Integrate with MongoDB
In this article, we will simulate the temperature and humidity data, and publish these data to EMQX Cloud via the MQTT protocol, and then we will use the EMQX Cloud Data Integrations to store the data to MongoDB.
Before you start, you will need to complete the following:
- A deployment (EMQX Cluster) has been created on EMQX Cloud.
- For Professional Plan users: Please complete Peering Connection Creation first, all IPs mentioned below refer to the internal network IP of the resource.(Professional Plan with a NAT gateway can also use public IP to connect to resources).
- For BYOC Plan users: Please establish a peering connection between the VPC where BYOC is deployed and the VPC where the resources are located. All IPs mentioned below refer to the internal IP of the resources. If you need to access the resources via public IP addresses, please configure a NAT gateway in your public cloud console for the VPC where BYOC is deployed.
MongoDB Configuration
Install MongoDB
bash# EMQX currently supports MongoDB 5.x drivers, not 6.x yet docker run --name mongo -d -p 27017:27017 mongo:5.0Enter Container
bashdocker exec -it mongo mongosh emqxInsert data into
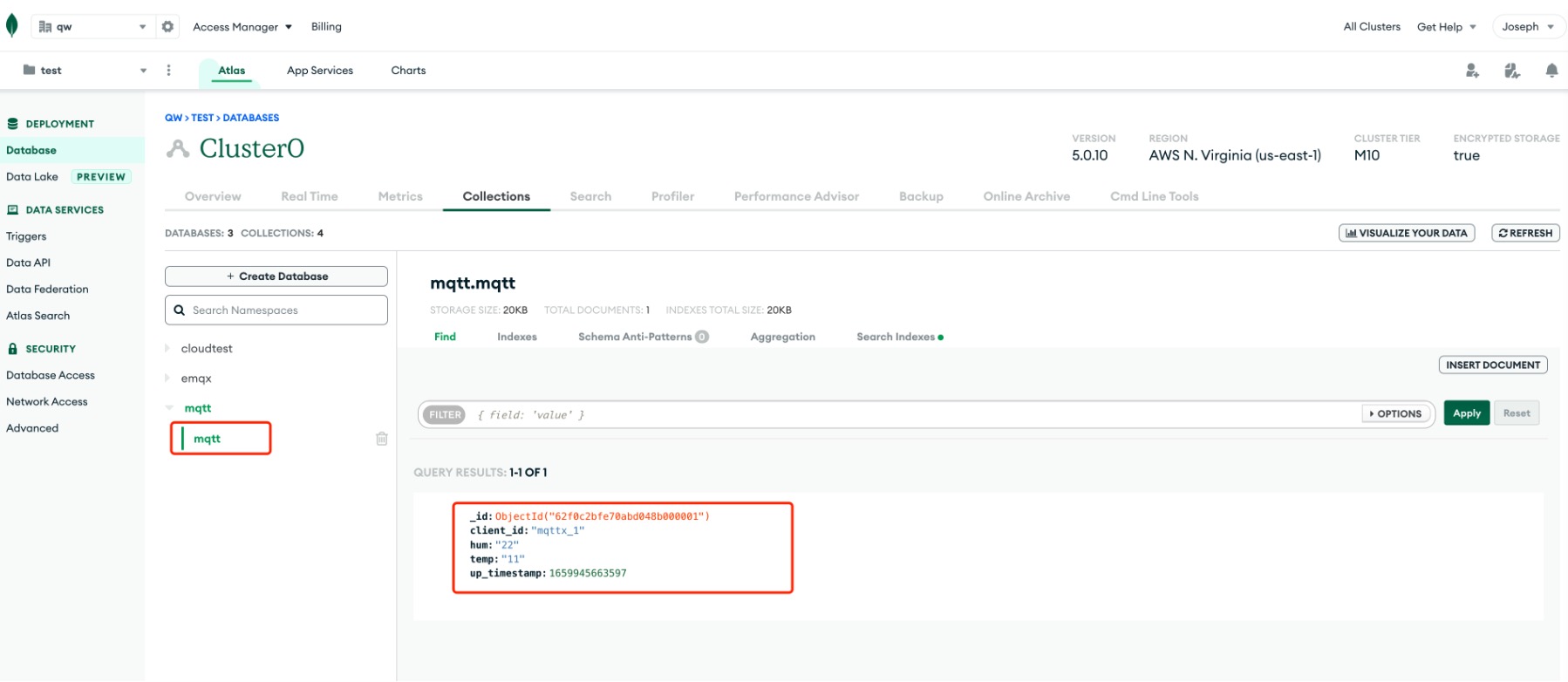
temp_humcollection and view the result.sqldb.temp_hum.insert({up_timestamp: 34256, client_id: 1, temp: 20, hum: 33}) db.temp_hum.find()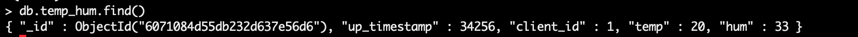
Data Integrations Configuration
Go to Deployment Details and click on Data Integrations on the left menu bar.
