ExProto Gateway
The Extension Protocol (ExProto) is a custom protocol parsing gateway implemented using gRPC communication. It allows users to develop gRPC services in their preferred programming languages, such as Java, Python, Go, and more. These services are designed to parse network protocols of devices and facilitate functions like device connection, authentication, and message transmission.
This page introduces the working principle of the ExProto gateway and how to configure and use the ExProto Gateway in EMQX.
How ExProto Gateway and gRPC Service Work
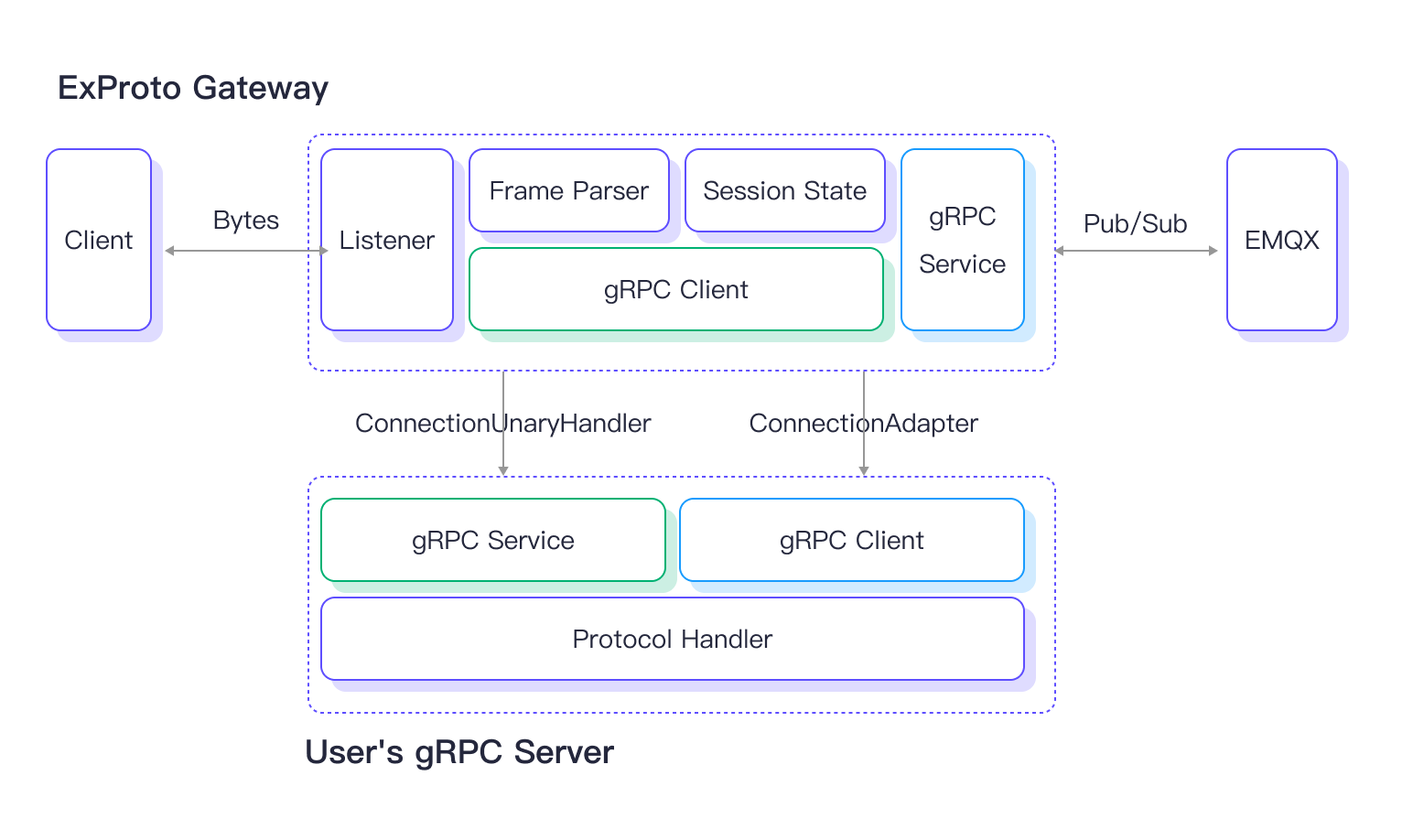
Once the ExProto gateway is enabled in EMQX, it listens on a specific port (e.g., 7993) for device connections. When it receives client device connections, it passes the byte data and events generated by the client device to the user's gRPC service. This requires a gRPC client in the ExProto gateway to invoke the methods of the ConnectionUnaryHandler service implemented in the user's gRPC server.
