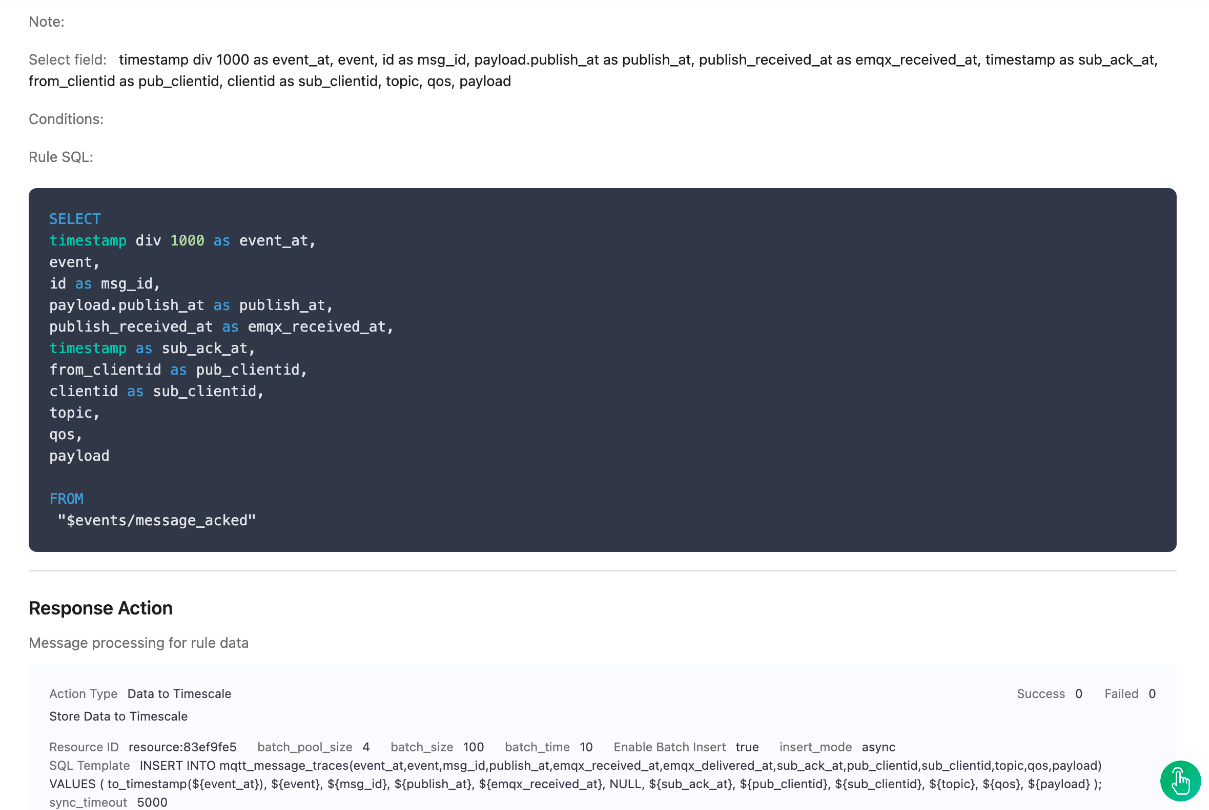
Click the Create button to complete the creation.