Create MongoDB Resource
Click on
MongoDB Single Modeunder the Data Persistence.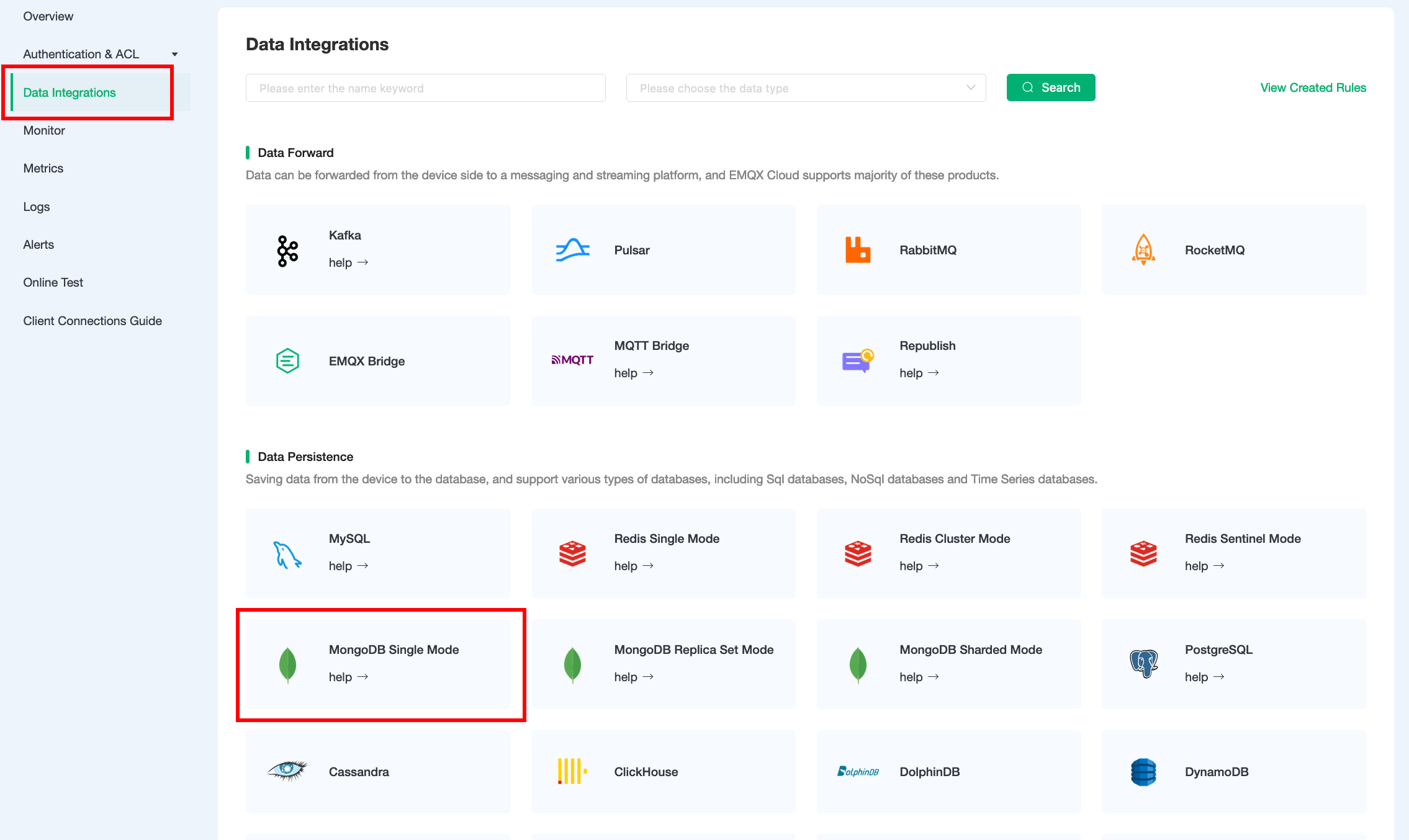
Fill in the information you have just created and click
Test. If there is an error, you should check if the database configuration is correct. Then click onNewto create MongoDB resource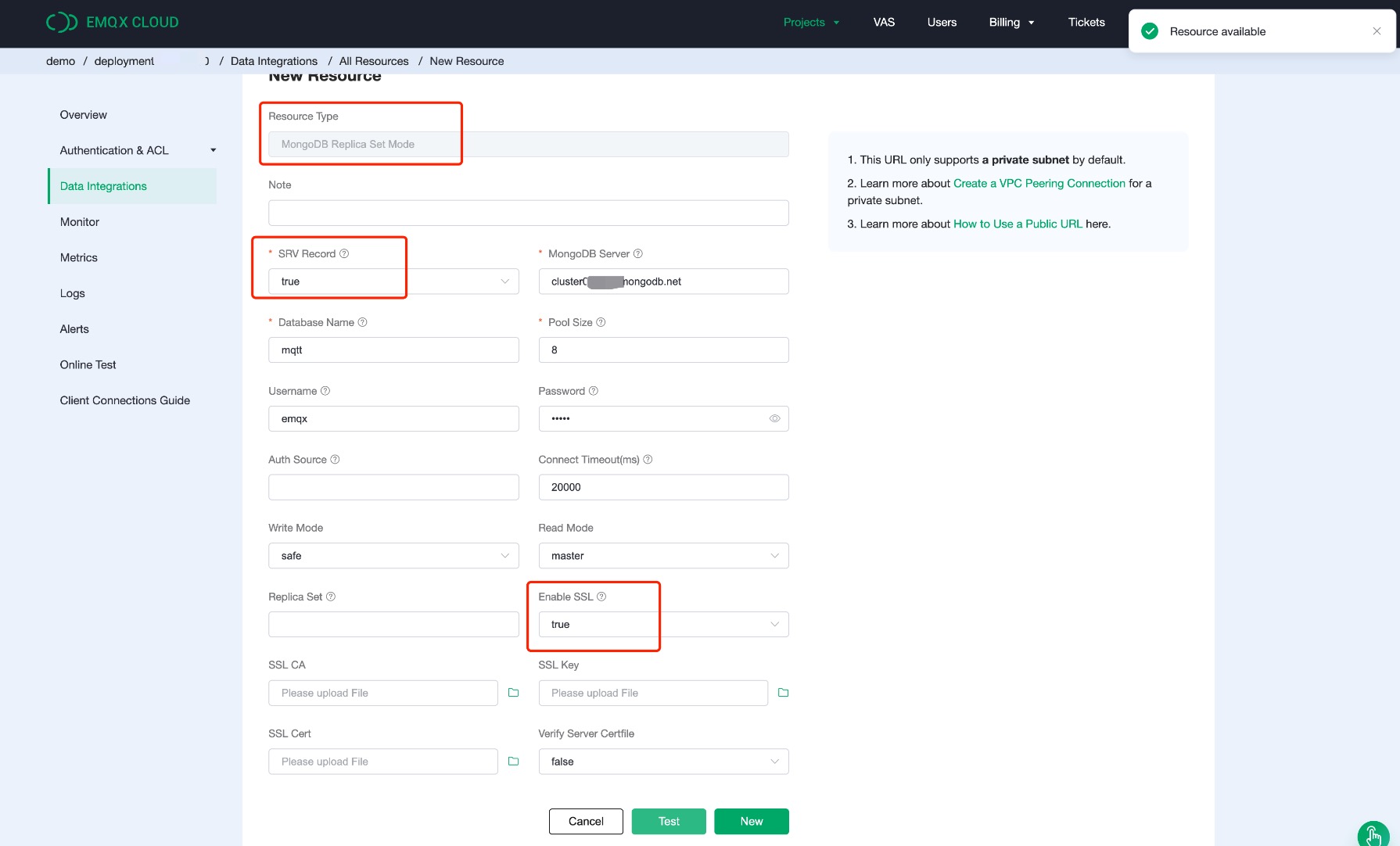
Create Rule
Choose the MongoDB resource under Configured Resources, click on
New Ruleand enter the following rule to match the SQL statement. In the following rule we read the timeup_timestampwhen the message is reported, the client ID, the message body (Payload) from thetemp_hum/emqxtopic and the temperature and humidity from the message body respectively.sqlSELECT timestamp div 1000 AS up_timestamp, clientid AS client_id, payload.temp AS temp, payload.hum AS hum FROM "temp_hum/emqx"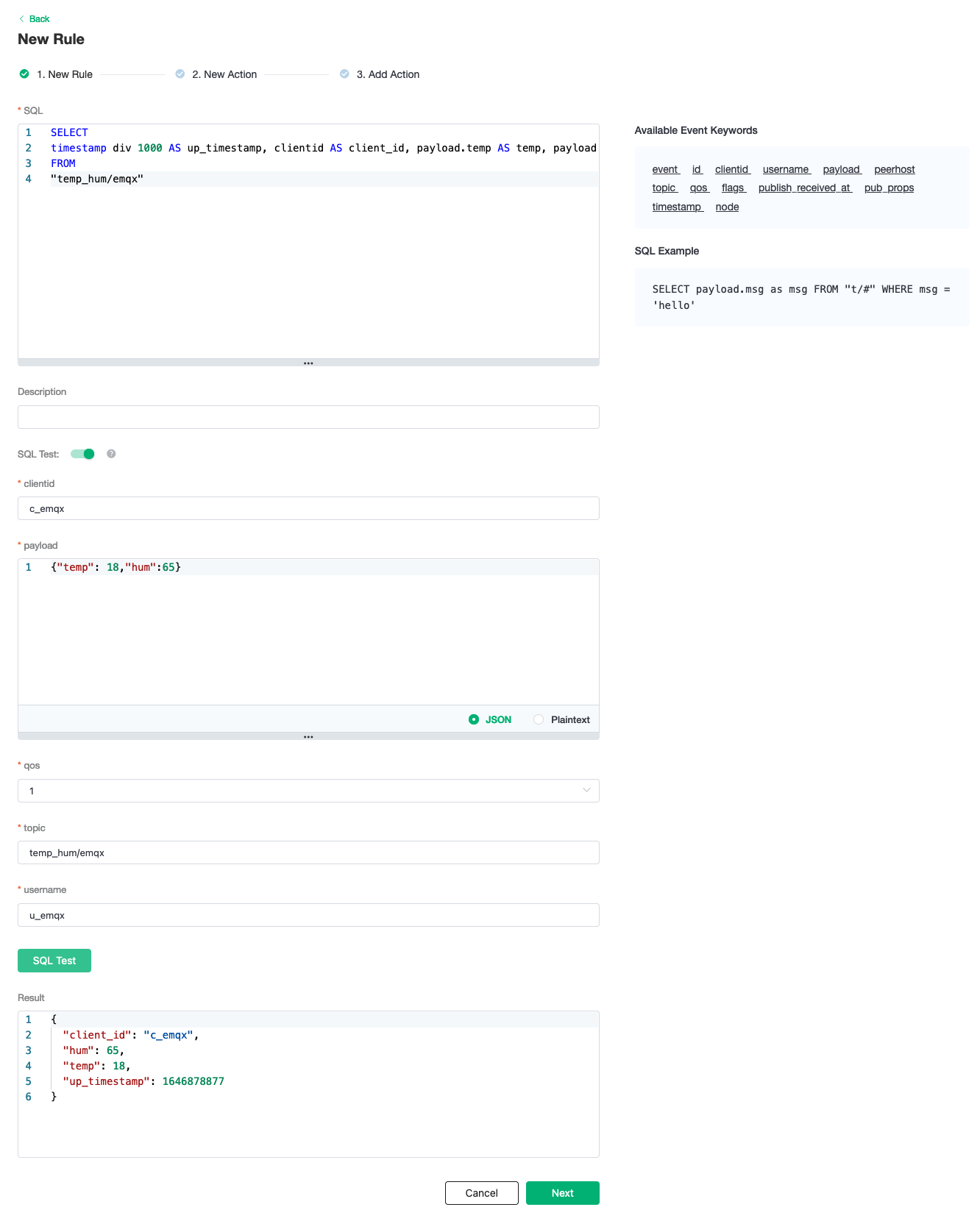
Create Action
Click on the