The gRPC service in the user's gRPC server receives the byte data and events from the ExProto Gateway, parses the client's network protocol and translate byte data and events into Pub/Sub requests, and sends them back to the ExProto gateway. The ConnectionAdapter service implemented in the ExProto gateway provides an interface for interacting with the user's gRPC Server. Through the ExProto gateway, the client device can then publish messages to EMQX, subscribe to topics, and manage client connections.
The illustration below shows the architecture of how the ExProto gateway and gRPC service work.
exproto.proto File
The exproto.proto file defines the interface between the ExProto gateway and the users' gRPC service. The file specifies the following two services:
ConnectionAdapterservice: Implemented by ExProto Gateway to provide an interface to the gRPC server.ConnectionUnaryHandlerservice: Implemented by the user's gRPC server to define the methods for handling the connection of client sockets and byte parsing.
ConnectionUnaryHandler Service
The ConnectionUnaryHandler service is implemented by users' gRPC server to handle the connection of client sockets and byte parsing.
This service includes the following methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| OnSocketCreated | Whenever a new Socket connects to the ExProto Gateway, this callback will be triggered. |
| OnSocketClosed | Whenever a Socket is closed, this callback will be triggered. |
| OnReceivedBytes | Whenever data is received from the client's socket, this callback will be triggered. |
| OnTimerTimeout | Whenever a timer times out, this callback will be triggered. |
| OnReceivedMessages | Whenever a message is received for the subscribed topic, this callback will be triggered. |
When the ExProto gateway calls these methods, it will pass a unique identifier conn in the parameters to mark which socket sent out this event. For example, in the OnSocketCreated function parameters:
message SocketCreatedRequest {
string conn = 1;
ConnInfo conninfo = 2;
}TIP
Since ExProto Gateway cannot recognize the start and end of private protocol message frames, if there is TCP packet sticking or splitting, it needs to be handled in the OnReceivedBytes callback.
ConnectionAdapter Service
The ConnectionAdapter service is implemented by the ExProto Gateway to provides functions for the gRPC service to initiate subscriptions, publish messages, start timers and close connections functions for managing connections. It includes the following methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Send | Send bytes to the specified connection. |
| Close | Close the specified connection. |
| Authenticate | Register a client with ExProto Gateway and complete the authentication. |
| StartTimer | To start a timer for the specified connection, typically used for liveness detecting. |
| Publish | Publish messages to emqx from the specified connection. |
| Subscribe | Create a subscription for the specified connection. |
| Unsubscribe | Delete a subscription for the specified connection. |
| RawPublish | Publish a message to EMQX. |
Enable ExProto Gateway
The ExProto gateway in EMQX can be configured and enabled through the Dashboard, REST API, or configuration file base.hocon. This section demonstrates how to enable ExProto gateway via the Dashboard.
On the EMQX Dashboard, click Management -> Gateways from the left navigation menu. On the Gateways page, all supported gateways are listed. Locate ExProto and click Setup in the Actions column. Then, you will be directed to the Initialize ExProto page.
TIP
If you are running EMQX in a cluster, the settings you made through the Dashboard or REST API will affect the whole cluster. If you only want to change the settings with one node, configure the gateway in base.hocon.
To simplify the configuration process, EMQX offers default values for all required fields on the Gateways page. If you don't need extensive customization, you can enable the ExProto Gateway in just 3 clicks:
- Click Next in the Basic Configuration step page to accept all the default settings.
- Then you will be directed to the Listeners step page, where EMQX has pre-configured a TCP listener on port 7993. Click Next again to confirm the setting.
- Click the Enable button to activate the ExProto Gateway.
Upon completing the gateway activation process, you can return to the Gateways page and see that the ExProto Gateway now displays an Enabled status.
The above configuration can also be configured with REST API:
Example Code:
curl -X 'PUT' 'http://127.0.0.1:18083/api/v5/gateway/exproto' \
-u <your-application-key>:<your-security-key> \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name": "exproto",
"enable": true,
"mountpoint": "exproto/",
"server": {
"bind": "0.0.0.0:9100"
}
"handler": {
"address": "http://127.0.0.1:9001"
"ssl_options": {"enable": false}
}
"listeners": [
{
"type": "tcp",
"bind": "7993",
"name": "default",
"max_conn_rate": 1000,
"max_connections": 1024000
}
]
}'For a detailed REST API description, see REST API.
If you have some customization needs, want to add more listeners, or add authentication rules, you can continue to read the Customize Your ExProto Gateway.
Customize Your ExProto Gateway
In addition to the default settings, EMQX provides a variety of configuration options to better accommodate your specific business requirements. This section offers an in-depth overview of the configuration options available on the Gateways page.
