Integrate with HStreamDB
HStreamDB is a streaming database designed for large-scale real-time data stream management, including access, storage, processing, and distribution. It uses standard SQL (and its streaming extensions) as the main interface language, with real-time as the main feature, and aims to simplify the operation and management of data streams and the development of real-time applications.
In this article, we will simulate temperature and humidity data and report it to EMQX Cloud via the MQTT protocol, and then use the EMQX Cloud data integrations to dump the data to HStreamDB.
Before you start, you need to complete the following operations:
- A deployment (EMQX Cluster) has been created on EMQX Cloud.
- For Professional Plan users: Please complete Peering Connection Creation first, all IPs mentioned below refer to the internal network IP of the resource.(Professional Plan with a NAT gateway can also use public IP to connect to resources).
- For BYOC Plan users: Please establish a peering connection between the VPC where BYOC is deployed and the VPC where the resources are located. All IPs mentioned below refer to the internal IP of the resources. If you need to access the resources via public IP addresses, please configure a NAT gateway in your public cloud console for the VPC where BYOC is deployed.
HStreamDB Configuration
HStreamDB Installation
To deploy, refer to the HStreamDB Help and create the hstream-client using the following command.
Create quick-start.yaml
bash## quick-start.yaml version: "3.5" services: hserver0: image: hstreamdb/hstream:v0.8.0 depends_on: - zookeeper - hstore ports: - "6570:6570" expose: - 6570 networks: - hstream-network volumes: - data_store:/data/store command: - bash - "-c" - | set -e /usr/local/script/wait-for-storage.sh hstore 6440 zookeeper 2181 600 \ /usr/local/bin/hstream-server \ --host 0.0.0.0 --port 6570 \ --internal-port 6571 \ --server-id 100 \ --address < server ip > \ --zkuri zookeeper:2181 \ --store-config /data/store/logdevice.conf \ --store-admin-host hstore --store-admin-port 6440 hserver1: image: hstreamdb/hstream:v0.8.0 depends_on: - zookeeper - hstore ports: - "6572:6572" expose: - 6572 networks: - hstream-network volumes: - data_store:/data/store command: - bash - "-c" - | set -e /usr/local/script/wait-for-storage.sh hstore 6440 zookeeper 2181 600 \ /usr/local/bin/hstream-server \ --host 0.0.0.0 --port 6572 \ --internal-port 6573 \ --server-id 101 \ --address < server ip > \ --zkuri zookeeper:2181 \ --store-config /data/store/logdevice.conf \ --store-admin-host hstore --store-admin-port 6440 hstream-http-server: image: hstreamdb/hstream:v0.8.0 depends_on: - hserver0 - hserver1 ports: - "6580:6580" expose: - 6580 networks: - hstream-network command: - bash - "-c" - | set -e /usr/local/bin/hstream-http-server \ -gRPCServerHost hserver \ -httpServerPort 6580 \ -gRPCServerPort 6570 hstore: image: hstreamdb/hstream:v0.8.0 networks: - hstream-network volumes: - data_store:/data/store command: - bash - "-c" - | set -ex /usr/local/bin/ld-dev-cluster --root /data/store \ --use-tcp --tcp-host $$(hostname -I | awk '{print $$1}') \ --user-admin-port 6440 \ --no-interactive zookeeper: image: zookeeper expose: - 2181 networks: - hstream-network volumes: - data_zk_data:/data - data_zk_datalog:/datalog networks: hstream-network: name: hstream-network volumes: data_store: name: quickstart_data_store data_zk_data: name: quickstart_data_zk_data data_zk_datalog: name: quickstart_data_zk_datalogStart HStreamDB service
bash# Launch in the same folder docker-compose -f quick-start.yaml up # Backstage start-up docker-compose -f quick-start.yaml up -dLaunching the SQL command line interface of HStreamDB
Use the following command to create the hstream-client :
bashdocker run -it --rm --name some-hstream-cli --network host hstreamdb/hstream:v0.8.0 hstream-client --port 6570 --client-id 1Access to the console.
bash__ _________________ _________ __ ___ / / / / ___/_ __/ __ \/ ____/ | / |/ / / /_/ /\__ \ / / / /_/ / __/ / /| | / /|_/ / / __ /___/ // / / _, _/ /___/ ___ |/ / / / /_/ /_//____//_/ /_/ |_/_____/_/ |_/_/ /_/ Command :h To show these help info :q To exit command line interface :help [sql_operation] To show full usage of sql statementStream creation
bash> CREATE STREAM temp_hum; temp_hum > SHOW STREAMS; temp_hum
EMQX Cloud Data Integration Configuration
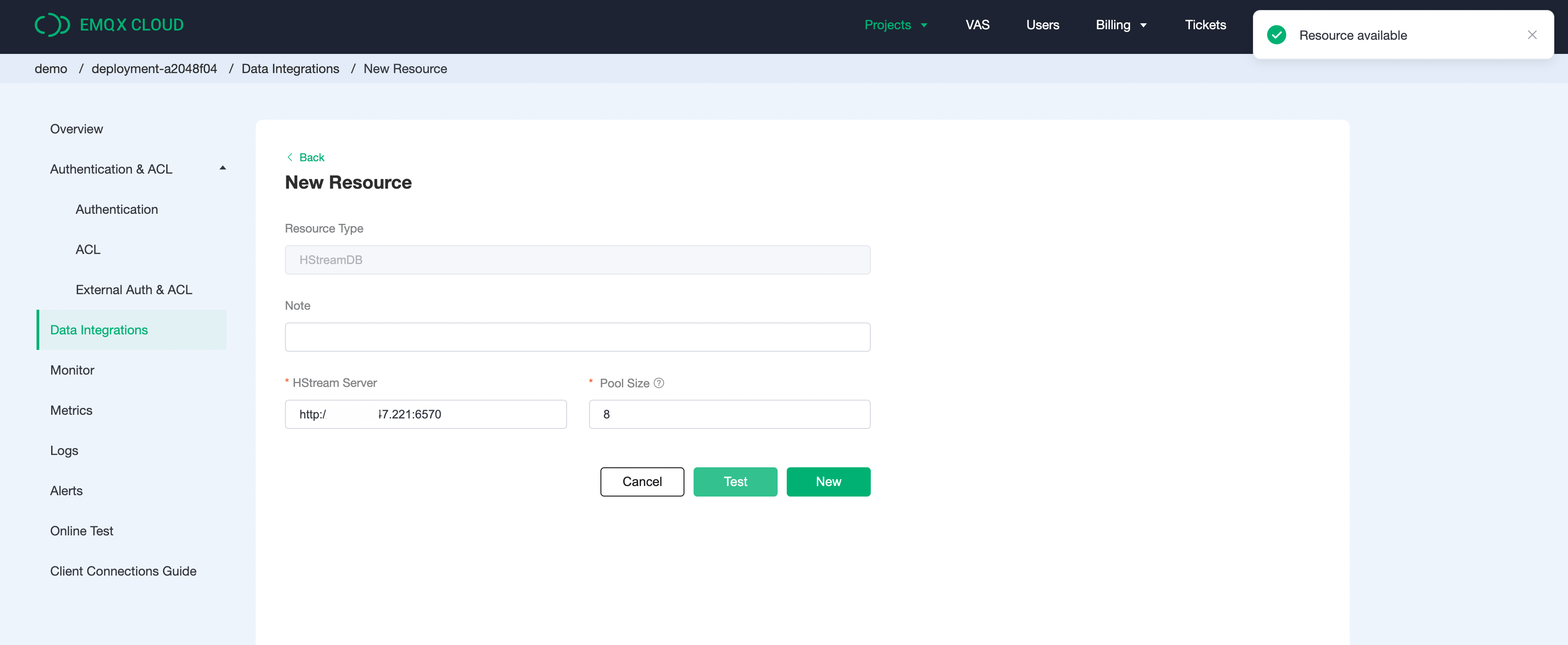
Create HStreamDB resource
Click on
Data Integrationin the left menu bar, find HStreamDB under Data Persistence, and click onNew Resource.
Fill in the information about the HStreamDB database you have just created and click on Test. If an error occurs, you should check if the database configuration is correct.
