PostgreSQL Authentication/Access Control
In addition to supporting the default authentication and authentication method, EMQX Cloud can also use an external PostgreSQL database as a data source to store large amounts of data and to facilitate integration with external device management systems.
Authentication Chain
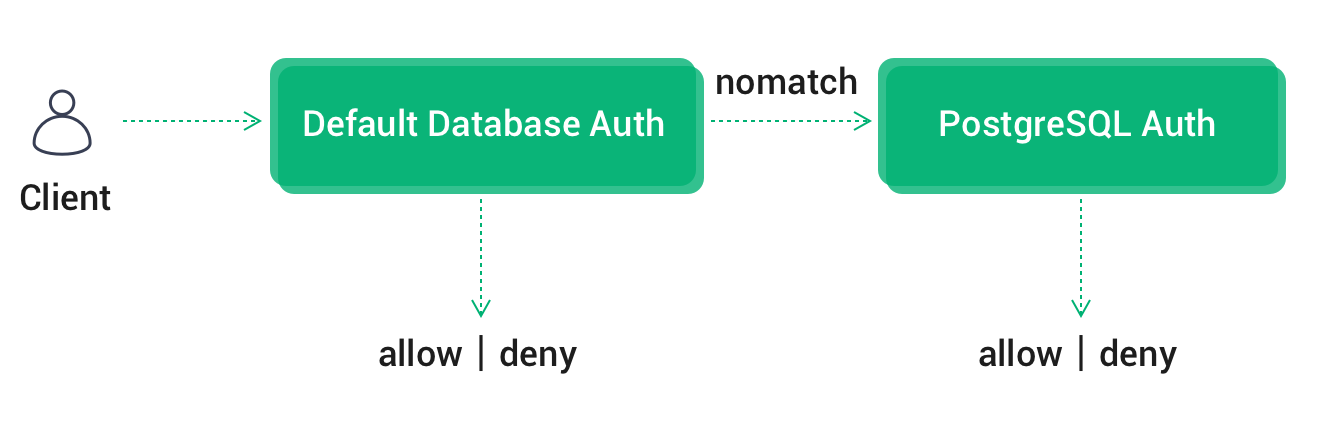
If default authentication is also enabled, EMQX Cloud will chain default authentication -> PostgreSQL authentication in the following order Authentication.
- Once authentication is successful, terminate the authentication chain and the client is accessible
- In case of authentication failure, terminate the chain and disable client access
ACL Authentication Chain
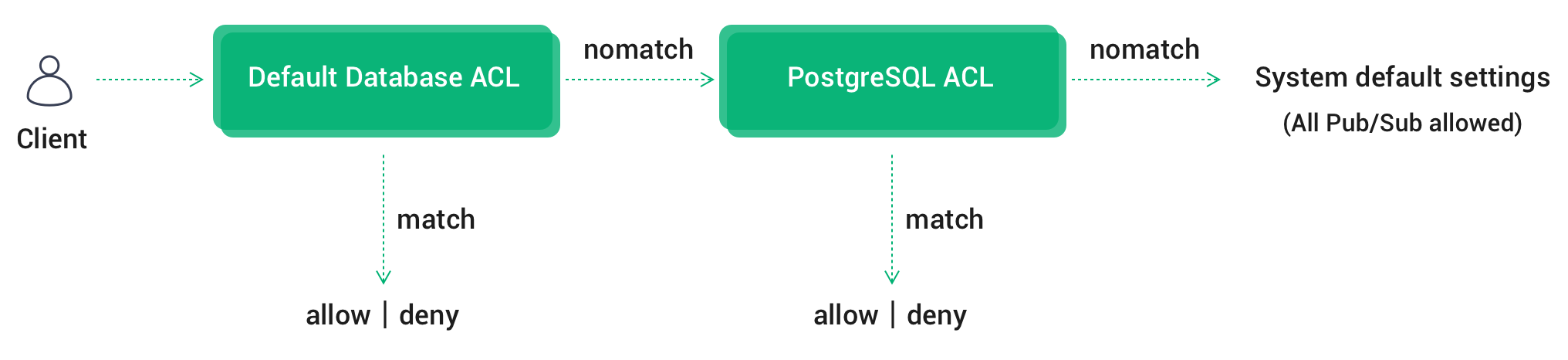
If multiple ACL modules are enabled at the same time, EMQX Cloud will chain authentication in the order of Default Authentication Database ACL-> PostgreSQL ACL-> System Defaults (All Pub/Sub allowed).