Basic Configuration
On the Gateways page, locate ExProto. Click Settings in the Actions column. On the Settings tab, you can customize your ConnectionUnaryHandler service address, ConnectionAdapter listening port, and set the MountPoint string for this gateway.
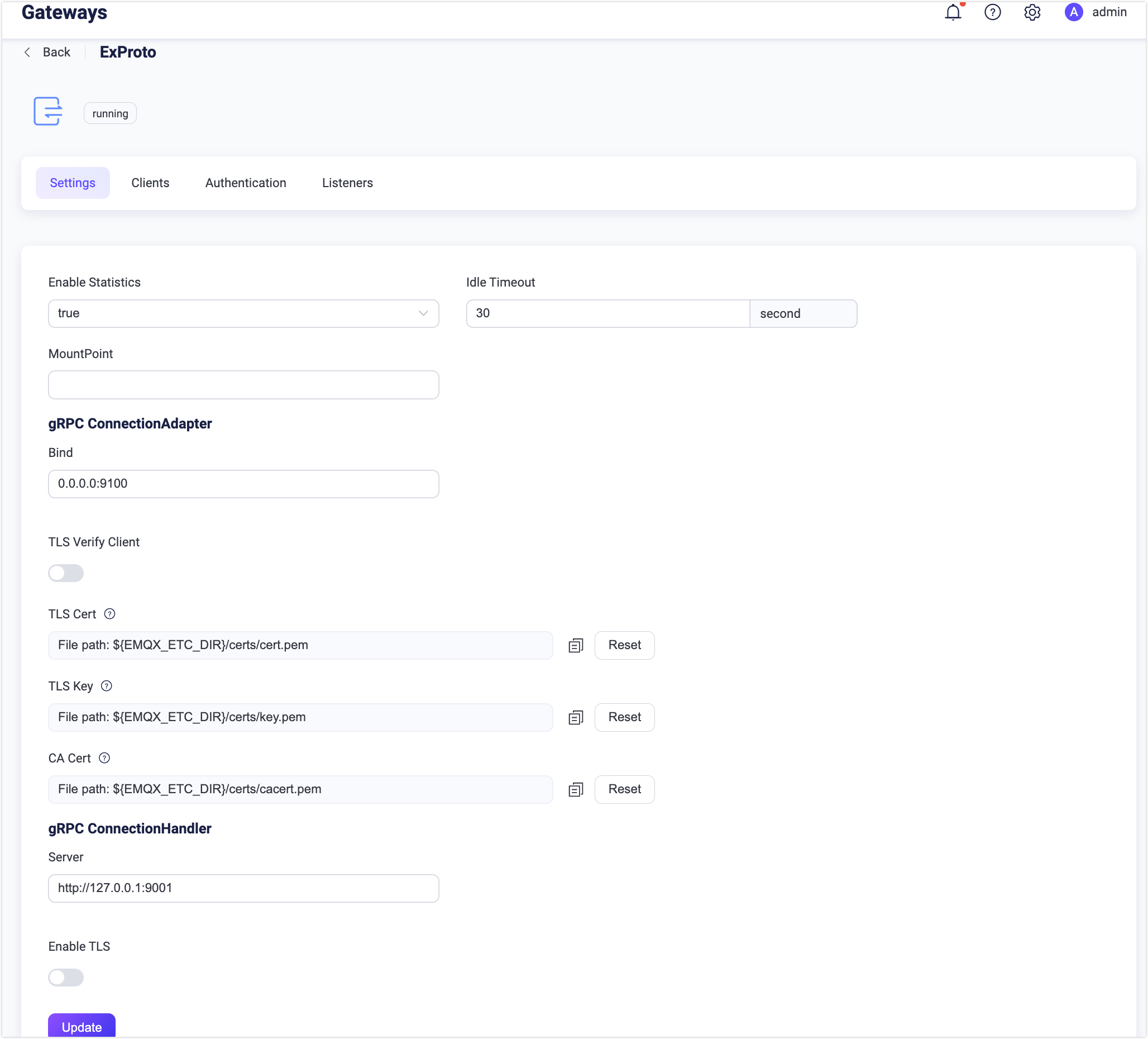
- Enable Statistics: Set whether to allow the Gateway to collect and report statistics; default:
true, optional values:true,false. - Idle Timeout: Set the duration (in seconds) of inactivity after which a connected client will be considered disconnected. Default:
30 s. - MountPoint: Set a string that is prefixed to all topics when publishing or subscribing, providing a way to implement message routing isolation between different protocols, for example,
mqttsn/. This topic prefix is managed by the gateway. Clients do not need to add this prefix explicitly when publishing and subscribing. - gRPC ConnectionAdapter: Set the configurations for starting the
ConnectionAdapterservice.- Bind: Listening address and port for the gRPC server; default: 0.0.0.0:9100.
