Use MQTT over QUIC
In EMQX 5.0, we introduce the MQTT over QUIC listener to help IoT users benefit from MQTT over QUIC. This section gives you a step-by-step guide on how to use MQTT over QUIC.
Prerequisites
Knowledge of MQTT over QUIC.
Environment
To test the MQTT over QUIC listener, you are recommended to use the Docker image and use the command below to enable the listener on port 14567:
docker run -d --name emqx \
-p 1883:1883 -p 8083:8083 \
-p 8084:8084 -p 8883:8883 \
-p 18083:18083 \
-p 14567:14567/udp \
-e EMQX_LISTENERS__QUIC__DEFAULT__keyfile="etc/certs/key.pem" \
-e EMQX_LISTENERS__QUIC__DEFAULT__certfile="etc/certs/cert.pem" \
-e EMQX_LISTENERS__QUIC__DEFAULT__ENABLED=true \
emqx/emqx:5.8.8For more information on running EMQX via Docker container, see Deploy with Docker.
Enable MQTT over QUIC
MQTT over QUIC is disabled by default, you need to manually enable this listener with the following steps:
- Open the configuration file
etc/base.hocon, add the following configuration:
listeners.quic.default {
enabled = true
bind = "0.0.0.0:14567"
keyfile = "etc/certs/key.pem"
certfile = "etc/certs/cert.pem"
}This configuration indicates that the QUIC listener is enabled on port 14567. Save the changes and restart EMQX to apply the configuration.
- Execute
emqx ctl listenersin CLI, and we can see that the MQTT over QUIC listener is enabled:
> emqx ctl listeners
quic:default
listen_on : :14567
acceptors : 16
proxy_protocol : undefined
running : true
ssl:default
listen_on : 0.0.0.0:8883
acceptors : 16
proxy_protocol : false
running : true
current_conn : 0
max_conns : 512000So far, we have enabled the MQTT over QUIC listener on EMQX, and then we will continue to connect the clients.
Client SDK and Tools
- NanoSDK: MQTT SDK in C language released by EMQ NanoMQ team, also supports protocols such as WebSocket and nanomsg/SP.
- NanoSDK-Python: Python binding of NanoSDK.
- NanoSDK-Java: Java JNA binding of NanoSDK.
- emqtt: MQTT client library in Erlang, supporting QUIC.
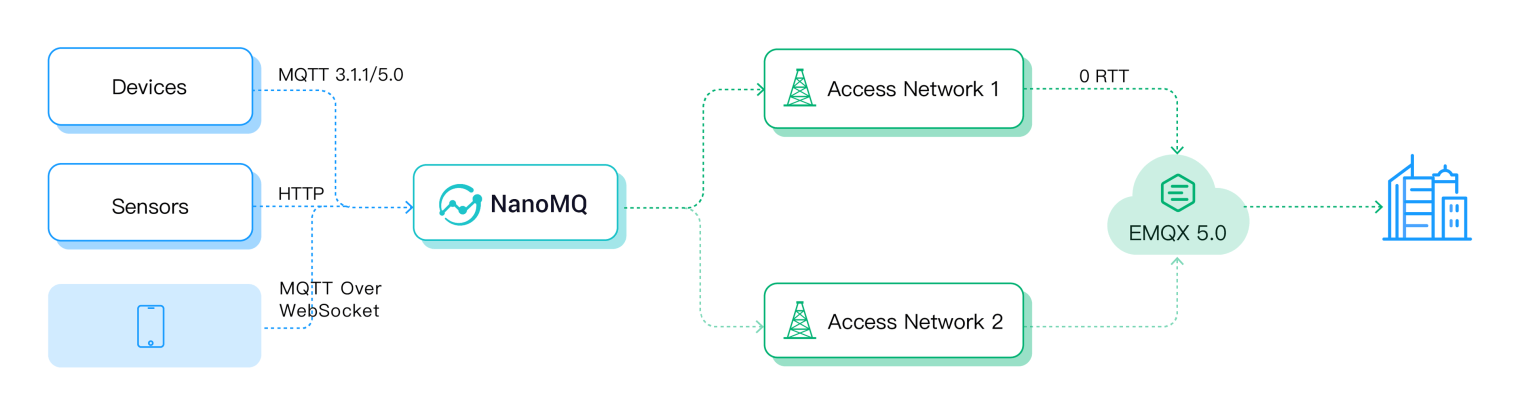
Besides the client library, EMQ provides MQTT over QUIC bridging with the edge computing product NanoMQ. You can use NanoMQ to bridge edge data to the cloud through QUIC, so you can use the MQTT over QUIC listener without needing too much development and integration effort.
Network Failover
As QUIC is based on the UDP protocol, many operators still have special routing strategies for UDP packets, often leading to QUIC connection failures or packet losses.
Therefore, MQTT over QUIC clients are designed with a fallback feature: the API layer can use unified operations to write services, and the transport layer can switch in real time according to network conditions. When QUIC is unavailable, it automatically switches to TCP/TLS 1.2 to ensure services under various network environments.
Example 1: MQTT over QUIC Through NanoSDK
NanoSDK is based on MsQuic, and it is the first Software Development Kit (SDK) to implement MQTT over QUIC in the C language, which is seamlessly compatible with EMQX 5.0. It adopts a fully asynchronous IO design, binds the QUIC Stream and MQTT connection mapping, realizes the built-in function of 0 RTT fast handshake reconnection, and supports multi-core task parallelism.
NanoSDK API works similarly to MQTT over TCP. You can create the MQTT client based on QUIC with one command line:
## Create MQTT over Quic client with NanoSDK
nng_mqtt_quic_client_open(&socket, url);For message sample code, see https://github.com/nanomq/NanoSDK/tree/main/demo.
After compiling, you can use the following command to connect to EMQX 5.0 on port 14567 for testing.
quic_client sub/pub mqtt-quic://127.0.0.1:14567 topic msgNanoSDK also provides bindings for Java) and Python:
Example 2: MQTT over QUIC Bridging via NanoMQ
NanoMQ is an ultra-lightweight and blazing-fast service for IoT edge, featuring cross-platform support, multi-threading, and support to MQTT over QUIC bridging.
It can convert the data from traditional MQTT clients into QUIC packets and send them to EMQX in the cloud, thus providing an option for end-side IoT devices that are hard to integrate or lack a suitable MQTT over QUIC SDK to use the QUIC protocol.
- Download and install NanoMQ:
git clone https://github.com/emqx/nanomq.git
cd nanomq ; git submodule update --init --recursive
mkdir build && cd build
cmake -G Ninja -DNNG_ENABLE_QUIC=ON ..
sudo ninja install- After the installation, we can configure the MQTT over QUIC bridging function and the related topics in the configuration file
/etc/nanomq.conf. The URL prefixmqtt-quicindicates that it is using QUIC as the MQTT transmission layer:
## Bridge address: host:port .
##
## Value: String
bridge.mqtt.emqx.address=mqtt-quic://127.0.0.1:14567For more information, please refer to NanoMQ - MQTT over QUIC Bridge.
MQTT over QUIC CLI Tool
NanoMQ also provides the test tool nanomq_cli, which contains MQTT over QUIC client tools so users can test the MQTT over QUIC function in EMQX 5.0:
nanomq_cli quic --help
Usage: quic conn <url>
quic sub <url> \<qos> \<topic>
quic pub <url> \<qos> \<topic> \<data>
## subscribe example
nanomq_cli quic sub mqtt-quic://54.75.171.11:14567 2 msgTo sum up, you can directly integrate NanoSDK into your project or use it with NanoMQ to realize QUIC access from the device side to the cloud.