Create Rule
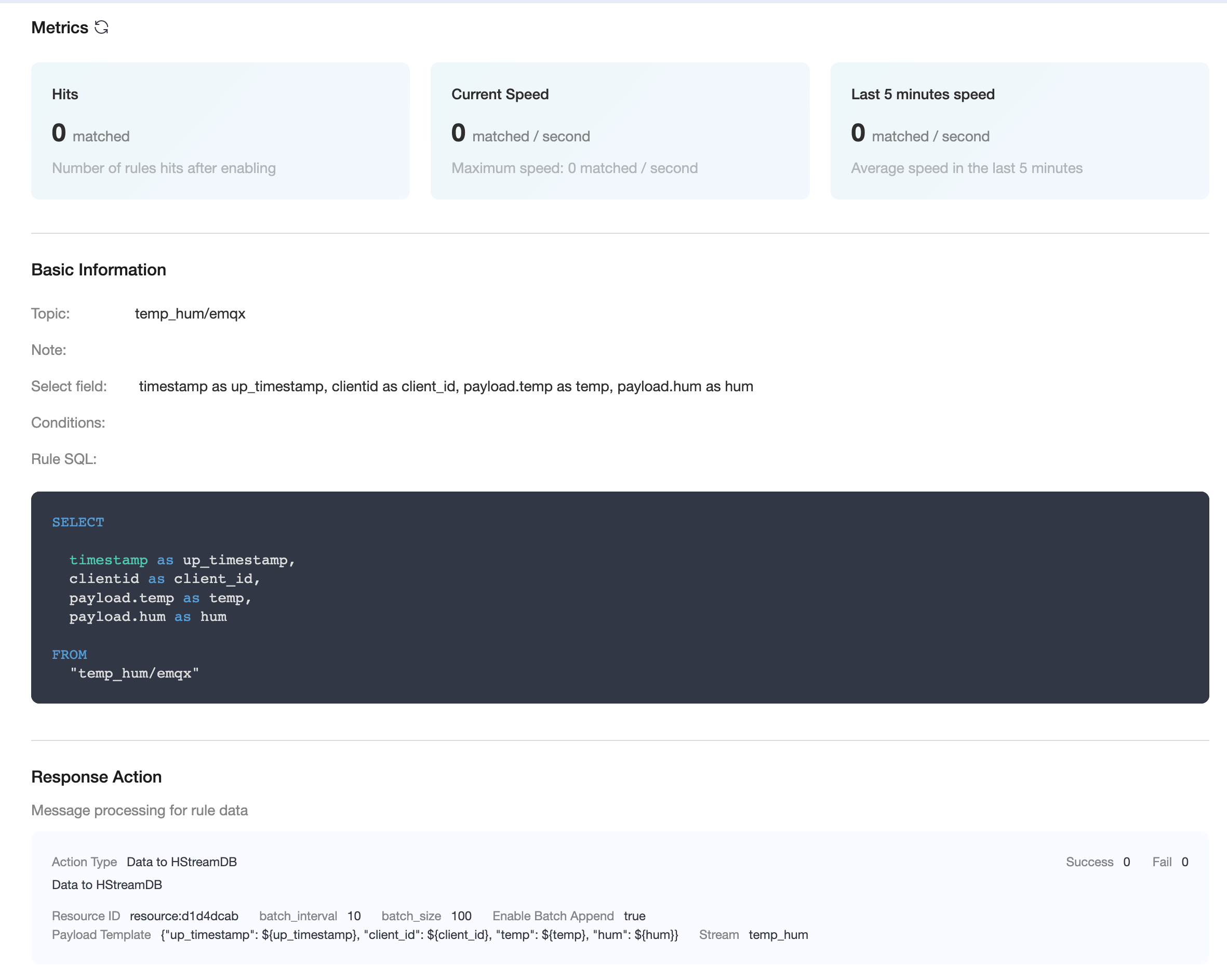
Once the resource is created click on New Rule and enter the following rule to match the SQL statement. In the following rule we read the message upload time
up_timestamp, the client ID, the message body (Payload) from thetemp_hum/emqxsubject and the temperature and humidity from the message body respectively.sqlSELECT timestamp as up_timestamp, clientid as client_id, payload.temp as temp, payload.hum as hum FROM "temp_hum/emqx"We can use the