- TLS Verify Client: Enable or disable peer verification; disabled by default. When enabled, you can configure the related TLS Cert, TLS Key, and CA Cert information, either by entering the content of the file or uploading it with the Select File button. For details, see Enable SSL/TLS Connections.
- Bind: Listening address and port for the gRPC server; default: 0.0.0.0:9100.
- gRPC ConnectionHandler: Set the callback server configurations that implemented ConnectionUnaryHandler.
- Server: The callback gRPC server address.
- Enable TLS: Enable the TLS connection for gRPC server; disabled by default. When enabled, you can further set the configurations below:
- TLS Verify: Enable or disable peer verification; disabled by default. When enabled, you can configure the related TLS Cert, TLS Key, and CA Cert information, either by entering the content of the file or uploading with the Select File button.
- SNI: Specify the host name to be used in TLS Server Name Indication extension.
- Enable TLS: Enable the TLS connection for gRPC server; disabled by default. When enabled, you can further set the configurations below:
- Server: The callback gRPC server address.
Add Listeners
By default, one TCP listener with the name of default is already configured on port 7993, which allows a maximum of 1,000 connections per second, and supports up to 1,024,000 concurrent connections. You can click the Listeners tab for more customized settings, including editing, deleting, or adding a new listener.
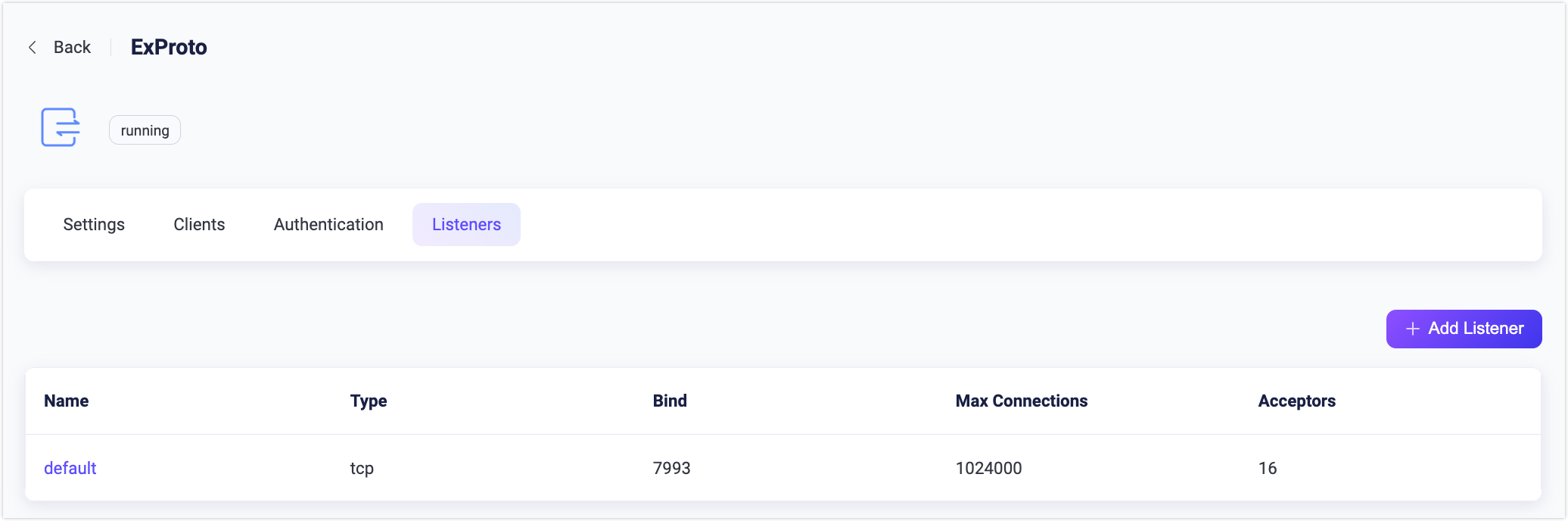
Click + Add Listener to open Add Listener page, where you can continue with the following configuration fields:
Basic settings
- Name: Set a unique identifier for the listener.
- Type: Select the protocol type, for ExProto, this can be either
udpordtls. - Bind: Set the port number on which the listener accepts incoming connections.
- MountPoint (optional): Set a string that is prefixed to all topics when publishing or subscribing, providing a way to implement message routing isolation between different protocols.
Listener Settings
- Acceptor: Set the size of the acceptor pool, default:
16. - Max Connections: Set the maximum number of concurrent connections that the listener can handle, default:
1024000. - Max Connection Rate: Set the maximum rate of new connections the listener can accept per second, default:
1000. - Proxy Protocol: Enable the Proxy Protocol V1/2 if the EMQX cluster is deployed behind HAProxy or NGINX; default:
false. - Proxy Protocol Timeout: Timeout for proxy protocol. EMQX will close the TCP connection if proxy protocol packet is not received within the timeout; default:
3seconds.
TCP Settings
- ActiveN: Set the
{active, N}option for the socket, that is, the number of incoming packets the socket can actively process. For details, see Erlang Documentation - setopts/2. - Buffer: Set the size of the buffer used to store incoming and outgoing packets, unit: KB.
- TCP_NODELAY: Set the TCP_NODELAY flag for the connections; default:
false. - SO_REUSEADDR: Set whether to allow local reuse of port numbers; default:
true. - Send Timeout: The TCP sends timeout for the connections, default:
15seconds. - Send Timeout Close: Close the connection if send timeout, default
true.
TLS Settings (for SSL listeners only)
You can set whether to enable the TLS Verify by setting the toggle switch. But before that, you need to configure the related TLS Cert, TLS Key, and CA Cert information, either by entering the content of the file or uploading with the Select File button. For details, see Enable SSL/TLS Connection.
Then you can continue to set:
- SSL Versions: Set the TLS versions supported, default:
tlsv1,tlsv1.1,tlsv1.2, andtlsv1.3。 - SSL Fail If No Peer Cert: Set whether EMQX will reject the connection if the client sends an empty certificate, default:
false, optional values:true,false. - CACert Depth: Set the maximum number of non-self-issued intermediate certificates that can be included in a valid certification path following the peer certificate, default,
10. - Key File Passphrase: Set the user's password, used only when the private key is password-protected.
Configure Authentication
ExProto Gateway supports various types of authenticators, such as:
- Built-in Database Authentication
- MySQL Authentication
- MongoDB Authentication
- PostgreSQL Authentication
- Redis Authentication
- HTTP Server Authentication
- JWT Authentication
- LDAP Authentication
The Client ID, Username, and Password of the client information are all derived from the parameters passed in the Authenticate method of the ConnectionAdapter.
This section takes the Dashboard as an example to illustrate how to do the authentication configuration.
On the ExProto page, click the Authentication tab.
Click + Create Authentication, select Password-Based as the Mechanism, and select HTTP Server as the Backend. Click Next. In Configuration, you can set the authentication rules. For a detailed explanation of each field on the page, you can refer to HTTP Server Authentication.
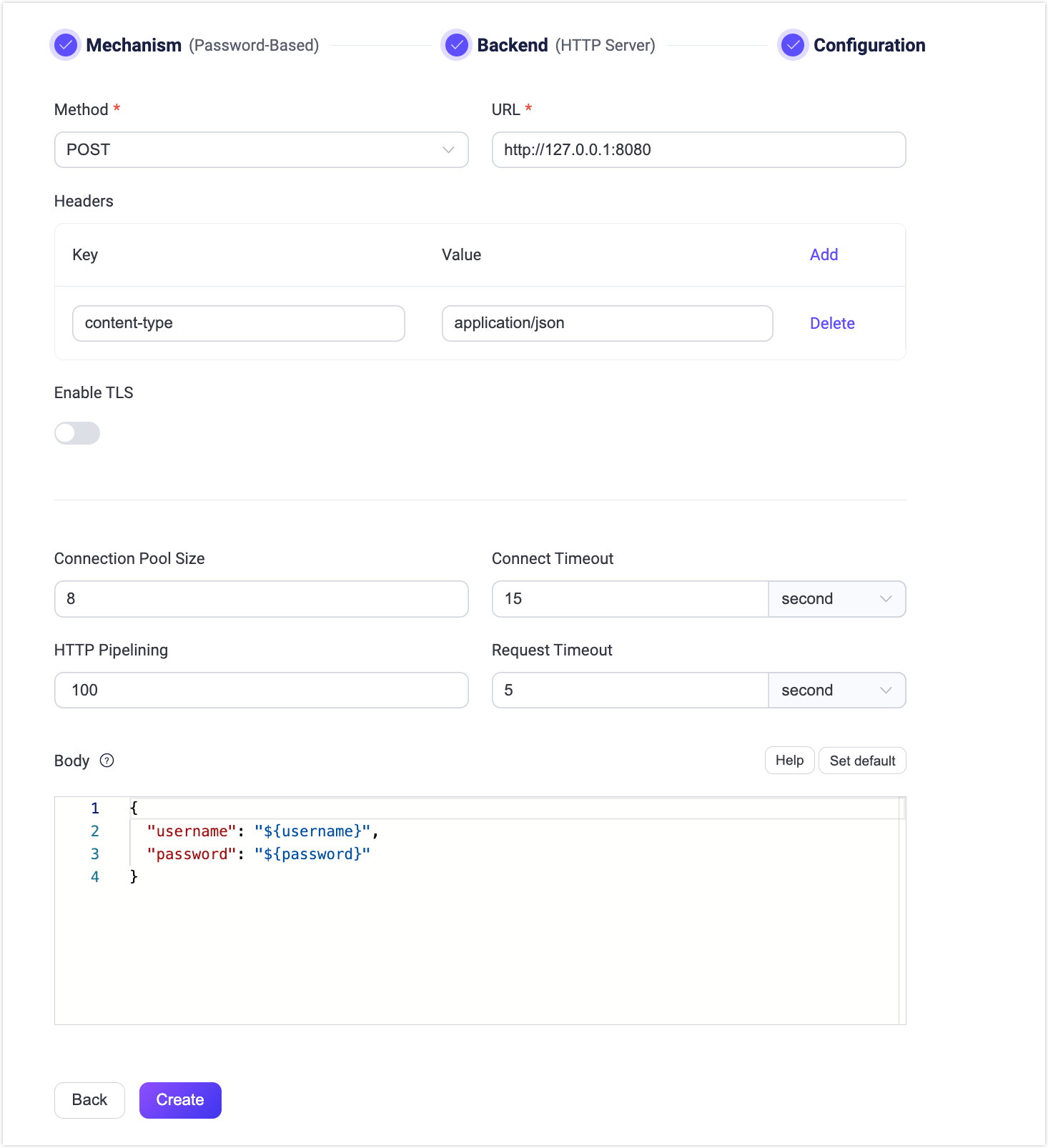
The above configuration can also be performed via REST API.
Example Code
curl -X 'POST' 'http://127.0.0.1:18083/api/v5/gateway/exproto/authentication' \
-u <your-application-key>:<your-security-key> \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"method": "post",
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8080",
"headers": {
"content-type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"username": "${username}",
"password": "${password}"
},
"pool_size": 8,
"connect_timeout": "5s",
"request_timeout": "5s",
"enable_pipelining": 100,
"ssl": {
"enable": false,
"verify": "verify_none"
},
"backend": "http",
"mechanism": "password_based",
"enable": true
}'Start an Example gRPC Service for Testing
This section demonstrates how ExProto gateway and the gRPC service work together by starting an example gRPC service.
In this demonstration, the telnet command is used to simulate a client that uses TCP protocol to send or receive messages. In the actual environment, it can be a device that implements custom private protocols and connects to the TCP listener on port 7993. The ExpProto gateway listens on port 7993 to receive client connections and it also listens on port 9100 and provides a ConnectionAdapter service defined in the exproto.proto file.
You can find programs in various languages in emqx-extension-examples as example gRPC services. In this demonstration, an echo program exproto-svr-python is used as an example gRPC service to implement the ConnectionUnaryHandler service using Python. It simply sends back any data received from a TCP client. In the actual environment, it publishes these upstream messages to EMQX, or subscribes to topics to receive messages from EMQX and delivers them to client connections.
The following steps take exproto-svr-python as an example:
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure you have completed the following:
Run EMQX 5.1.0 or above and enable the ExProto gateway with default configurations.
Install Python 3.7 or above, and install the following dependencies:
python -m pip install grpcio python -m pip install grpcio-tools
On the same machine with EMQX running, clone the sample code and enter the directory
exproto-svr-python:bashgit clone https://github.com/emqx/emqx-extension-examples cd exproto-svr-pythonStart the gRPC Server using the following command:
python exproto_server.pyAfter a successful start, an output similar to the following will be printed:
ConnectionUnaryHandler started successfully, listening on 9001 Tips: If the Listener of EMQX ExProto gateway listen on 7993: You can use the telnet to test the server, for example: telnet 127.0.0.1 7993 Waiting for client connections...Use
telenetto access the port7993that Exproto gateway is listening on. EnterHi, this is tcp client!to test if the gRPC Server is working properly. For example:$ telnet 127.0.0.1 7993 Trying 127.0.0.1... Connected to 127.0.0.1. Escape character is '^]'. Hi, this is tcp client! Hi, this is tcp client!Go to EMQX Dashboard and click Management -> Gateways from the left navigation menu. Click Clients of ExProto. On the ExProto page, you can see the client you connect to using telnet.
