Data Analysis
The ECP data analysis functionality is the core interactive interface of the industrial data integration module, providing you with a complete workflow from browsing data sources, building queries to analyzing results. Unlike NeuronEX's single-point data analysis, ECP can aggregate data from all NeuronEX instances, achieving unified cross-node data analysis and insights.
Main Functional Features
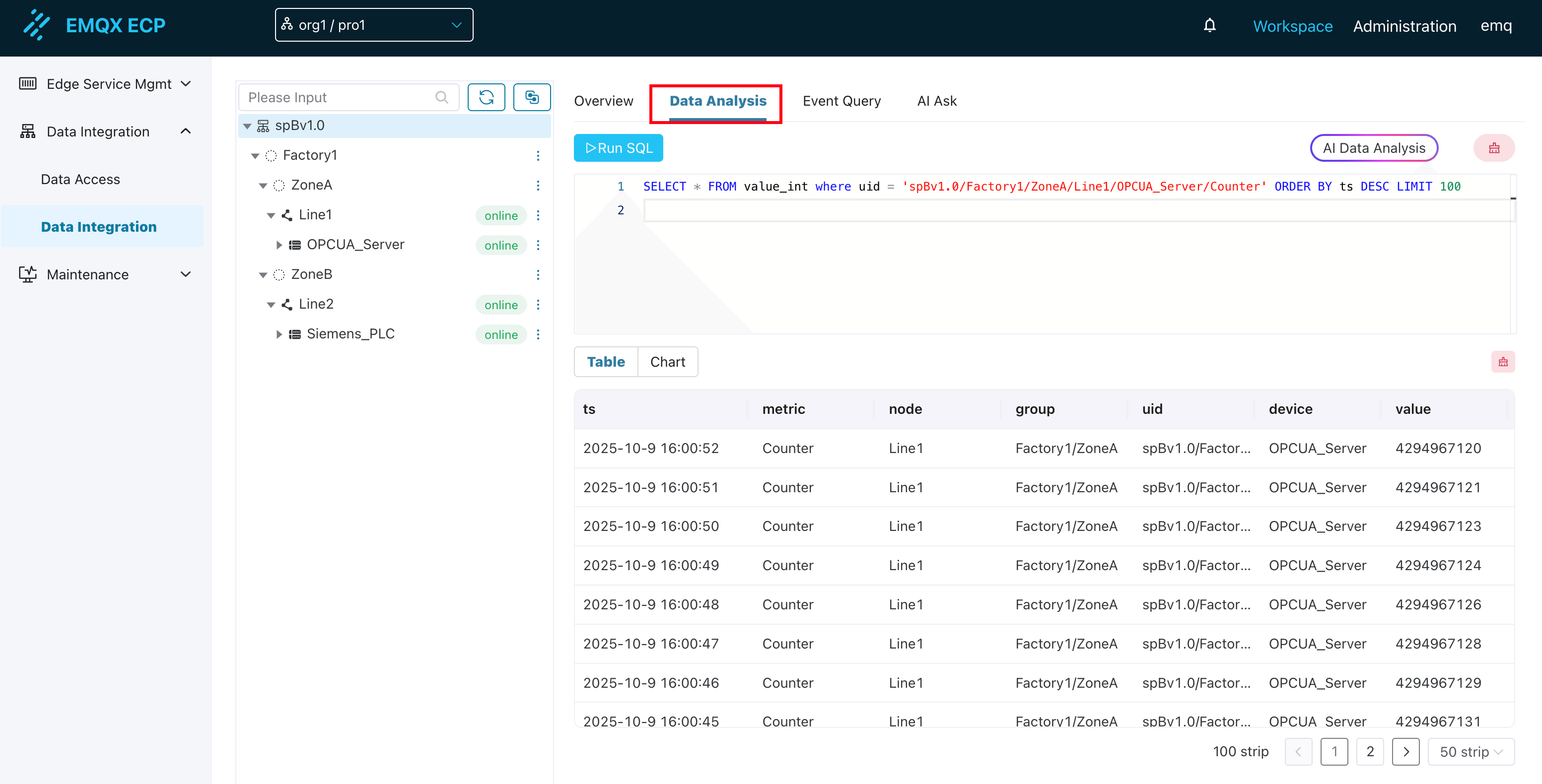
1. Unified Entry and Interface Layout
Unified Entry: All data browsing, SQL query, and result display functions are integrated into the unified "Data Analysis" page.
Clear Layout: The page adopts a three-column layout:
- Left Data Source Navigation Area: Displays industrial data modeling information from all NeuronEX instances in a tree structure
- Upper Right SQL Input and Configuration Area: Used for writing and executing SQL queries
- Bottom Result Display Area: Shows query results (table or chart)
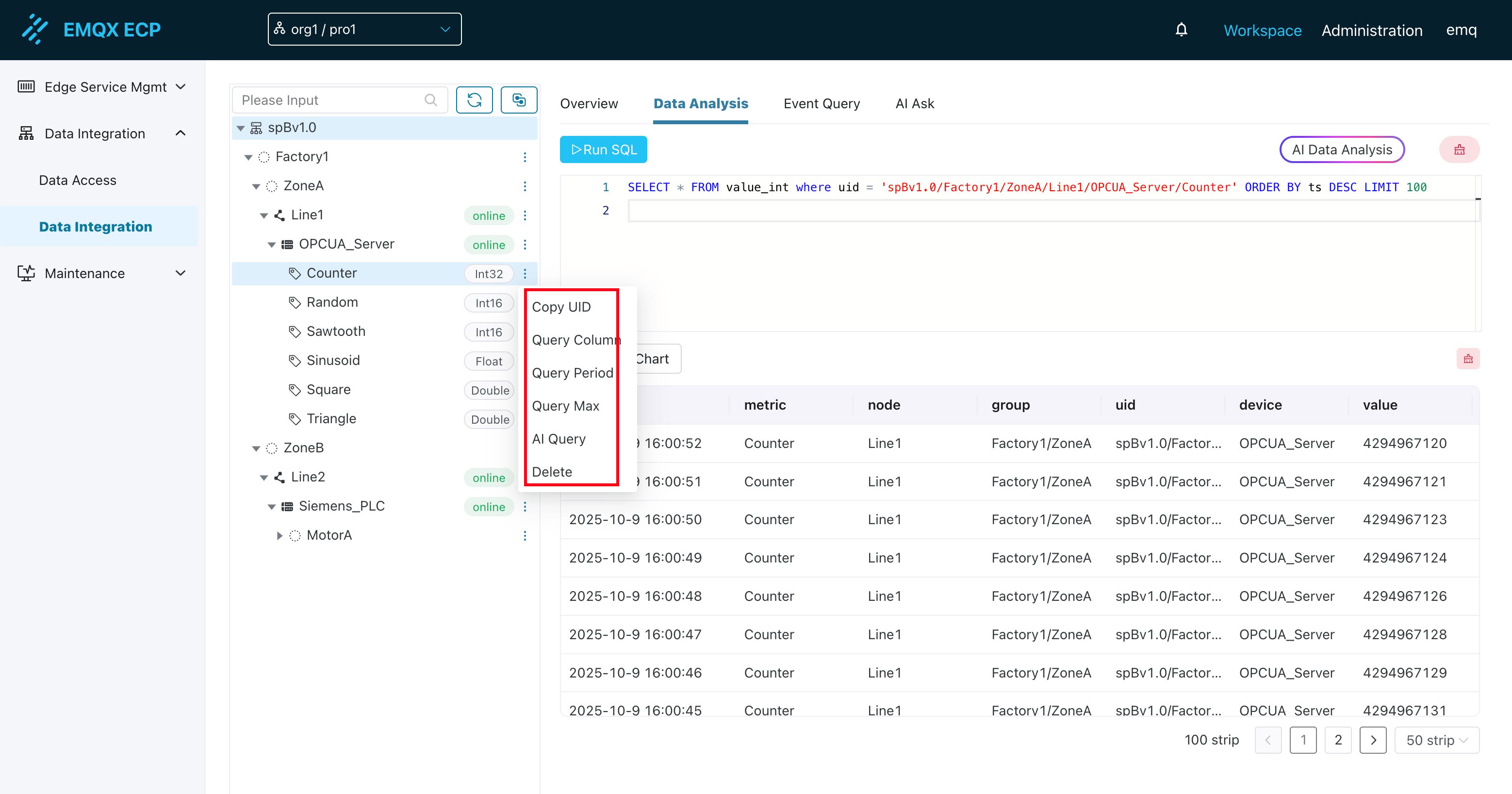
2. Data Source Tree Directory
Structured Display: The left side clearly lists all virtual nodes, edge nodes, device nodes, and specific data tags from NeuronEX instances in a tree structure.
Type Display: Each tag is clearly marked with its data type stored in Datalayers (e.g., Int32, Float, Bool, String), helping users build correct queries.
Convenient Operations:
- Refresh: Supports manual refresh of the tree directory to get the latest node and tag information
- Tag Search: Provides tag name search functionality to quickly locate target tags
- Switch Alias: Can switch display between original names and custom aliases
SQL Query Examples: After selecting a data tag, the system automatically provides common SQL query examples:
- Query Latest Data: Query recent data for this tag
- Query Time Range Data: Query data within a specified time range for this tag
- Query Maximum Value: Query the maximum value of this tag
- AI Smart Query: Generate complex queries through natural language
3. Intelligent SQL Input Area
Assisted Writing:
- Keyword Hints: Provides automatic completion hints for common SQL keywords when entering SQL
- Syntax Highlighting: Performs syntax highlighting on SQL statements to improve readability
- Line Number Display: Facilitates locating and debugging
Query Restrictions:
- Single Query: Currently supports executing a single SQL query statement
- Query Type Restriction: Only accepts query-type SQL statements (SELECT). To ensure data security and system stability, data definition or modification operations such as CREATE TABLE, INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE are not supported
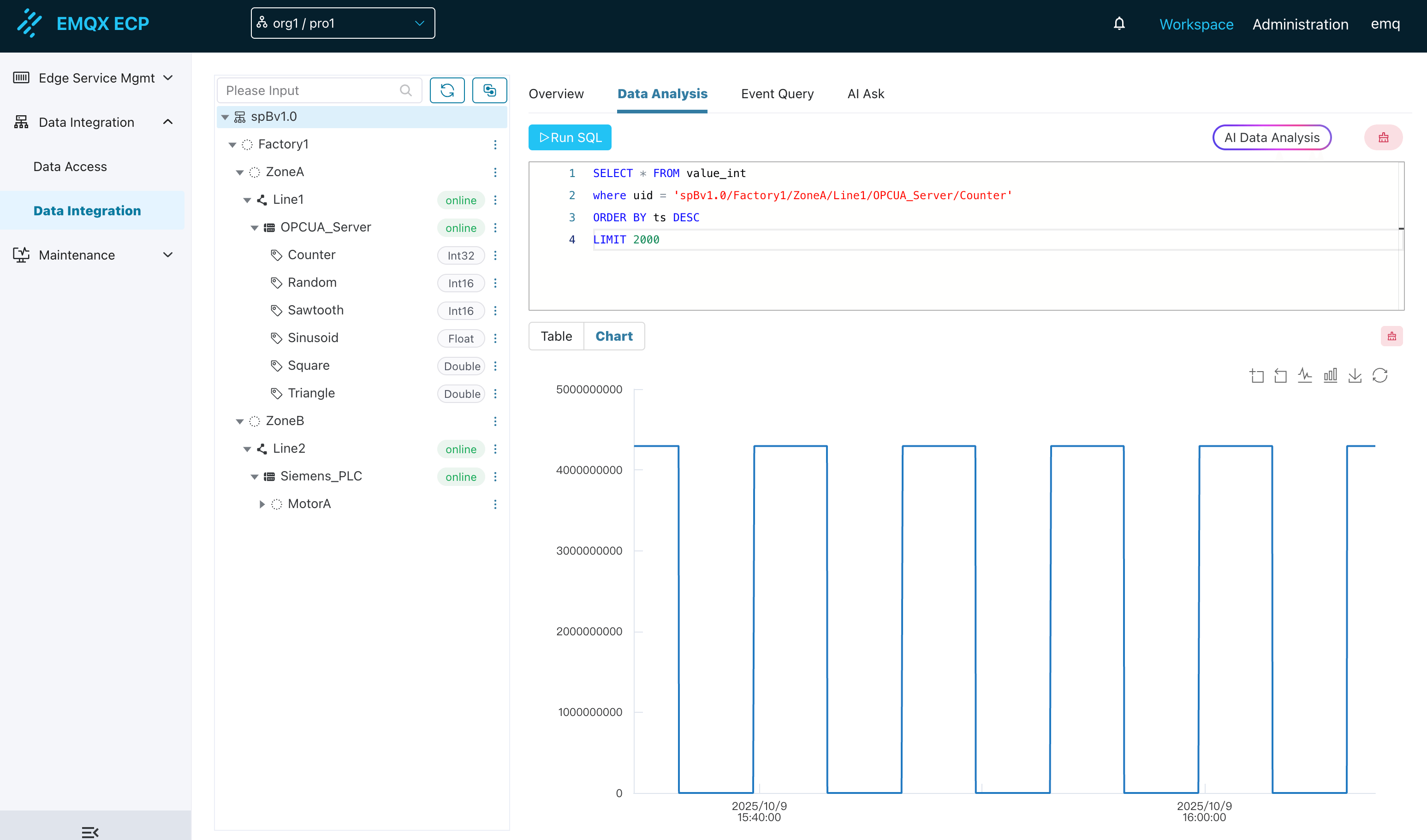
4. Result Display Area
Multi-View Display: Each successfully executed SQL query result will be displayed in this area in the form of a table or chart.