Nextbutton in the bottom to enter action view. Select the resource created in the first step, selectData Persistence - Data to MongoDBforAction Typeand enter the following data to insert into the SQL template.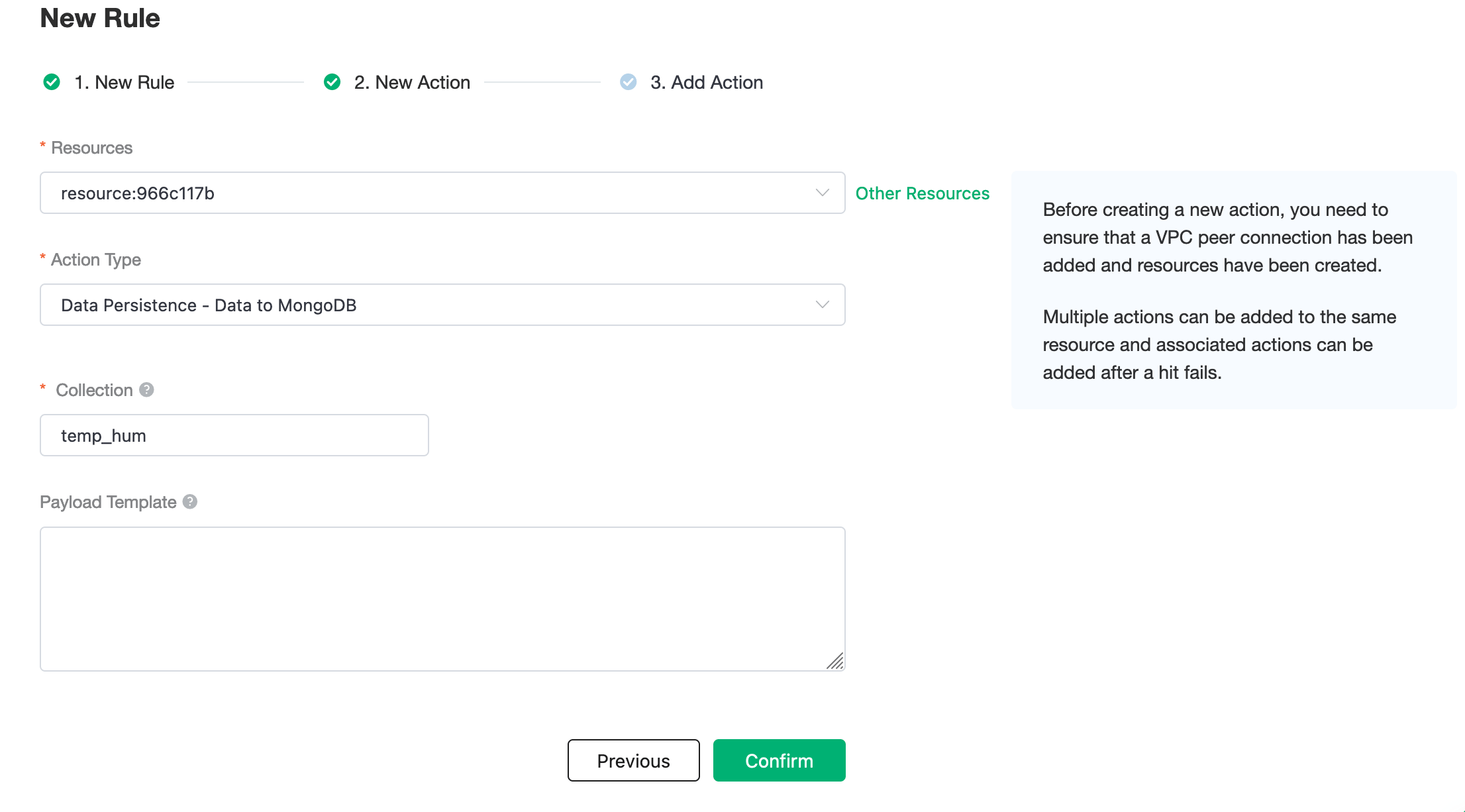
Click on
Confirmto create action.View Resource Detail
Click on the resource to see the detail.