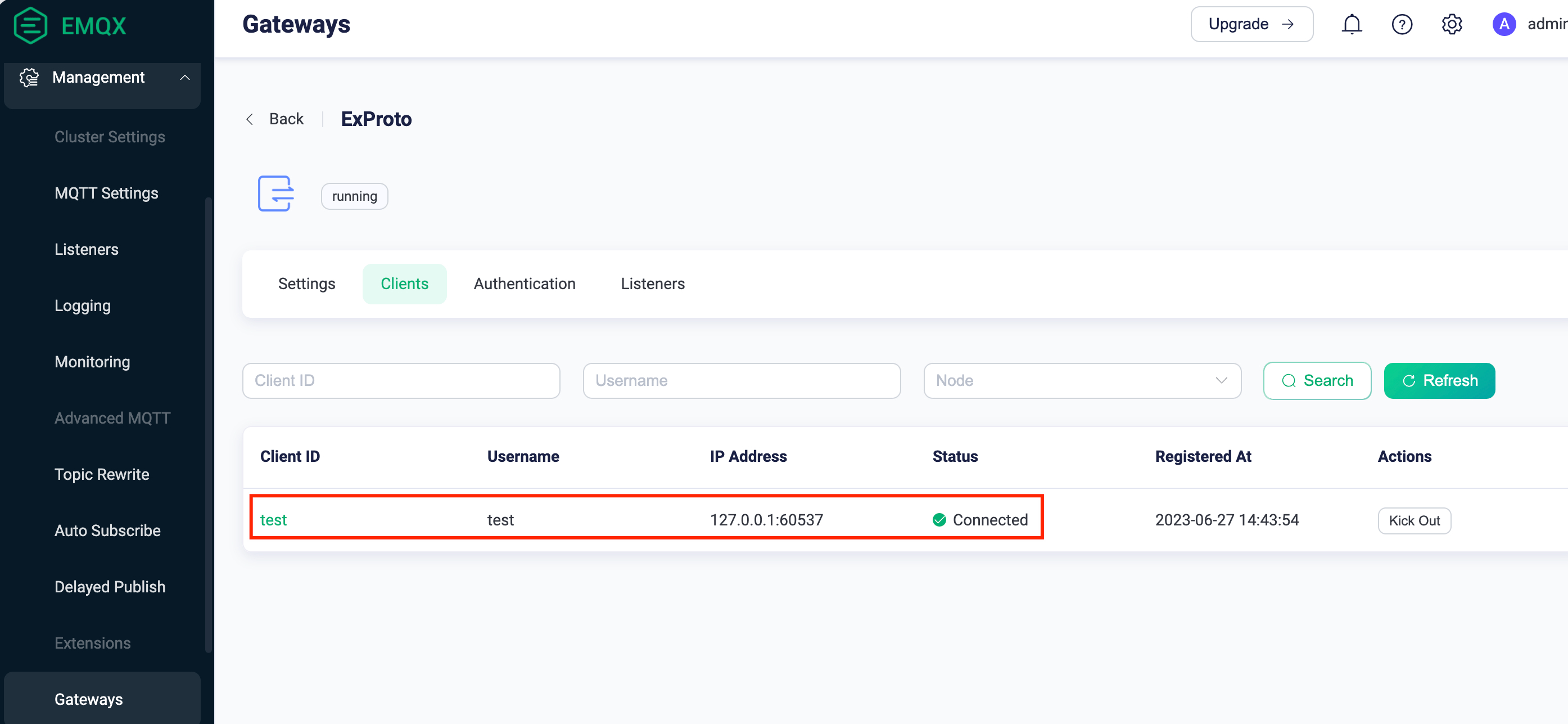
Sequence Diagram of the Example
The diagram below shows the sequence of connections and message delivery in this example.