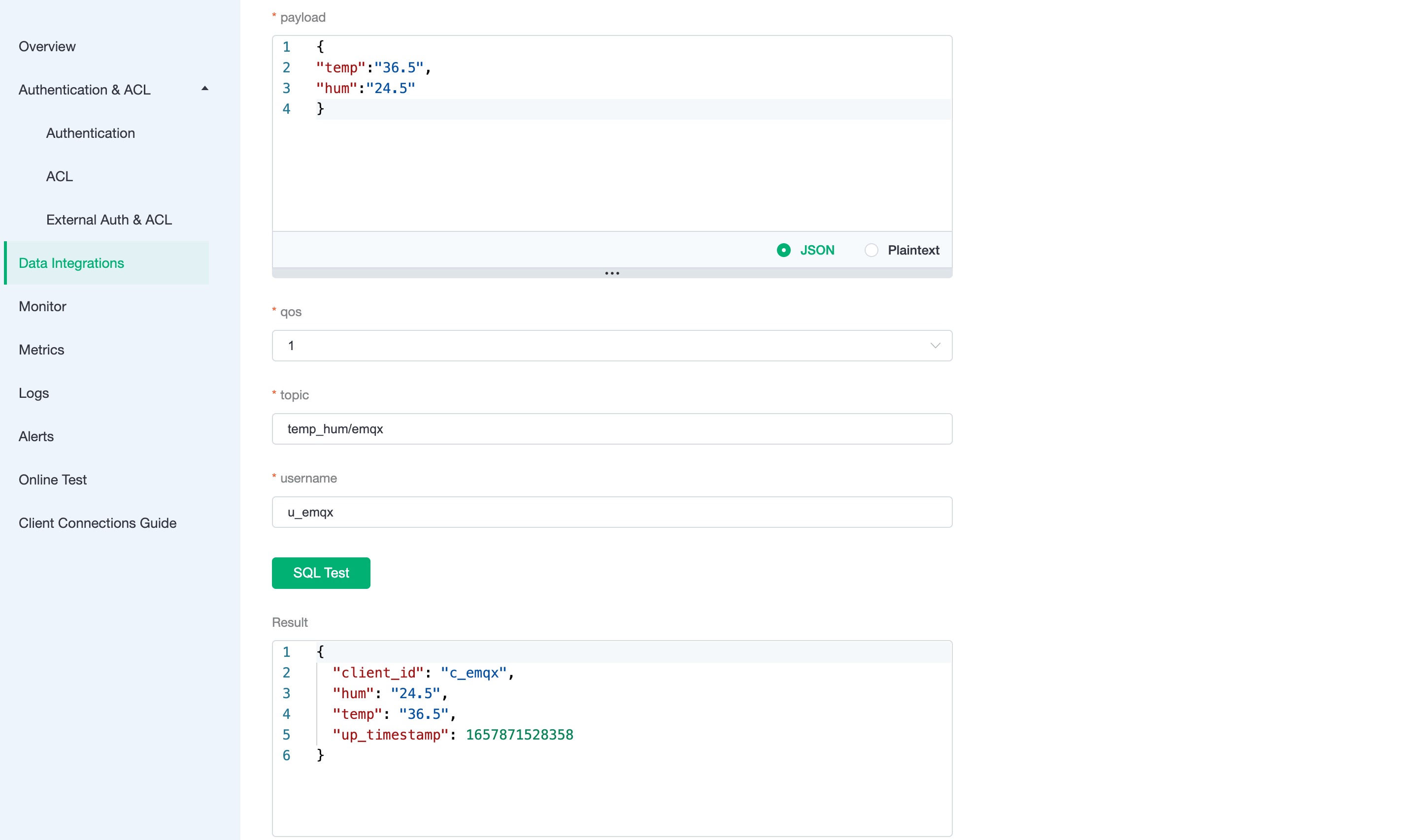
SQL testto test and see the results.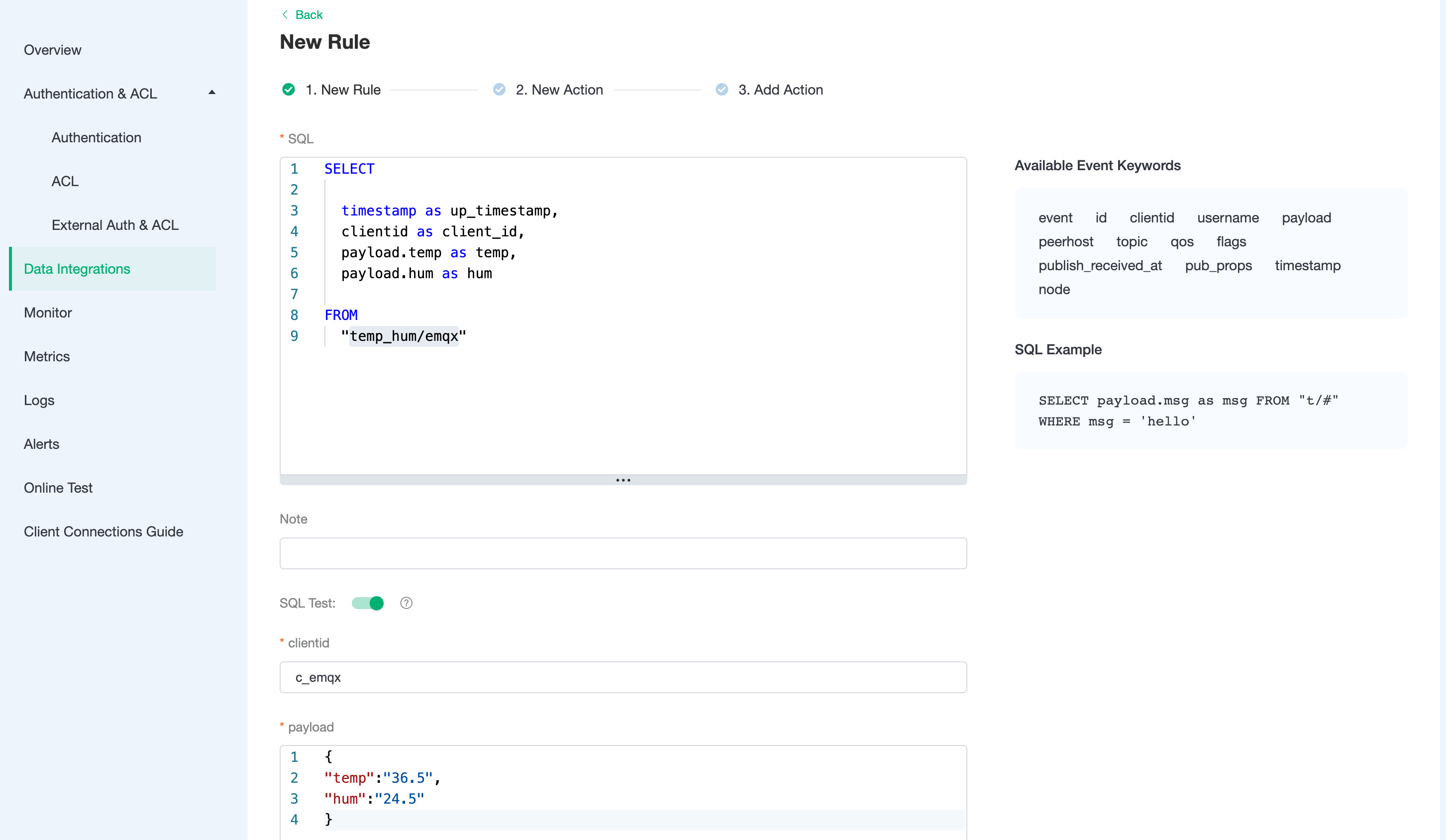
Add Action
Click next to the action screen, select the resource created in the first step, select
Data Persistence - Save Data to HStreamDBfor the action type and enter the parameters, which are defined in the following table.Parameter Name Definition Type Stream Stream name, no variables allowed String Ordering Key Partition key, use variable String Enable Bulk Insertion Enables or disables bulk writing, default is on Boolean Maximum number of batches Maximum number of message entries in a batch Integer Max Batch Interval (ms) Maximum interval between batches, in milliseconds Integer Message content template Content of the message message to be written Binary Insert the message content template and click on Confirm.
sql{"up_timestamp": ${up_timestamp}, "client_id": ${client_id}, "temp": ${temp}, "hum": ${hum}}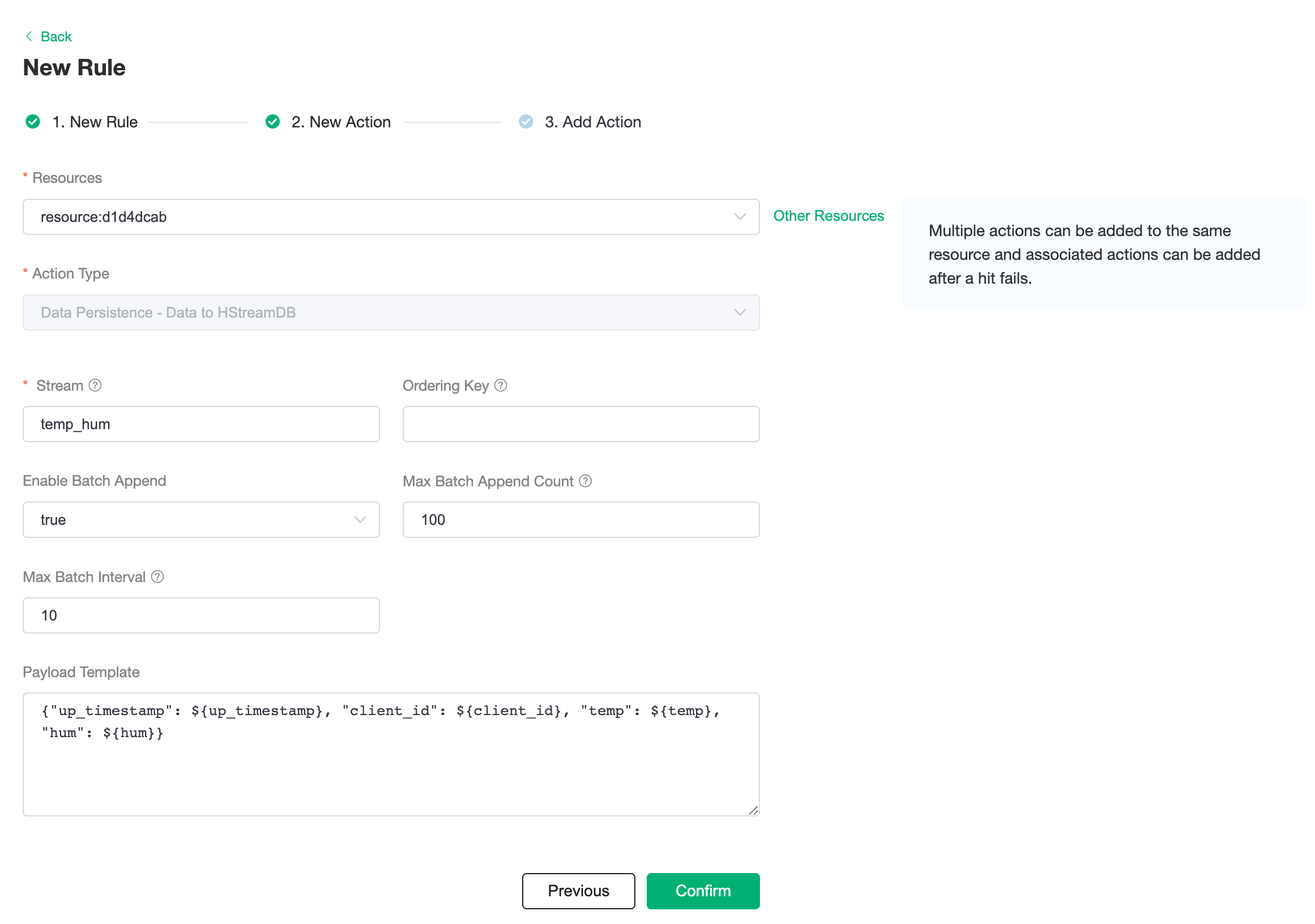
View Resource Detail
Once the action has been created, return to the list and click on the resource to view the resource details and rule monitoring information.
