JWT Authentication
JSON Web Token (JWT) is a token-based authentication mechanism. It does not rely on the server to retain client authentication information or session information. EMQX supports using JWT for user authentication.
Prerequisite
Knowledge about basic EMQX authentication concepts
Authentication Principle
The client carries the JWT in the connection request, and EMQX uses the pre-configured secret or public key to verify the JWT signature. If the user configures a JWKS endpoint, the JWT authenticator will verify the JWT signature using the list of public keys queried from the JWKS endpoint.
If the signature verification is successful, the JWT authenticator proceeds to check the claims. The JWT authenticator actively checks the validity of the JWT based on these claims such as iat (Issued At), nbf (Not Before), and exp (Expiration Time). Additional custom claims can also be specified for verification. The client is granted access only if both the signature and claims verifications are successful.
Starting from EMQX version 5.7.0, JWT authentication includes an option to disconnect clients after their JWT expires. The configuration parameter disconnect_after_expire is set to true by default. To keep clients connected even after their JWT has expired, you can set this parameter to false.
Best Practice
The JWT authenticator essentially only checks the signature of the JWT, which means that the JWT authenticator does not guarantee the legitimacy of the client's identity.
The best practice is to deploy an independent authentication server. The client first accesses the authentication server, the authentication server verifies the identity of the client, and issues JWT for the legitimate client, and then the client uses the obtained JWT to connect to EMQX.
TIP
Since the payload in the JWT is only Base64 encoded, anyone who gets the JWT can decode the payload to get the original information by Base64 decoding. Therefore, it is not recommended to store some sensitive data in the payload of JWT.
To reduce the possibility of JWT leakage and theft, it is recommended to set a reasonable validity period and also enable TLS to encrypt client connections.
Access Control List (Optional)
The Access Control List (ACL) is an optional extension of an authentication result to control the client's permissions after login. The JWT can include an acl field to specify the client's permissions.
See Access Control List (ACL) for more information.
Client Attributes
Starting from EMQX v5.7.0, you can use the optional client_attrs field in the JWT Payload to set client attributes. Please note that both the keys and values must be of string type.
Example:
{
"exp": 1654254601,
"username": "emqx_u",
"client_attrs": {
"role": "admin",