Use Python SDK to Simulate Message Delivery
Use the Python SDK to send messages to the
emqx/testtopic as a publisher. The message QoS level is greater than 0.python# python 3.8 import random import time from datetime import datetime from paho.mqtt import client as mqtt_client broker = 'x.x.x.x' port = 1883 topic = "emqx/test" # generate client ID with pub prefix randomly client_id = f'python-mqtt-{random.randint(0, 1000)}' username = 'xxx' password = 'xxx' def connect_mqtt(): def on_connect(client, userdata, flags, rc): if rc == 0: print("Connected to MQTT Broker!") else: print("Failed to connect, return code %d\n", rc) client = mqtt_client.Client(client_id) # client.tls_set(ca_certs='./server-ca.crt') client.username_pw_set(username, password) client.on_connect = on_connect client.connect(broker, port) return client def publish(client): msg_count = 0 while True: time.sleep(1) timestamp_ms = int(datetime.utcnow().timestamp() * 1000) msg = f'{{"publish_at": {timestamp_ms}, "msg": {msg_count}}}' result = client.publish(topic, msg, qos=1) # result: [0, 1] status = result[0] if status == 0: print(f"Send `{msg}` to topic `{topic}`") else: print(f"Failed to send message to topic {topic}") msg_count += 1 def run(): client = connect_mqtt() client.loop_start() publish(client) if __name__ == '__main__': run()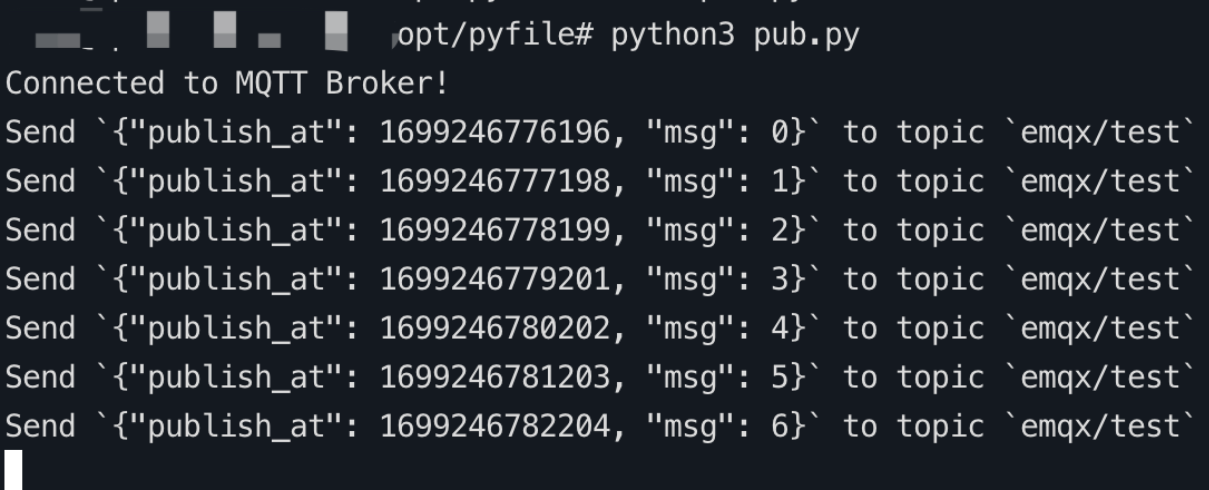
Use the Python SDK to subscribe to the topics
emqx/testas a subscriber.python# python3.8 import random from paho.mqtt import client as mqtt_client broker = 'x.x.x.x' port = 1883 topic = "emqx/test" # generate client ID with pub prefix randomly client_id = f'python-mqtt-{random.randint(0, 100)}' username = 'xxx' password = 'xxx' def connect_mqtt() -> mqtt_client: def on_connect(client, userdata, flags, rc): if rc == 0: print("Connected to MQTT Broker!") else: print("Failed to connect, return code %d\n", rc) client = mqtt_client.Client(client_id) # client.tls_set(ca_certs='./server-ca.crt') client.username_pw_set(username, password) client.on_connect = on_connect client.connect(broker, port) return client def subscribe(client: mqtt_client): def on_message(client, userdata, msg): print(f"Received `{msg.payload.decode()}` from `{msg.topic}` topic") client.subscribe(topic, qos=1) client.on_message = on_message def run(): client = connect_mqtt() subscribe(client) client.loop_forever() if __name__ == '__main__': run()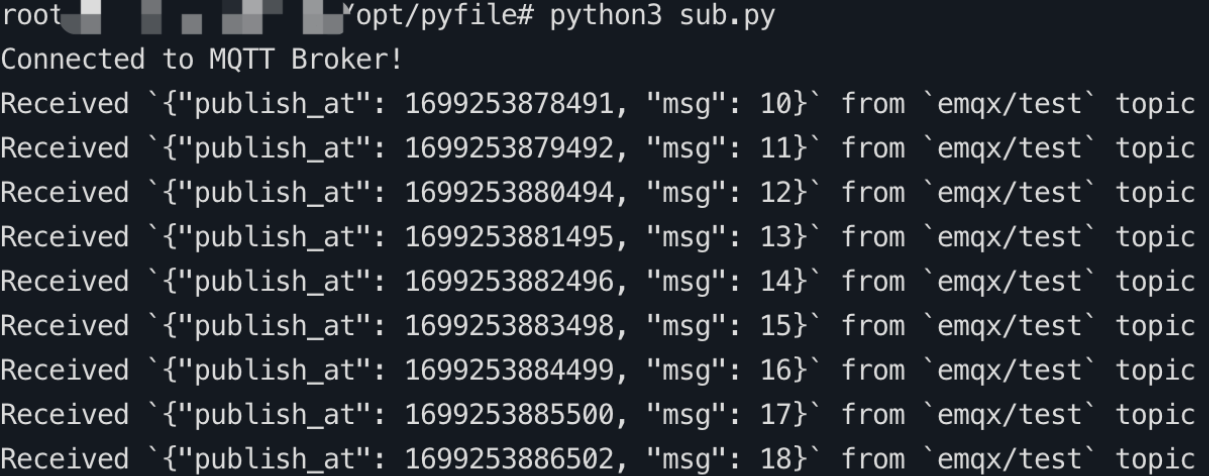
View Message Latency
This section provides some SQL query statements that can help retrieve the information from TimescaleDB, such as the latency of all messages on the EMQX Cloud platform, including from the publisher to the server, within the server itself, and from the server to the subscriber.
How to Calculate Delay
- Pub_Client to EMQX Delay:
publish_received_attimestamp minuspublish_attimestamp. - EMQX Processing Delay:
message_deliveredtimestamp minuspublish_received_attimestamp. - EMQX to Sub_Client Delay:
message_acked timestamptimestamp minusmessage_delivered timestamptimestamp. - Total Transmission Delay:
message_ackedtimestamp minuspublish_attimestamp.
TIP
- If a message lacks a
publish_attimestamp, calculating the Client to EMQX Delay is not possible. - Without QoS 0, the
message_ackedevent will not trigger, making the calculation of EMQX to Subscribing Client Delay impossible.
Use Query Statement Examples
Query the database to retrieve the average message latency from the database for the past hour.
sqlSELECT AVG(emqx_received_at - publish_at) AS avg_delay FROM mqtt_message_traces WHERE event_at >= NOW() - INTERVAL '1 hour' AND publish_at IS NOT NULL AND emqx_received_at IS NOT NULL;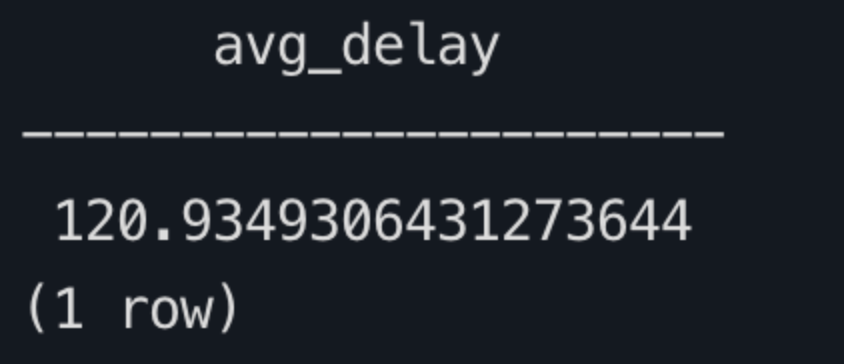
Query the database to retrieve the average publishing client delay within the past hour.
sqlSELECT AVG(emqx_received_at - publish_at) AS avg_publish_delay FROM mqtt_message_traces WHERE event_at >= NOW() - INTERVAL '1 hour' AND publish_at IS NOT NULL AND emqx_received_at IS NOT NULL;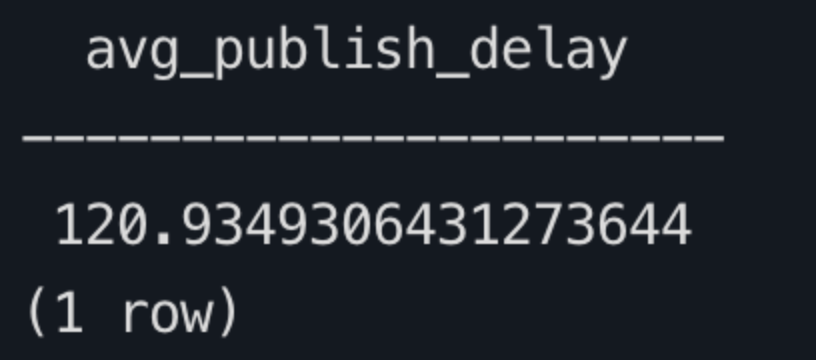
Query the database for the average subscription latency of subscribing clients during the past hour and return the top 10 records.
sqlWITH message_events AS ( SELECT msg_id, sub_clientid, -- Add sub_clientid here MAX(CASE WHEN event = 'message.acked' THEN sub_ack_at END) AS event_ma, MAX(CASE WHEN event = 'message.delivered' THEN emqx_delivered_at END) AS event_md FROM mqtt_message_traces WHERE event IN ('message.acked', 'message.delivered') AND event_at >= NOW() - INTERVAL '1 hour' GROUP BY msg_id, sub_clientid -- Include sub_clientid in grouping ) SELECT msg_id, sub_clientid, -- Include sub_clientid in the result AVG(event_ma - event_md) AS avg_subscription_delay FROM message_events WHERE event_ma IS NOT NULL AND event_md IS NOT NULL GROUP BY msg_id, sub_clientid -- Group by msg_id and sub_clientid ORDER BY avg_subscription_delay DESC LIMIT 10;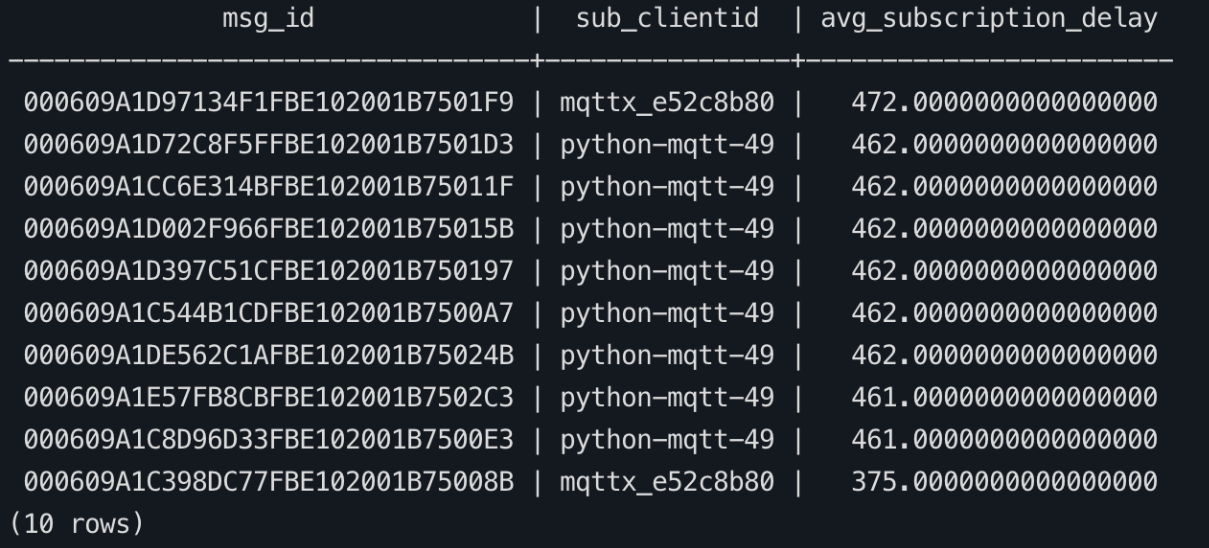
Query the database to retrieve the average delay for each message ID across all stages within the past hour. Sort the results in descending order based on the total transmission delay (utilizing publishing delay if there is no acknowledgment delay). Return the top 10 records.
sqlWITH relevant_messages AS ( SELECT * FROM mqtt_message_traces WHERE event_at >= NOW() - INTERVAL '1 hour' ) SELECT t1.msg_id, ROUND(AVG(t1.emqx_received_at - t1.publish_at)) AS client_to_emqx_delay, ROUND(AVG(t2.emqx_delivered_at - t1.emqx_received_at)) AS emqx_processing_delay, ROUND(AVG(t3.sub_ack_at - t2.emqx_delivered_at)) AS emqx_to_subscriber_delay, ROUND(AVG(t3.sub_ack_at - t1.publish_at)) AS total_message_delay FROM relevant_messages t1 JOIN relevant_messages t2 ON t1.msg_id = t2.msg_id AND t2.event = 'message.delivered' JOIN relevant_messages t3 ON t1.msg_id = t3.msg_id AND t3.event = 'message.acked' GROUP BY t1.msg_id ORDER BY total_message_delay DESC LIMIT 10;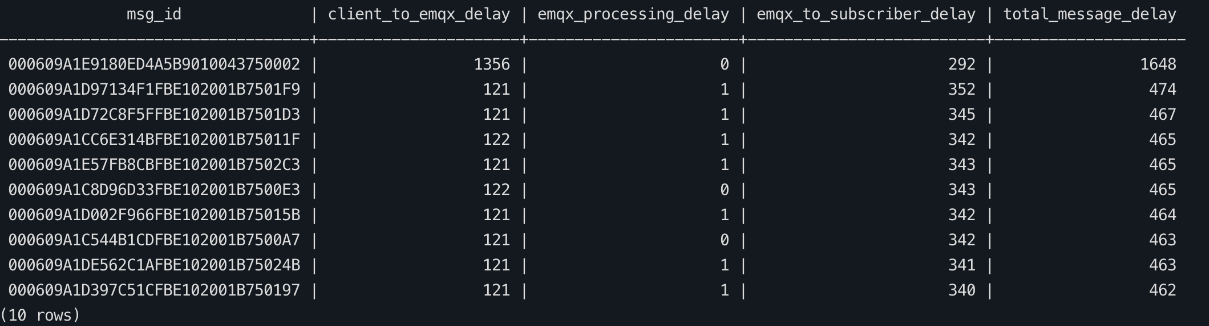
Query the database to retrieve the average message delay for each publishing client ID within the past hour from the database. Sort the results in descending order based on the publishing delay and return the top 10 records.
sqlSELECT pub_clientid, AVG(emqx_received_at - publish_at) AS avg_publish_delay FROM mqtt_message_traces WHERE event_at >= NOW() - INTERVAL '1 hour' AND publish_at IS NOT NULL AND emqx_received_at IS NOT NULL GROUP BY pub_clientid ORDER BY avg_publish_delay DESC LIMIT 10;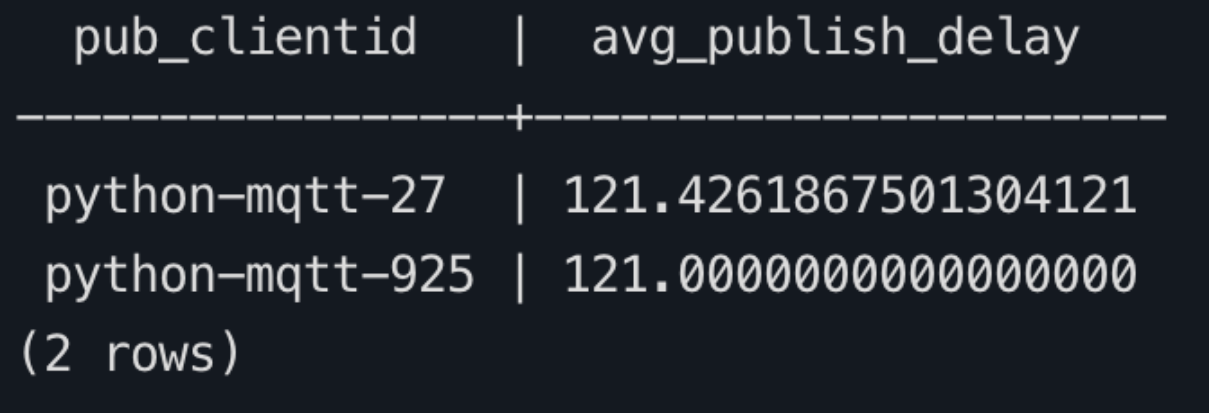
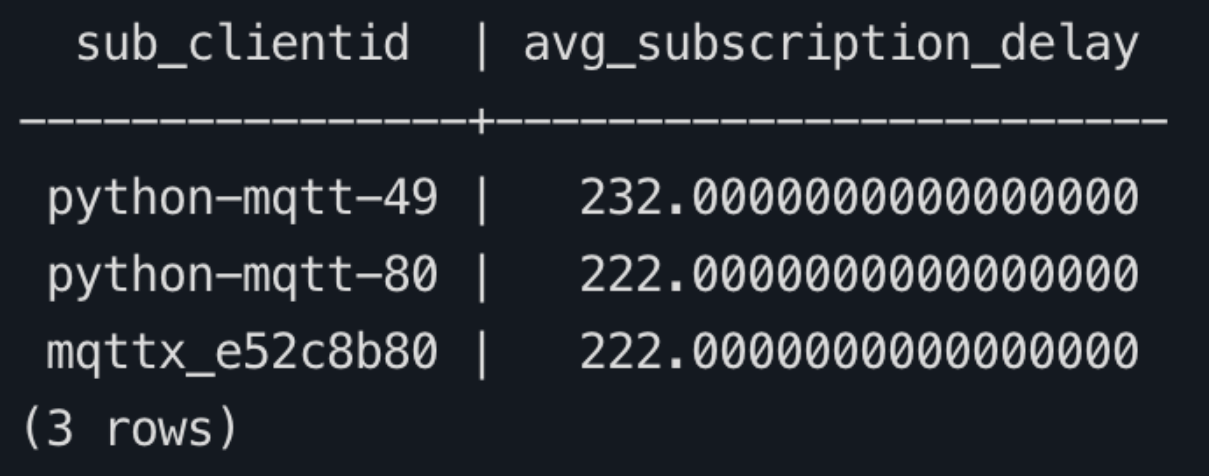
Query the database to retrieve the average message delay for each subscribing client ID within the past hour. Return the top 10 records in descending order based on the delay.
sqlWITH message_events AS ( SELECT sub_clientid, MAX(CASE WHEN event = 'message.acked' THEN sub_ack_at END) AS event_ma, MAX(CASE WHEN event = 'message.delivered' THEN emqx_delivered_at END) AS event_md FROM mqtt_message_traces WHERE event IN ('message.acked', 'message.delivered') AND event_at >= NOW() - INTERVAL '1 hour' AND sub_clientid IS NOT NULL GROUP BY sub_clientid ) SELECT sub_clientid, AVG(event_ma - event_md) AS avg_subscription_delay FROM message_events WHERE event_ma IS NOT NULL AND event_md IS NOT NULL GROUP BY sub_clientid ORDER BY avg_subscription_delay DESC LIMIT 10;