- Once the authentication is passed, terminate the chain and allow the client to pass the authentication
- Once authentication has failed, terminate the chain and deny the client to pass authentication
- Until the last ACL module fails to authenticate, authenticate according to the System default settings --- (All Pub/Sub allowed)
PostgreSQL Configuration
PostgreSQL installation
bashdocker run -d --name postgresql -p 5432:5432 -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=public postgres:13database creation
bashdocker exec -it postgresql psql -U postgres CREATE database emqx; \c emqxAuthentication table creation
Using the following SQL statement will create the
mqtt_usertable which will be used to store user authentication data.sqlCREATE TABLE mqtt_user ( id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, username CHARACTER VARYING(100), password CHARACTER VARYING(100), salt CHARACTER VARYING(40), UNIQUE (username) );Field Description:
- username: username of the connecting client, a value of $all means that the rule applies to all users
- password: the password parameter of the connected client
- salt: password with salt string
You can use AS syntax in SQL to rename the field to specify password, or set the salt value to a fixed value.
Access Control Table Creation
The following SQL statement will create the
mqtt_acltable, which will be used to store the authentication data of topic subscription and publishing privileges.sqlCREATE TABLE mqtt_acl ( id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, allow INTEGER, ipaddr CHARACTER VARYING(60), username CHARACTER VARYING(100), clientid CHARACTER VARYING(100), access INTEGER, topic CHARACTER VARYING(100) );Field descriptions.
- allow: prohibit (0), allow (1)
- ipaddr: set IP address
- username: the username of the connecting client, if the value here is set to $all, the rule applies to all users
- clientid: client id of the connected client
- access: allowed operations: subscribe (1), publish (2), both subscribe and publish (3)
- topic: the topic of the control, you can use wildcards, and you can add placeholders in the topic to match the client information, for example, t/%c will replace the topic with the current clientid when matching
Authentication/access control configuration
Click
Authentication & Authentication-External Authentication & Authorizationin the left menu bar of EMQX Cloud deployment, and select PostgreSQL Authentication/Access Control.
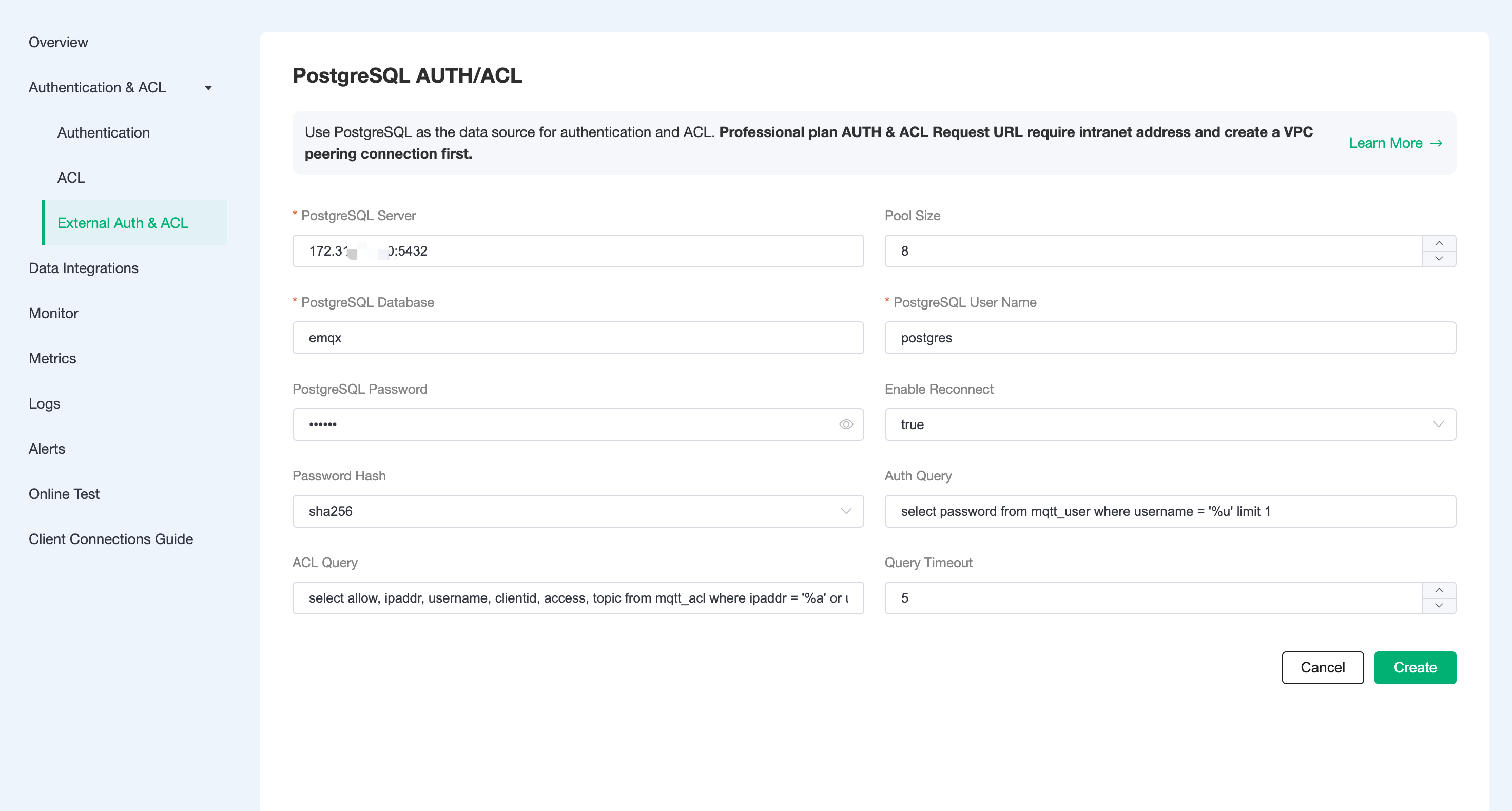
Click
Configure Authenticationto enter the PostgreSQL Authentication/Access Control page, fill in the information and create a new authentication.TIP
- For Basic Plan users: Please fill in the public address for the server address.
