Use Built-in Database
You can use the built-in database of EMQX as a low-cost and out-of-the-box option for password authentication. After enabling, EMQX will save the client credentials in its built-in database (based on Mnesia) and manage data via REST API and Dashboard. This page introduces how to use the EMQX Dashboard and configuration items to configure the authentication using the built-in database.
TIP
Knowledge about basic EMQX authentication concepts
Configure with Dashboard
You can use EMQX Dashboard to set the built-in database for password authentication.
- In the EMQX Dashboard, click Access Control -> Authentication from the left navigation menu.
- On the Authentication page, click Create in the top right corner.
- Click to select Password-Based as Mechanism, and Built-in Database as Backend to go to the Configuration tab, as shown below.
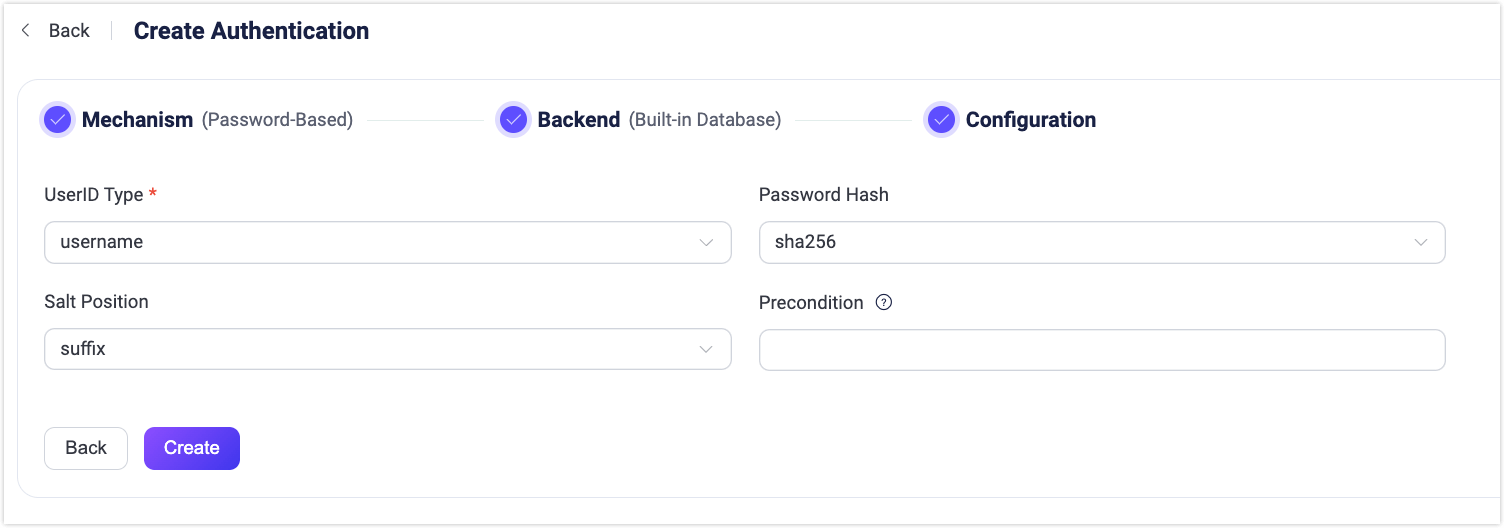
Follow the instructions below to configure the authentication backend:
UserID Type: Specify the fields for client ID authentication; Options:
username,clientid(corresponding to theUsernameorClient Identifierfields in theCONNECTmessage sent by the MQTT client).Password Hash: Select the password hashing algorithm applied to plain-text passwords before results are stored in the database. Available options are
plain,md5,sha,sha256,sha512,bcrypt, andpbkdf2. Additional configurations depend on the selected algorithm:- For
md5,sha,sha256orsha512:- Salt Position: Determines how salt (random data) is mixed with the password. Options are
suffix,prefix, ordisable. You can keep the default value unless you migrate user credentials from external storage into the EMQX built-in database. - Resulting hash is represented as a string of hexadecimal characters, and compared case-insensitively with the stored credential.
- Salt Position: Determines how salt (random data) is mixed with the password. Options are
- For
plain:- Salt Position: should be
disable.
- Salt Position: should be
- For
bcrypt:- Salt Rounds: Defines the number of times the hash function is applied, expressed as 2Salt Rounds, also known as the "cost factor". The default value is
10, with a permissible range of5to10. A higher value is recommended for enhanced security. Note: Increasing the cost factor by 1 doubles the necessary time for authentication.
- Salt Rounds: Defines the number of times the hash function is applied, expressed as 2Salt Rounds, also known as the "cost factor". The default value is
- For
pbkdf2:- Pseudorandom Function: Selects the hash function that generates the key, such as
sha256. - Iteration Count: Sets the number of times the hash function is executed. The default is
4096. - Derived Key Length (optional): Specifies the length in bytes of the generated key. If left blank, the length will default to that determined by the selected pseudorandom function.
- Resulting hash is represented as a string of hexadecimal characters, and compared case-insensitively with the stored credential.
- Pseudorandom Function: Selects the hash function that generates the key, such as
- For
Precondition: A Variform expression used to control whether this Built-in Database authenticator should be applied to a client connection. The expression is evaluated against attributes from the client (such as
username,clientid,listener, etc.). The authenticator will only be invoked if the expression evaluates to the string"true". Otherwise, it will be skipped. For more information about the precondition, see Authenticator Preconditions.
After you finish the settings, click Create.
Configure with Configuration Items
You can also configure the authentication through configuration items.
Example:
{
backend = "built_in_database"
mechanism = "password_based"
password_hash_algorithm {
name = "sha256",
salt_position = "suffix"
}
user_id_type = "username"
}Migrate from External Storage to EMQX Built-in Database
To migrate user credentials from external storage to the EMQX built-in database, you can use .csv or .json files for batch import. For operating details, see Import User.