Table Display:
- Default display method, clearly presenting query-returned data in row-column structure
- Supports basic table operations such as pagination and sorting
- Displays data count and pagination information
Chart Display:
- Support Condition: If the SQL query result contains timestamp fields and numeric fields, the system will automatically support switching the result to chart view
- Chart Types:
- Line Chart: Suitable for showing trend changes in time-series data
- Bar Chart: Suitable for comparing data volumes across different categories or time points
- Interactive Features:
- Chart Zoom: Supports partial zoom of the chart to view details
- Save and Download: Supports saving the current chart as an image file (such as PNG) for local download
- Legend Interaction: Click the legend to show/hide corresponding series for focused analysis
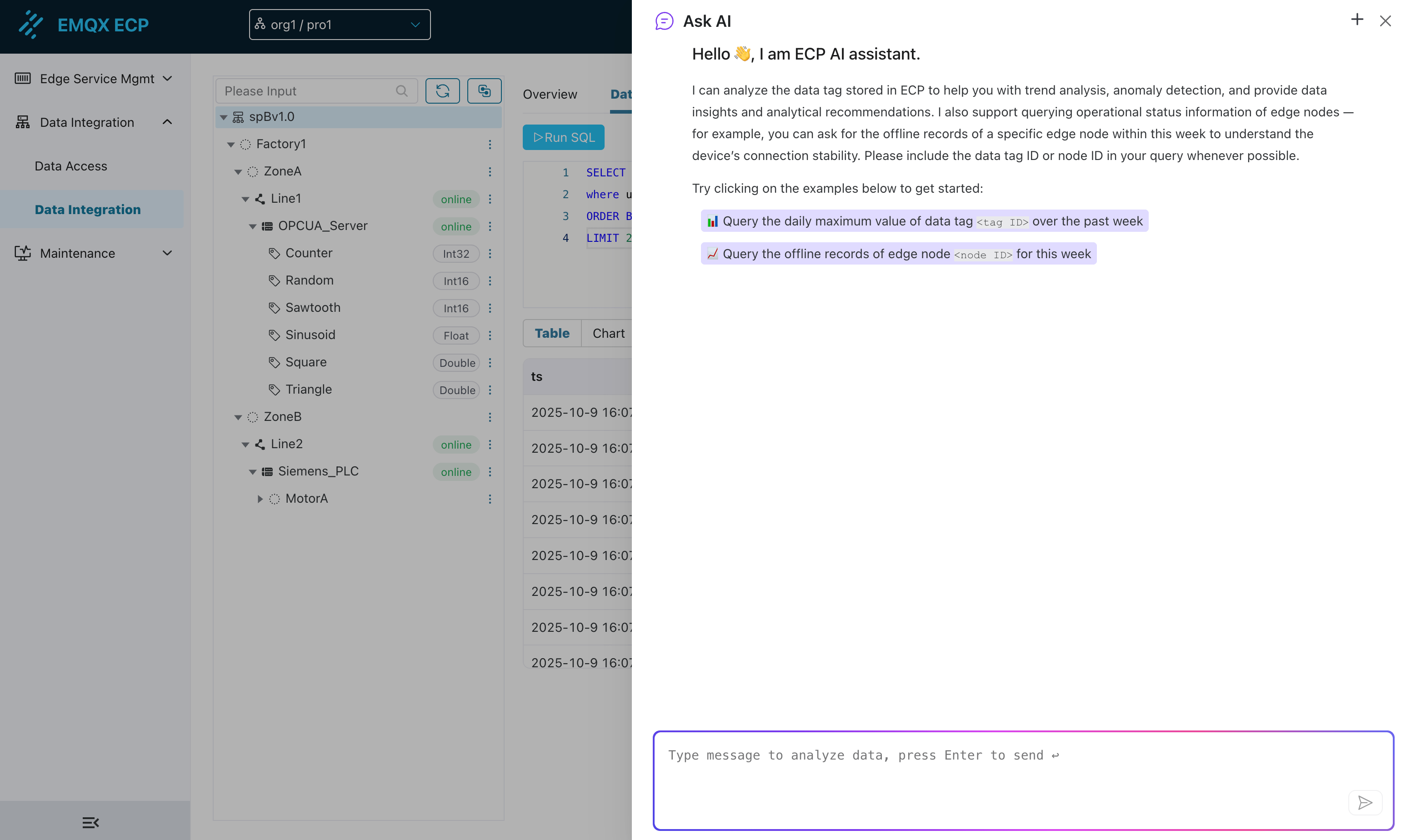
5. AI Data Analysis Assistant Integration
The "Data Analysis" page deeply integrates the AI data analysis assistant, aiming to help users build and optimize SQL queries more easily.
UI Entry:
- Through the "AI Data Analysis" button in the upper right corner of the page, click to open the AI interaction dialog
- The tag operation menu also provides a quick entry for "AI Smart Query"
AI Interaction Box:
- Default Page Guidance: When opening the AI dialog from the main entry, it provides guidance prompts, informing users that ECP stores data by data type in separate tables (value_int, value_float, value_bool, value_string), and suggests users provide tag UID and data type when asking questions
- Tag Context Pre-filling: When entering from the tag "AI Smart Query" entry, the tag UID and corresponding data table information will be automatically pre-filled into the dialog or passed as context
AI Core Capabilities:
- Natural Language to SQL: Convert user's natural language query requirements into correct SQL statements
- SQL Iterative Correction: When generated SQL fails to execute, AI can intelligently analyze error causes and perform multiple rounds of iterative corrections until generating successfully executable SQL
- Cross-Node Analysis: Supports analyzing data from multiple NeuronEX instances, providing global perspective data insights
Data Table Structure Description
ECP's data integration functionality stores tag data in different data tables according to data types:
| Data Type | Storage Table Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Int16/Int32/Int64 | value_int | Integer type data |
| Float/Double | value_float | Floating-point type data |
| Bool | value_bool | Boolean type data |
| String | value_string | String type data |
Common Field Description:
uid: Unique identifier of the tagts: Data timestampvalue: Data value
Usage Examples
Basic Query Examples
Query the latest 100 records of a single tag:
SELECT * FROM value_int
WHERE uid = 'spBv1.0/Factory1/ZoneA/Line1/OPCUA_Server/Counter'
ORDER BY ts DESC
LIMIT 100Prerequisites
- ECP data integration functionality has been correctly configured and connected to EMQX
- At least one NeuronEX instance is reporting data
- Datalayers database is running normally and has stored historical data
- If you need to use the AI query functionality, please ensure AI-related services and models are correctly configured
Best Practices
Data Query Optimization:
- Reasonably use time range filtering to avoid querying excessively large datasets
- Use tag UID for precise queries to improve query efficiency
- Use LIMIT to restrict the number of returned results
Cross-Node Analysis:
- Utilize the hierarchical structure of UID for grouping and aggregation
- Focus on data comparison across different factories, zones, and production lines
- Establish standardized data naming conventions
AI Assistant Usage:
- Provide clear data analysis requirement descriptions
- Combine specific business scenarios and metrics
- Leverage AI to generate complex data analysis queries
Through ECP's data analysis functionality, you can fully utilize the powerful capabilities of SQL and the intelligent assistance of AI to deeply explore industrial data from multiple NeuronEX instances, gaining global data insights and business value.