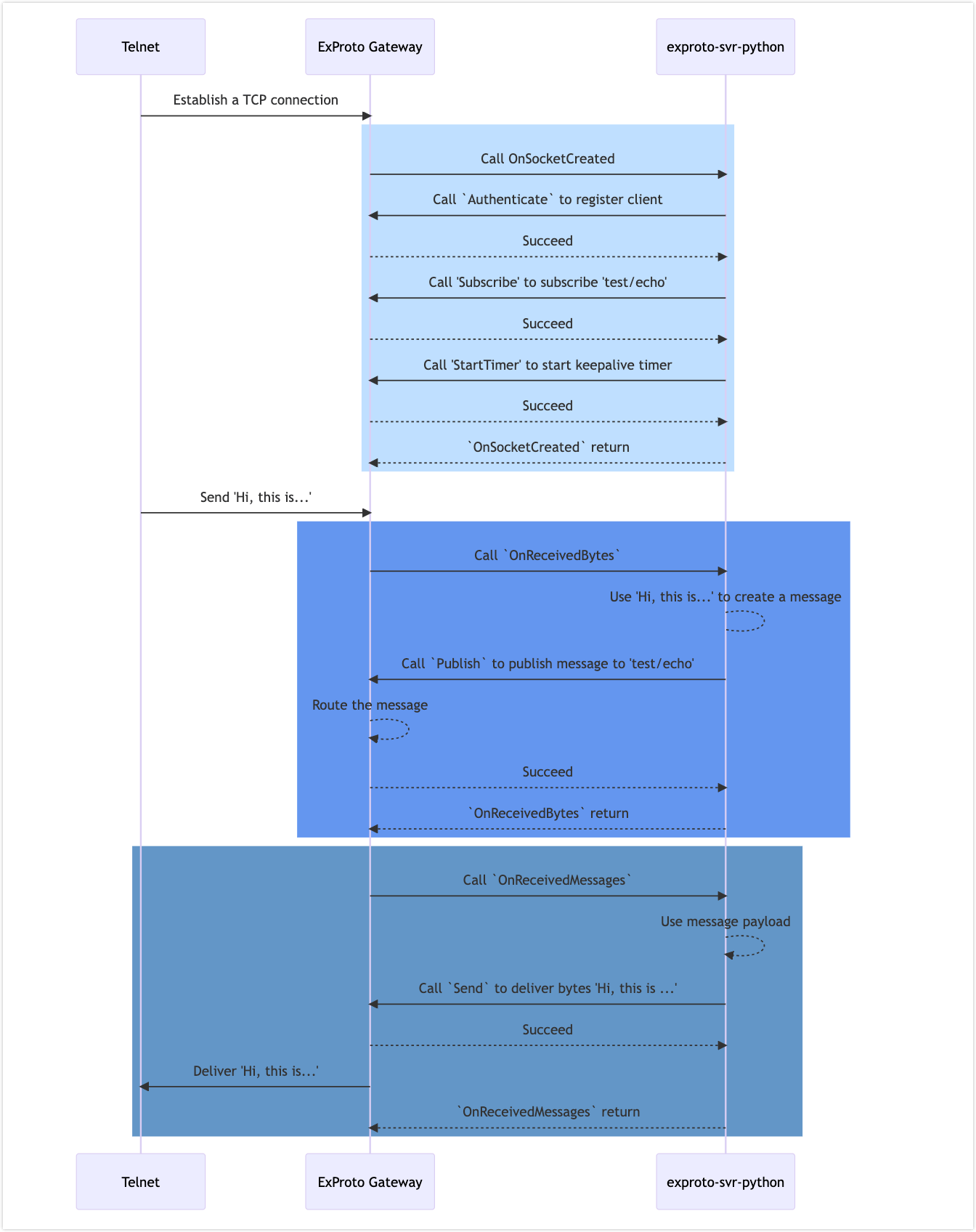 > exproto-svr-python: Succeed
> exproto-svr-python: Succeed exproto-svr-python ->> ExProto Gateway: Call 'Subscribe' to subscribe 'test/echo' ExProto Gateway -->> exproto-svr-python: Succeed exproto-svr-python ->> ExProto Gateway: Call 'StartTimer' to start keepalive timer ExProto Gateway -->> exproto-svr-python: Succeed exproto-svr-python -->> ExProto Gateway: OnSocketCreated return end Telnet ->> ExProto Gateway: Send 'Hi, this is...' rect rgb(100,150, 240) ExProto Gateway ->> exproto-svr-python: Call OnReceivedBytes exproto-svr-python --> exproto-svr-python: Use 'Hi, this is...' to create a message exproto-svr-python ->> ExProto Gateway: Call Publish to publish message to 'test/echo' ExProto Gateway -->> ExProto Gateway: Route the message ExProto Gateway -->> exproto-svr-python: Succeed exproto-svr-python -->> ExProto Gateway: OnReceivedBytes return end rect rgb(100, 150, 200) ExProto Gateway ->> exproto-svr-python: Call OnReceivedMessages exproto-svr-python -->> exproto-svr-python: Use message payload exproto-svr-python ->> ExProto Gateway: Call Send to deliver bytes 'Hi, this is ...' ExProto Gateway -->> exproto-svr-python: Succeed ExProto Gateway ->> Telnet: Deliver 'Hi, this is...' exproto-svr-python -->> ExProto Gateway: OnReceivedMessages return end ```-->