Use HTTP Service
EMQX supports using an external HTTP service for password authentication. After enabling, when a client initiates a connect request, EMQX will use the received information to construct an HTTP request and determine whether to accept the request based on the query result, achieving a complex authentication logic.
Prerequisite
Knowledge about basic EMQX authentication concepts
HTTP Request and Response
The authentication process is similar to an HTTP API call where EMQX, as the requesting client, constructs and initiates a request to the HTTP service in the format required by the "API", and the HTTP service returns the result as required by the "client".
- The response encoding format
content-typemust beapplication/json. - The authentication result is marked by
resultin the body, with option value:allow,deny,ignore. - Superuser is marked by
is_superuserin the body, option value:true,false. - Starting from EMQX v5.7.0, you can set client attributes using the optional
client_attrsfield. Note that both keys and values must be strings. - Starting from EMQX v5.8.0, you can set an optional
aclfield in the response body to specify the client's permissions. See Access Control List (ACL) for more information. - Starting from EMQX v5.8.0, you can set an optional
expire_atfield in the response body to specify the expiration time of the client's authenticity, forcing the client to disconnect and get reauthenticated at reconnection. The value is a Unix timestamp in seconds. - The HTTP response status code
Status Codeshould be200or204, the4xx/5xxstatus code returned will ignore the body and determine the result to beignoreand continue with the authentication chain.
Example response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Headers: Content-Type: application/json
...
Body:
{
"result": "allow", // "allow" | "deny" | "ignore"
"is_superuser": false, // options: true | false, default value: false
"client_attrs": { // optional (since v5.7.0)
"role": "admin",
"sn": "10c61f1a1f47"
}
"expire_at": 1654254601, // optional (since v5.8.0)
"acl": // optional (since v5.8.0)
[
{
"permission": "allow",
"action": "subscribe",
"topic": "eq t/1/#",
"qos": [1]
},
{
"permission": "deny",
"action": "all",
"topic": "t/3"
}
]
}EMQX 4.x Compatibility Notes
In EMQX 4.x, only HTTP status code is used, but body is discarded, for example, 200 for allow and 403 for deny. Due to the lack of expressiveness, it has been redesigned to make use of HTTP body, and thus is not compatible with EMQX 5.0.
Configure with Dashboard
You can use EMQX Dashboard to finish the relevant configuration.
- In the EMQX Dashboard, click Access Control -> Authentication from the left navigation menu.
- On the Authentication page, click Create in the top right corner.
- Click to select Password-Based as Mechanism, and HTTP Server as Backend to go to the Configuration tab, as shown below.
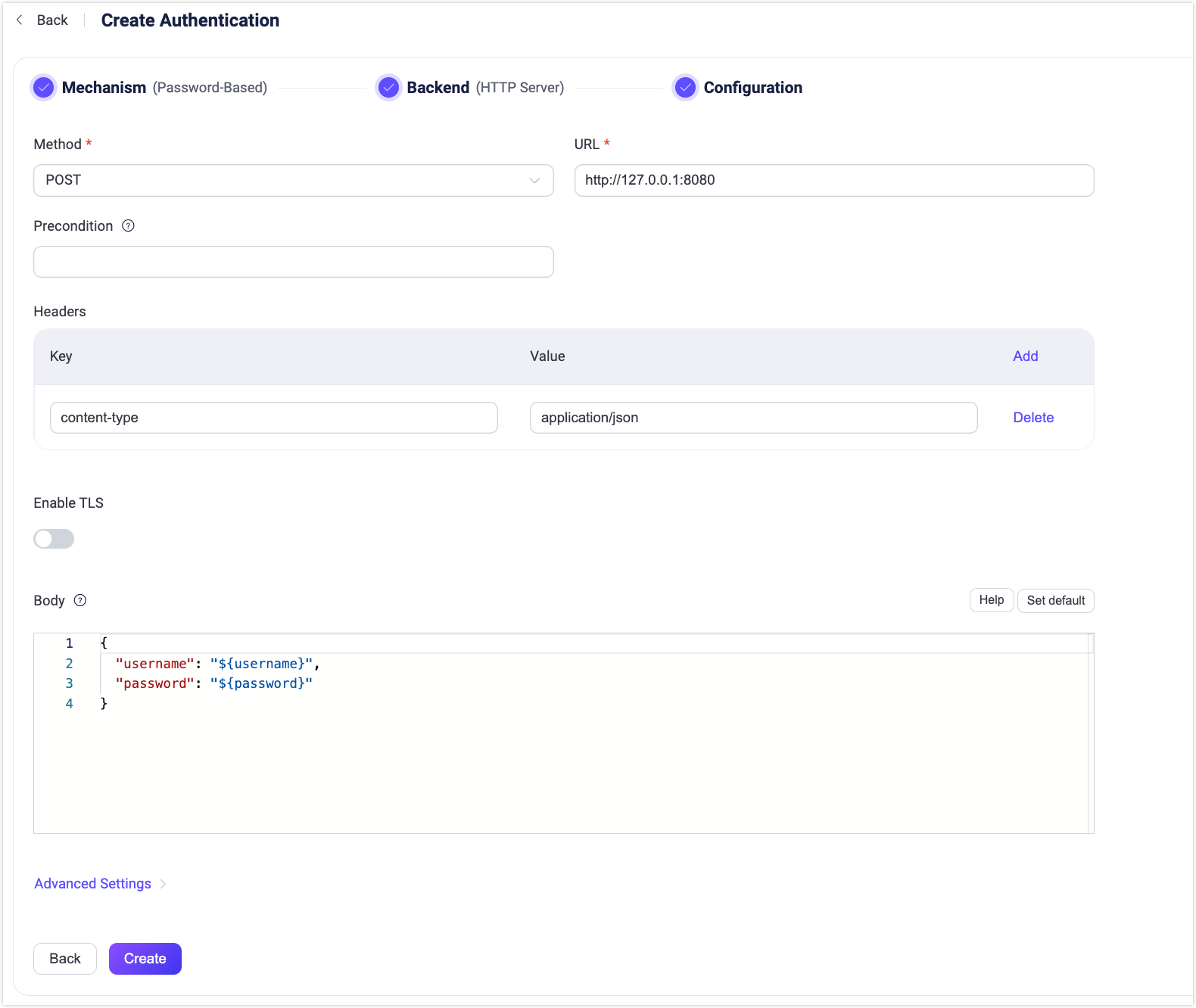
Follow the instructions below to configure the authentication backend:
Method: Select HTTP request method, optional values:
get,postTIP
The
POSTmethod is recommended. When using theGETmethod, some sensitive information (such as plain text passwords) may be exposed via HTTP server logs. Also, for untrusted environments, please use HTTPS.URL: Enter the URL address of the HTTP service.
Precondition: A Variform expression used to control whether this HTTP Server authenticator should be applied to a client connection. The expression is evaluated against attributes from the client (such as
username,clientid,listener, etc.). The authenticator will only be invoked if the expression evaluates to the string"true". Otherwise, it will be skipped. For more information about the precondition, see Authenticator Preconditions.Headers (optional): HTTP request header. You can add several headers. Keys and values support using placeholders.
Enable TLS: Turn on the toggle switch if you want to enable TLS. For more information on enabling TLS, see Network and TLS.
Body: Request template; for
POSTrequests, it is sent as a JSON in the request body; forGETrequests, it is encoded as a Query String in the URL. Mapping keys and values support using placeholders.Advanced Settings:
Pool size (optional): Input an integer value to define the number of concurrent connections from an EMQX node to an HTTP server. Default:
8.Connect Timeout (optional): Specify the waiting period before EMQX assumes the connection is timed out. Units supported include milliseconds, second, minute, and hour.
HTTP Pipelining (optional): Input a positive integer to specify the maximum number of HTTP requests that can be sent without waiting for a response; default value:
100.Request Timeout (optional): Specify the waiting period before EMQX assumes the request is timed out. Units supported include milliseconds, second, minute, and hour.
After you finish the settings, click Create.
Configure with Configuration Items
You can configure the EMQX HTTP authenticator with EMQX configuration items.
Below are the HTTP POST and GET request examples: