Integrate with MongoDB
This authorizer implements authorization checks by matching publish/subscribe requests against lists of rules stored in the MongoDB database.
Prerequisite
Knowledge about basic EMQX authorization concepts
Data Schema and Query Statement
MongoDB authorizer supports storing authorization rules as MongoDB documents. Users need to provide a query template to make sure that the result contains the following fields:
permission: Specifies the applied action if the rule matches. Available values aredenyorallow.action: Specifies the request for which the rule is relevant. Possible values arepublish,subscribe, orall.topic/topics: Specifies one or a list of topics the rule applies to. Supports topic filters and topic placeholders.qos(optional): Specifies the QoS levels that the current rule applies to. Value options are0,1,2. It can also be a number array to specify multiple QoS levels. The default is all QoS levels.retain(optional): Indicates whether the rule allows publishing retained messages. Value options are0,1,ortrue,false. By default, retained messages are allowed.
Deny client with username emqx_u to publish to topic t/1 with QoS 1:
> db.mqtt_acl.insertOne(
{
"username": "emqx_u",
"clientid": "emqx_c",
"ipaddress": "127.0.0.1",
"permission": "deny",
"action": "publish",
"qos": 1,
"topics": ["t/1"]
}
);
{
acknowledged: true,
insertedId: ObjectId("62b4a1a0e693ae0233bc3e98")
}The corresponding configuration parameters are:
collection = "mqtt_acl"
filter { username = "${username}" }TIP
When there is a significant number of users in the system, optimize and index the collection to be queried beforehand to shorten the query response time and reduce the load for EMQX.
For this MongoDB data schema, the corresponding Dashboard configuration parameter is Filter: { username = "${username}" }.
Configure with Dashboard
You can use EMQX Dashboard to configure how to use MongoDB for user authorization.
On EMQX Dashboard, click Access Control -> Authorization on the left navigation tree to enter the Authorization page.
Click Create at the top right corner, then click to select MongoDB as Backend. Click Next. The Configuration tab is shown below.
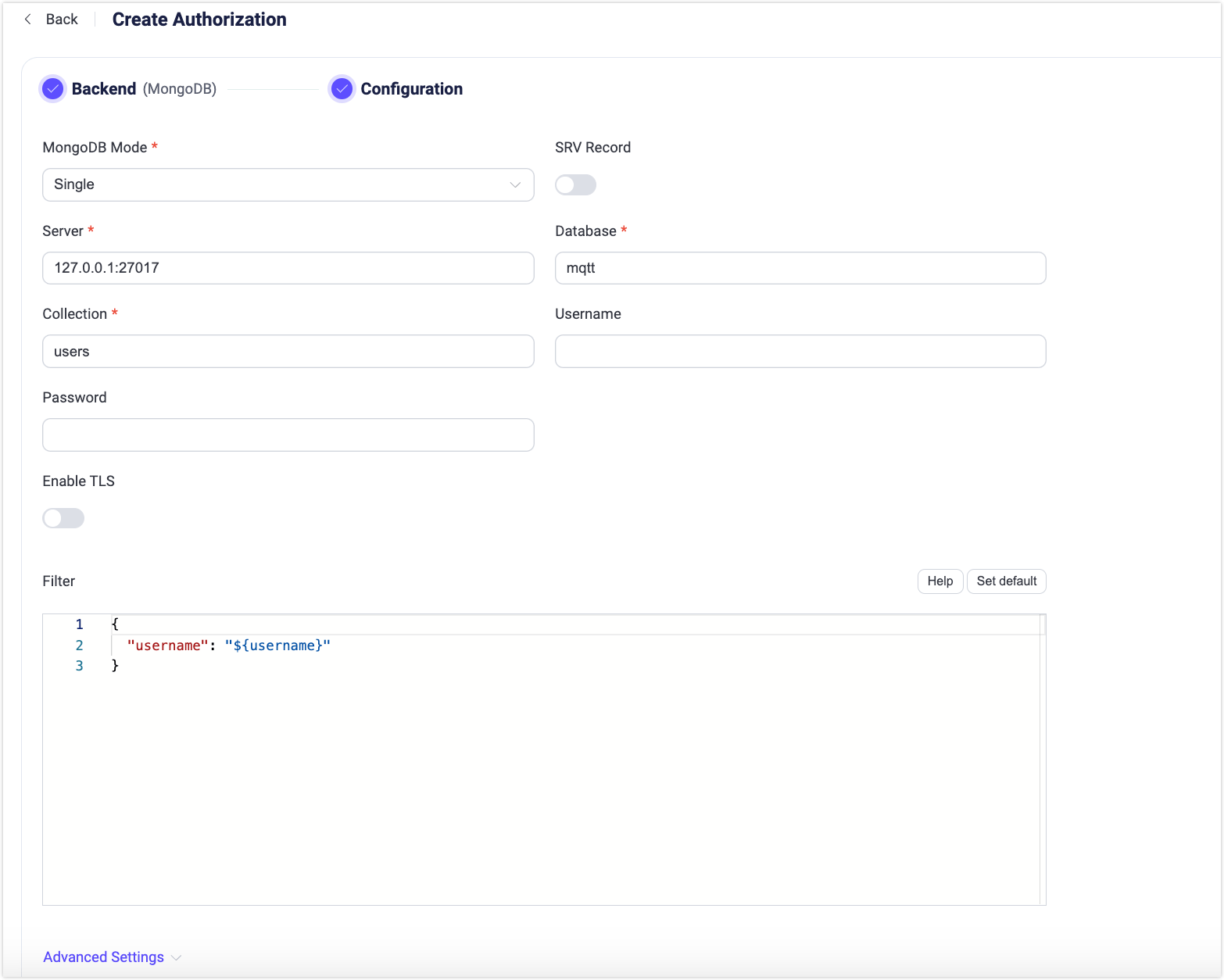
Follow the instructions below to configure the settings.
Connect: Fill in the information needed to connect MongDB.
- MongoDB Mode: Select how MongoDB is deployed, including
Single,Replica Set, andSharding. - Server: Specify the server address that EMQX is to connect (
host:port). - Database: MongoDB database name.
- Collection: Name of MongoDB collection where authorization rules are stored; Data type: strings.
- Username: Specify MongoDB user name.
- Password: Specify MongDB user password.
TLS Configuration: Turn on the toggle switch if you want to enable TLS.
Filter: A map interpreted as MongoDB selector for credential lookup. Placeholders are supported.
Advanced Settings:
Auth Source: Specify the authentication source to use when connecting to MongoDB. This could be a specific database or a MongoDB authentication database that manages user credentials.
Use Legacy Protocol: Select whether to use MongoDB's legacy protocol for communicating with the database. Options are
auto,true, andfalse. The default isauto, which will attempt to automatically determine if the newer protocol is supported.Record Limit: Limit the number of authorization records to fetch from MongoDB.
Skip: Set the number of authorization records to skip when retrieving the list of records.
Pool size (optional): Input an integer value to define the number of concurrent connections from an EMQX node to MongoDB. Default:
8.Connect Timeout (optional): Specify the waiting period before EMQX assumes the connection is timed out. Units supported include milliseconds, second, minute, and hour.
- MongoDB Mode: Select how MongoDB is deployed, including
Click Create to finish the settings.
Configure with Configuration Items
You can configure the EMQX MongoDB authorizer with EMQX configuration items.
The MongoDB authorizer is identified by type mongodb. The authorizer supports connecting to MongoDB running in 3 types of deployment modes.
Sample configuration: