REST API-Based MQTT 5.0 SCRAM Authentication
EMQX supports MQTT 5.0 enhanced authentication using REST API, implementing the Salted Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (SCRAM). The SCRAM authenticator utilizes an external web resource to retrieve the necessary authentication data in this implementation. When enabled, and a client initiates a connection request with SCRAM, EMQX uses the provided username to construct an HTTP request to the external service, obtaining the authentication data required for the authentication process.
While SCRAM is inherently a lightweight and simple authentication mechanism, this implementation enhances its functionality by integrating with an external REST API. This allows EMQX to securely and efficiently retrieve authentication data from various external systems, supporting more complex authentication scenarios.
Prerequisites
- Familiarity with basic EMQX authentication concepts.
- SCRAM authenticator is only supported for MQTT 5.0 connections.
- This authenticator is not an implementation of the RFC 7804: Salted Challenge Response HTTP Authentication Mechanism.
HTTP Request and Response
The authentication process is similar to an HTTP API call. EMQX acts as the client, constructing and sending an HTTP request to an external HTTP service. The service responds with the required authentication data corresponding to the username.
Response Format Requirements
To ensure successful authentication, the HTTP response must adhere to the following criteria:
- Content-Type: The response must be encoded as
application/json. - Authentication Data: Must include
stored_key,server_key, andsalt, all encoded in hexadecimal. - Superuser Indicator: Use the
is_superuserfield, with possible valuestrueorfalse. - Client Attributes: Optionally, you can specify client attributes using the
client_attrsfield. Both keys and values must be strings. - Access Control List (ACL): Optionally include an
aclfield to define the client's permissions. Refer to the Access Control List for more details. - Expiration Time: Optionally, you can set the
expire_atfield to specify when the client's authentication expires, after which the client must disconnect and re-authenticate. The value should be a Unix timestamp in seconds. - HTTP Status Code: The HTTP response should return a
200 OKstatus code. Any4xxor5xxstatus codes will be interpreted asignore, and the authentication chain will proceed without this authenticator.
Example HTTP Response
The following example illustrates the expected structure and content of the HTTP response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Headers: Content-Type: application/json
...
Body:
{
"stored_key": "008F5E0CC6316BB172F511E93E4756EEA876B5B5125F1CD2FD69A2C30F9A0D73",
"server_key": "81466E185EC642AFAE1EFA75953735D6C0934D099149AAAB601D59F8F8162580",
"salt": "6633653634383437393466356532333165656435346432393464366165393137"
"is_superuser": true, // options: true | false, default value: false
"client_attrs": { // optional
"role": "admin",
"sn": "10c61f1a1f47"
}
"expire_at": 1654254601, // optional
"acl": // optional
[
{
"permission": "allow",
"action": "subscribe",
"topic": "eq t/1/#",
"qos": [1]
},
{
"permission": "deny",
"action": "all",
"topic": "t/3"
}
]
}Configure Authenticator with Dashboard
You can configure the SCRAM authenticator through the EMQX Dashboard.
Login to the EMQX Dashboard.
In the left navigation menu, click Access Control -> Authentication to open the Authentication page.
Click Create in the top right corner.
Select SCRAM as the Mechanism and HTTP Server as the Backend. By clicking Next, you will enter the Configuration step page, as shown below.
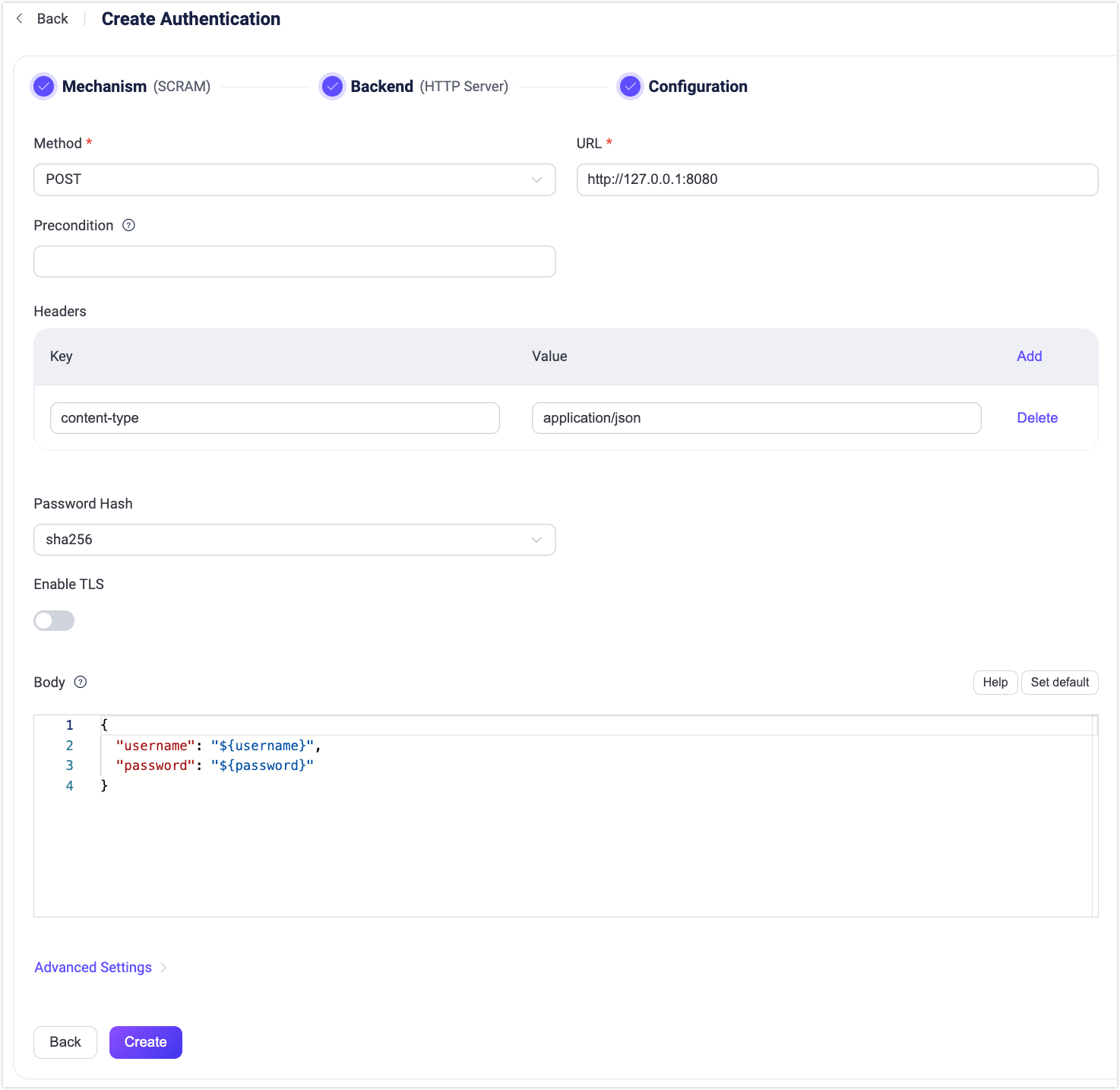
Configure the following settings for the backend:
Method: Select the HTTP request method (
GETorPOST).TIP
The
POSTmethod is recommended to avoid exposing sensitive information, such as passwords, in server logs. For untrusted environments, use HTTPS.URL: Enter the URL of the HTTP service.
Precondition: A Variform expression used to control whether this HTTP Server authenticator should be applied to a client connection. The expression is evaluated against attributes from the client (such as
username,clientid,listener, etc.). The authenticator will only be invoked if the expression evaluates to the string"true". Otherwise, it will be skipped. For more information about the precondition, see Authentication Preconditions.Headers (optional): Specify any additional HTTP request headers.
Authentication Configuration:
- Password Hash: Select the password hash algorithm (
sha256orsha512). - Enable TLS: Enable TLS by toggling the switch. For more details on enabling TLS, see TLS for External Resource Access.
- Body: Define the request template. For
POSTrequests, it’s sent as JSON in the request body; forGETrequests, it’s encoded as a Query String in the URL. Use placeholders to map keys and values.
- Password Hash: Select the password hash algorithm (
Advanced Settings:
- Connection Pool size (optional): Set the number (integer value) of concurrent connections from an EMQX node to the HTTP server. Default:
8. - Connect Timeout (optional): Specify the waiting period before EMQX assumes the connection is timed out. Supported units:
milliseconds,second,minute,hour. - HTTP Pipelining (optional): Enter a positive integer to specify the maximum number of HTTP requests that can be sent without waiting for a response. Default:
100. - Request Timeout (optional): Specify the waiting period before EMQX assumes the request is timed out. Supported units:
milliseconds,second,minute,hour. - Iteration Count (optional): Set the SCRAM iteration count. Default:
4096.
- Connection Pool size (optional): Set the number (integer value) of concurrent connections from an EMQX node to the HTTP server. Default:
After completing the configuration, click Create to finalize the settings.