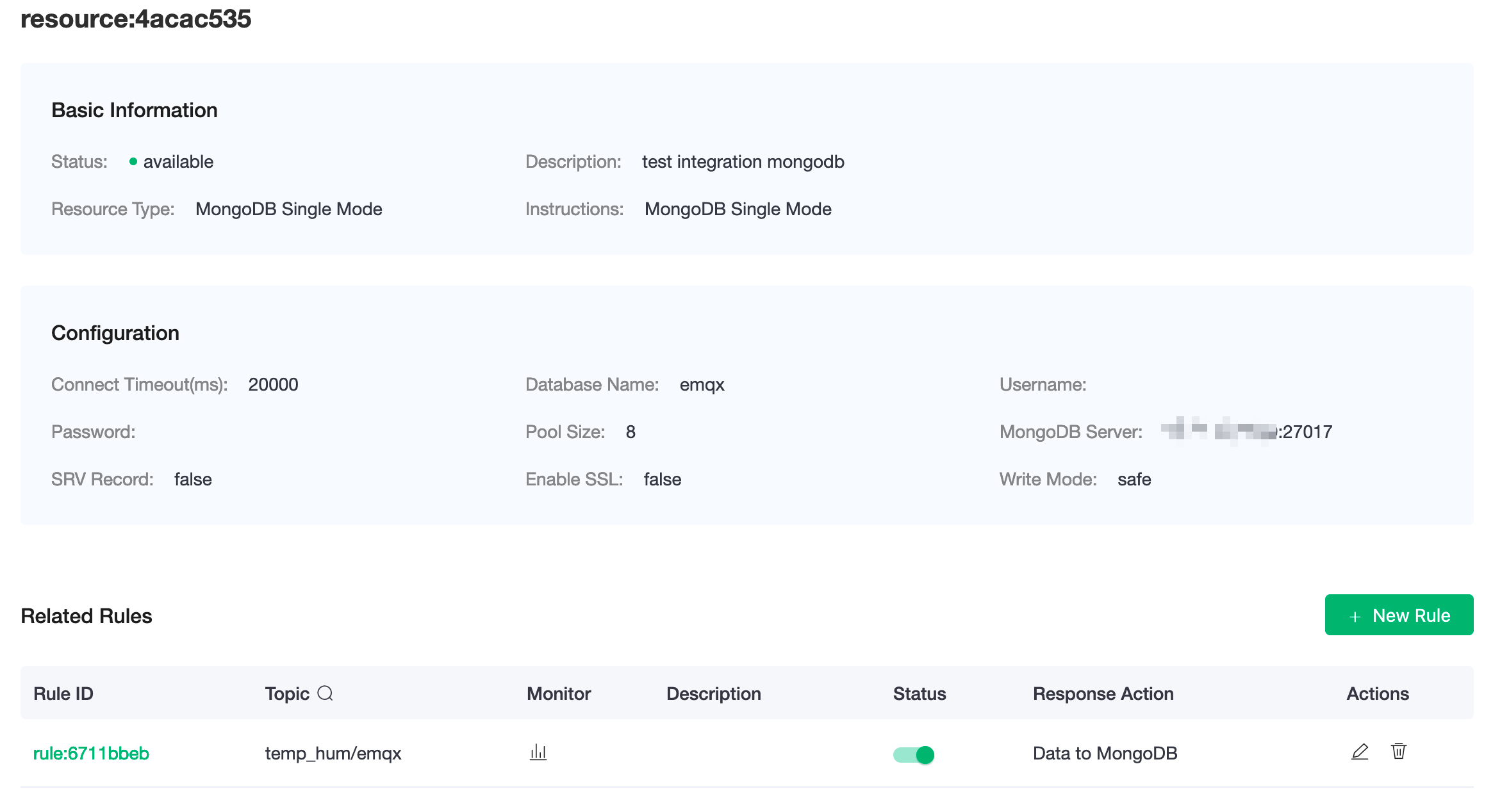
Check Rules Monitoring
Click the monitor icon of rule to see the metrics
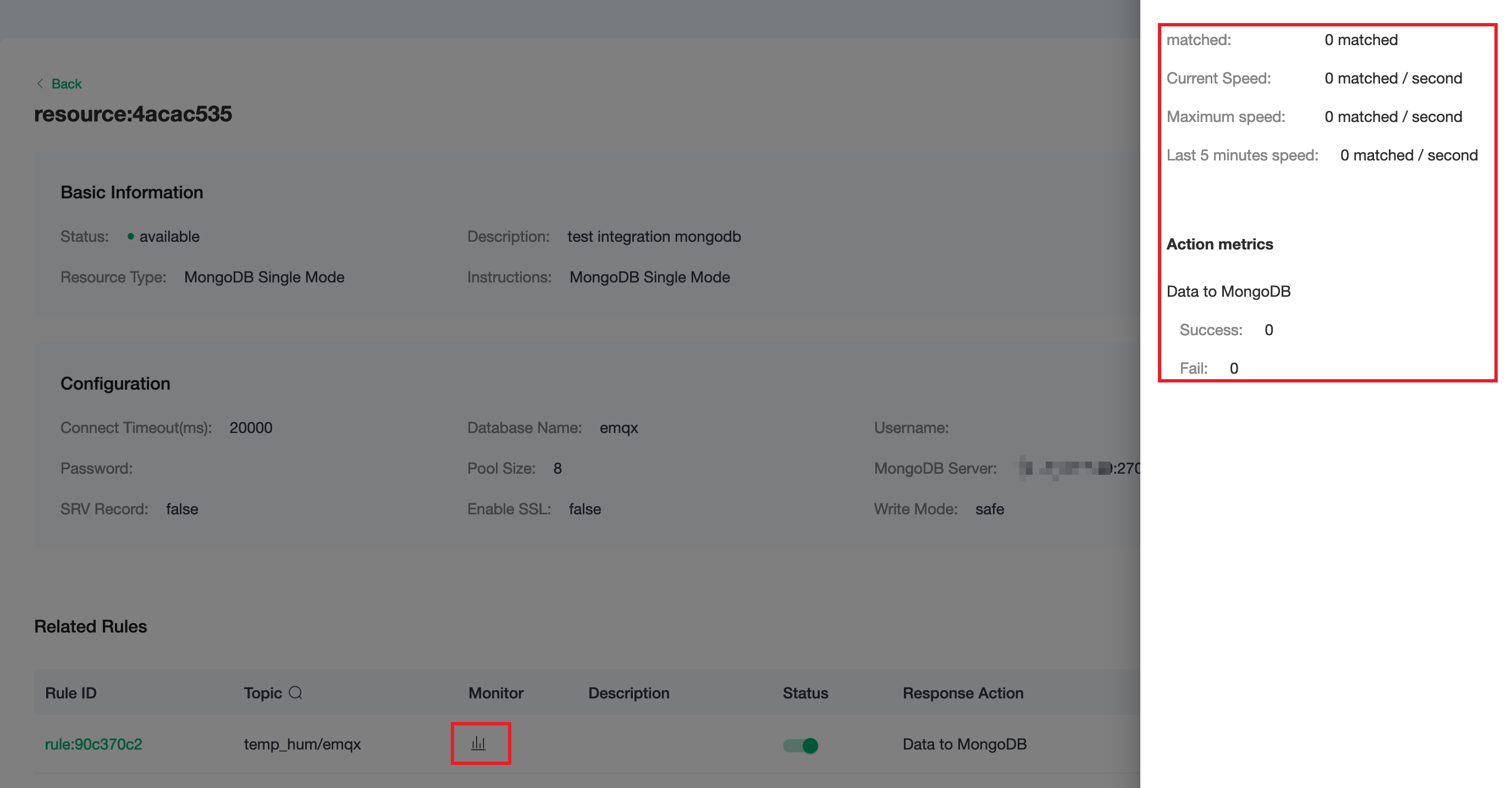
Test
Use MQTTX to simulate publishing temperature and humidity data
You need to replace broker.emqx.io with the deployment connection address you have created and add the client-side authentication information in the EMQX Dashboard.
View stored results
db.temp_hum.find()