- For Professional Plan users: Please complete Peering Connection Creation first, then fill in the internal network address for the server address.
- For BYOC Plan users: Please establish a peering connection between the VPC where BYOC is deployed and the VPC where the resources are located, then fill in the internal network address for the server address.
- If you are prompted with Init resource failure! check whether the server address is correct, and whether the security group is enabled.
Principle of permission authentication
When authenticating, EMQX Cloud will use the current client information to populate and execute the username and password authentication SQL configured by the user, and query the authentication data in the database of the client.
select password from mqtt_user where username = '%u' limit 1;You can use the following placeholders in the authentication SQL, which will be automatically populated with the client information when EMQX Cloud is executed: :
- %u: username
- %c: clientid
- %P: plaintext password
You can adapt the authentication SQL to your business needs, such as adding multiple query conditions, using database preprocessing functions, to achieve more business-related functionality. But in any case, the authentication SQL needs to meet the following conditions:
- The query result must contain a password field. EMQX Cloud uses this field to compare with the client password. If other encryption methods other than plain are selected, the password field in the
mqtt_usertable needs to insert the string encrypted by the corresponding encryption algorithm. - If the salt configuration is enabled, the query result must contain the salt field, which is used by EMQX Cloud as the salt value.
- There can only be one query result, and only the first result is taken as valid data when there are multiple results.
The default configuration example data is as follows.
INSERT INTO mqtt_user (id, username, password, salt) VALUES (1, 'emqx', 'efa1f375d76194fa51a3556a97e641e61685f914d446979da50a551a4333ffd7', NULL);With PostgreSQL authentication enabled, you can connect via username: emqx, password: public.
Access control principle
When access control authentication is performed for topic subscription and publication, EMQX Cloud will use the current client information to populate and execute the user-configured access control authentication SQL to find the data related to the client from PostgreSQL and then perform authentication.
select allow, ipaddr, username, clientid, access, topic from mqtt_acl where ipaddr = '%a' or username = '%u' or username = '$all' or clientid = '%c';You can use the following placeholders in the authentication SQL, which will be automatically populated with client information by EMQX Cloud when executed: :
- %u: username
- %c: clientid
- %a: client IP address
- %P: plaintext password
The following example data is configured by default.
-- All users are not allowed to subscribe to system topics
INSERT INTO mqtt_acl (allow, ipaddr, username, clientid, access, topic) VALUES (0, NULL, '$all', NULL, 1, '$SYS/#');
-- Allow clients on 10.59.1.100 to subscribe to system topics
INSERT INTO mqtt_acl (allow, ipaddr, username, clientid, access, topic) VALUES (1, '10.59.1.100', NULL, NULL, 1, '$SYS/#');
-- Disable client subscription to /smarthome/+/temperature topic
INSERT INTO mqtt_acl (allow, ipaddr, username, clientid, access, topic) VALUES (0, NULL, '$all', NULL, 1, '/smarthome/+/temperature');
-- Allow clients to subscribe to the /smarthome/${clientid}/temperature topic containing their own Client ID
INSERT INTO mqtt_acl (allow, ipaddr, username, clientid, access, topic) VALUES (1, NULL, '$all', NULL, 1, '/smarthome/%c/temperature');Encryption rules
Most external authentication on EMQX Cloud can be enabled with the hash method, and only the cipher text of the password is stored in the data source to ensure data security. When hashing is enabled, you can specify a salt for each client and configure the salt rules, and the password stored in the database is the cipher text processed according to the salt rules and the hashing method.
Available from: Salting rules and hashing methods。
## unsalted, plaintext
plain
## No salt, hash only
sha256
## salt prefix: use sha256 to encrypt the salt + password concatenated string
salt,sha256
## salt suffix: encrypted with sha256 password + salt concatenated string
sha256,salt
## pbkdf2 with macfun iterations dklen
## macfun: md4, md5, ripemd160, sha, sha224, sha256, sha384, sha512
pbkdf2, sha256, 1000, 20