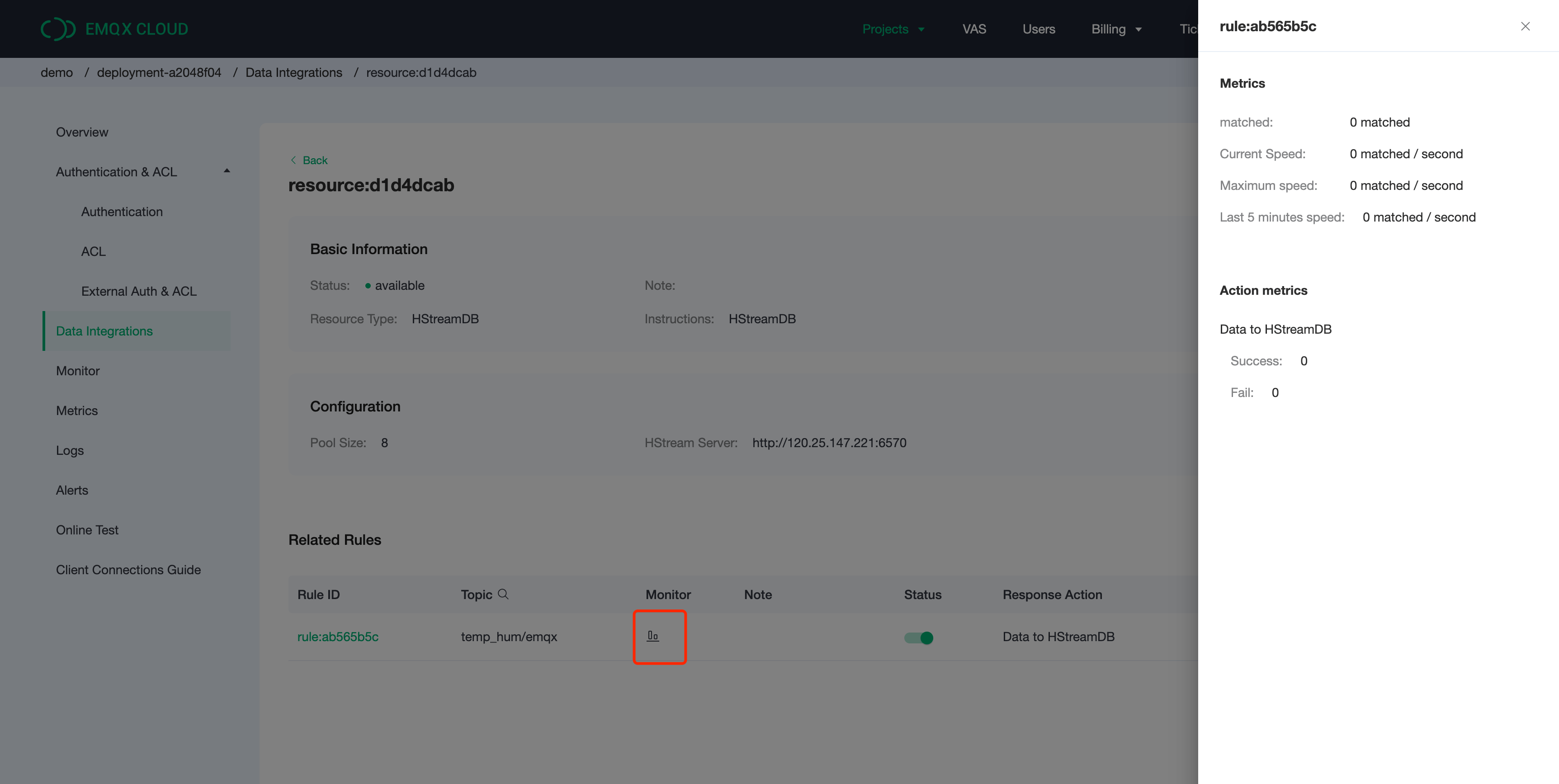
Check Rules Monitoring
The rule details screen allows you to view rule and action details by clicking on the rule.
Test
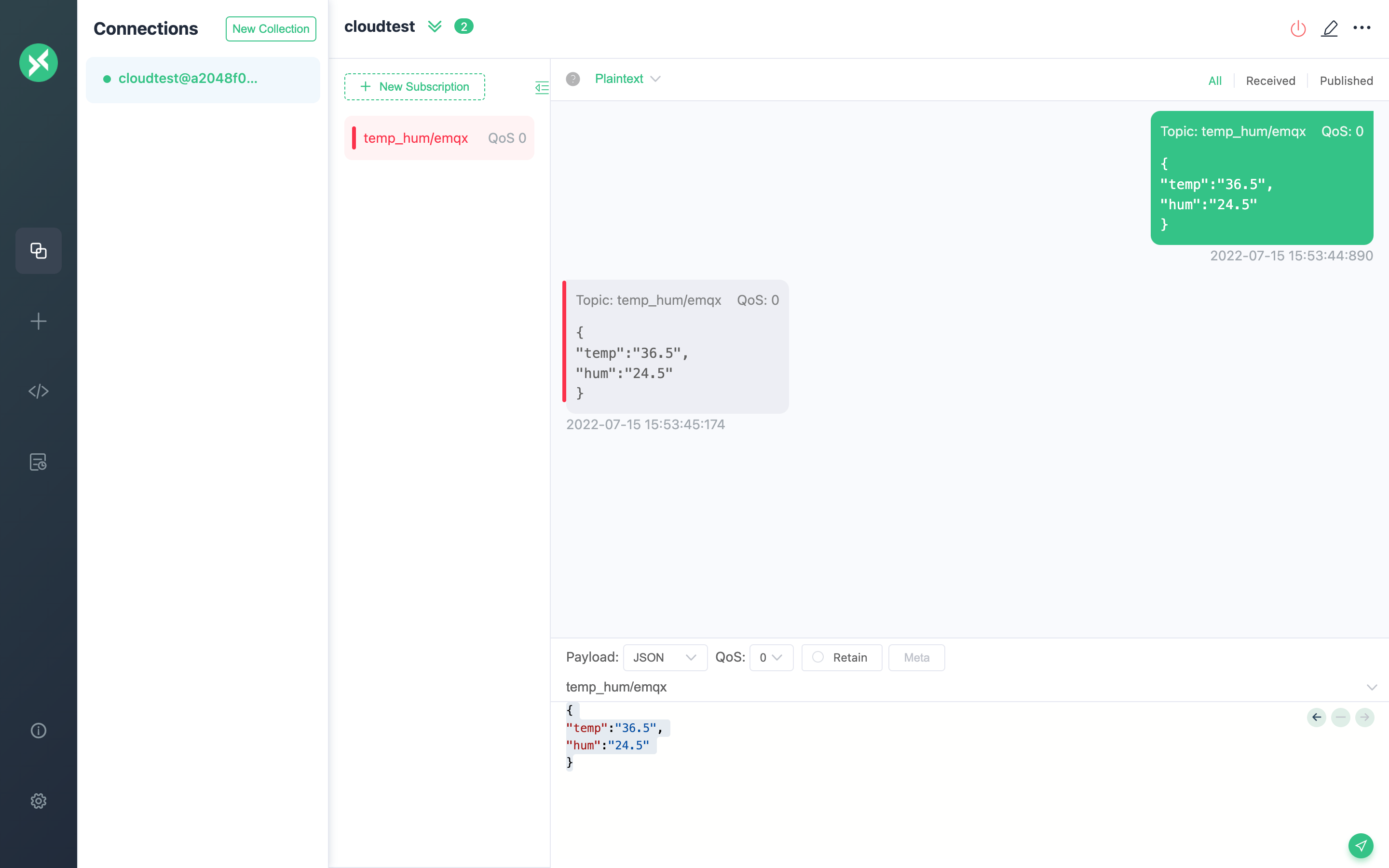
Use MQTTX to connect the deployment
You need to replace broker.emqx.io with the created deployment connection address, and add client authentication information to the EMQX Cloud Dashboard.
topic:
temp_hum/emqxpayload:
json{ "temp": "36.4", "hum": "23.5" }
View the data saving results
The data has been written to HStreamDB and you can use any consumption method to consume the message.
The consumption tool fetcher based on the HStream Golang SDK is used in this example, and the result is as follows.
sql./fetcher -s f1 -n temp_hum -p <server ip>:6570 -c cons1 -v