"sn": "10c61f1a1f47"
}
}Configure JWT Authentication in Dashboard
Select Access Control -> Authentication from the left navigation menu.
On the Authentication page, click Create in the top right corner. Click to select JWT as the Mechanism, and click Next. Skip the Backend selection and go to the Configuration tab.
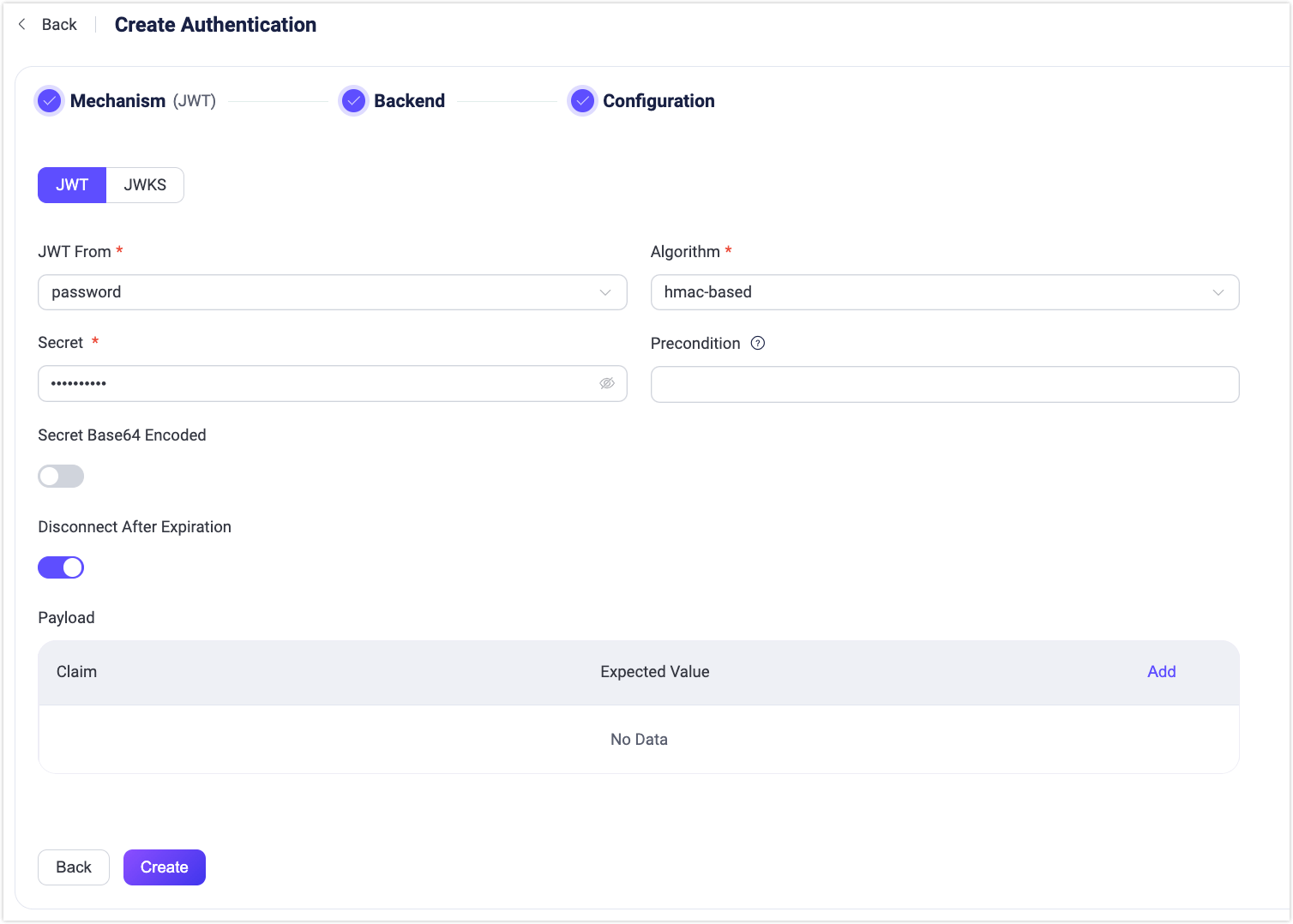
Configure the following options:
JWT From: Determines where the JWT is located in the client connection request. Available options are
passwordandusername, corresponding to thePasswordandUsernamefields in the MQTTCONNECTpacket for MQTT clients.Algorithm: Specify the encryption algorithm of JWT. Optional values are
hmac-basedandpublic-key. Each selection dictates different configuration requirements.hmac-based: Uses a symmetric key for both generating and verifying the JWT's signature. Supported algorithms include HS256, HS384, and HS512. Configuration must include:Secret: The key used to verify the signature, identical to the one used for signature generation.Secret Base64 Encode: Configures whether theSecretis Base64 encoded, which determines if EMQX needs to decode the secret during signature verification.
public-key: Uses a private key to generate the JWT's signature and a public key for verification. Supported algorithms are RS256, RS384, RS512, ES256, ES384, and ES512. Configuration must include:Public Key: Specify the public key in PEM format used to verify the signature.
Precondition: A Variform expression used to control whether this JWT authenticator should be applied to a client connection. The expression is evaluated against attributes from the client (such as
username,clientid,listener, etc.). The authenticator will only be invoked if the expression evaluates to the string"true". Otherwise, it will be skipped. For more information about the precondition, see Authentication Preconditions.Disconnect After Expiration: Configures whether to disconnect clients after their JWT expires, enabled by default.
Payload: Specify additional claims checks that the user wants to perform. Users can define multiple key-value pairs with the Claim and Expacted Value fields, where the key is used to find the corresponding claim in the JWT, so it needs to have the same name as the JWT claim to be checked, and the value is used to compare with the actual value of the claim. Currently, the placeholders supported are
${clientid}and${username}.
Click Create to complete the configuration.
EMQX also supports periodically obtaining the latest JWKS from the JWKS endpoint, which is essentially a set of public keys used to verify any JWT issued by the authorization server and signed using the RSA or ECDSA algorithm. If you want to use this feature, you need to switch to the JWKS configuration page.
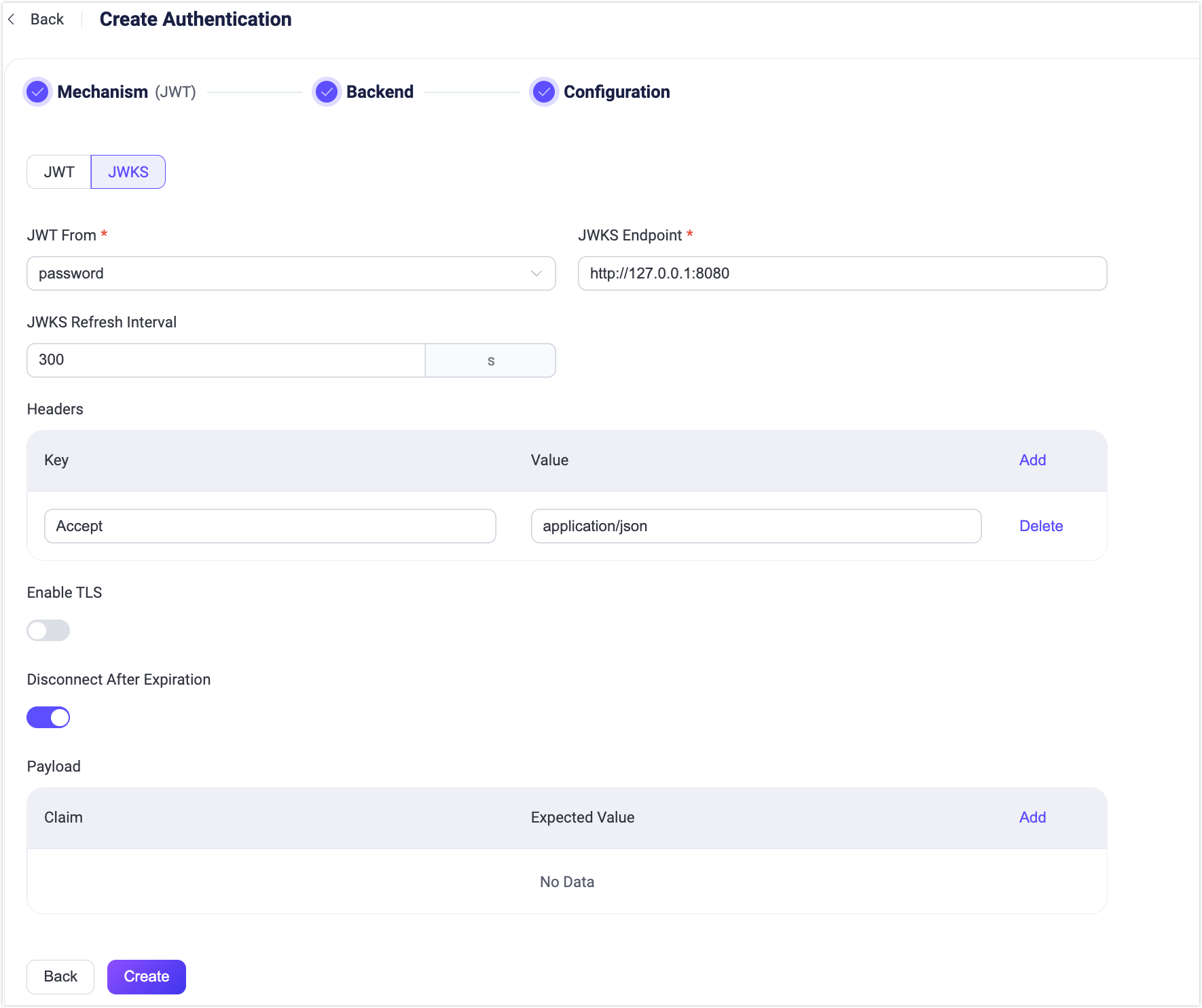
You need to configure the following JWKS-specific configuration items:
- JWKS Server: Specify the server endpoint address for EMQX to query JWKS, the endpoint needs to support GET requests and return a JWKS that conforms to the specification.
- JWKS Refresh Interval: Specify the refresh interval of JWKS, that is, the interval for EMQX to query JWKS.
- Headers: Specify any additional HTTP headers that must be included in the requests to the JWKS server. Adding these HTTP headers ensures that the requests to the JWKS server are properly formatted according to your server's requirements. This configuration allows users to add key-value pairs, for example:
- Key:
Accept - Value:
application/json
- Key:
Click Create to complete the configuration.