Authorization
EMQX provides powerful access control capabilities, and EMQX Dashboard offers out-of-the-box authorization management features. Through a visual interface, users can quickly configure EMQX's authorization mechanisms without writing code or manually editing configuration files. This enables control over MQTT client operations such as publishing and subscribing immediately after connection, facilitating secure configurations for various levels and scenarios. On the Authorization page, you can quickly create and manage various authorization resources.
Create Authorization
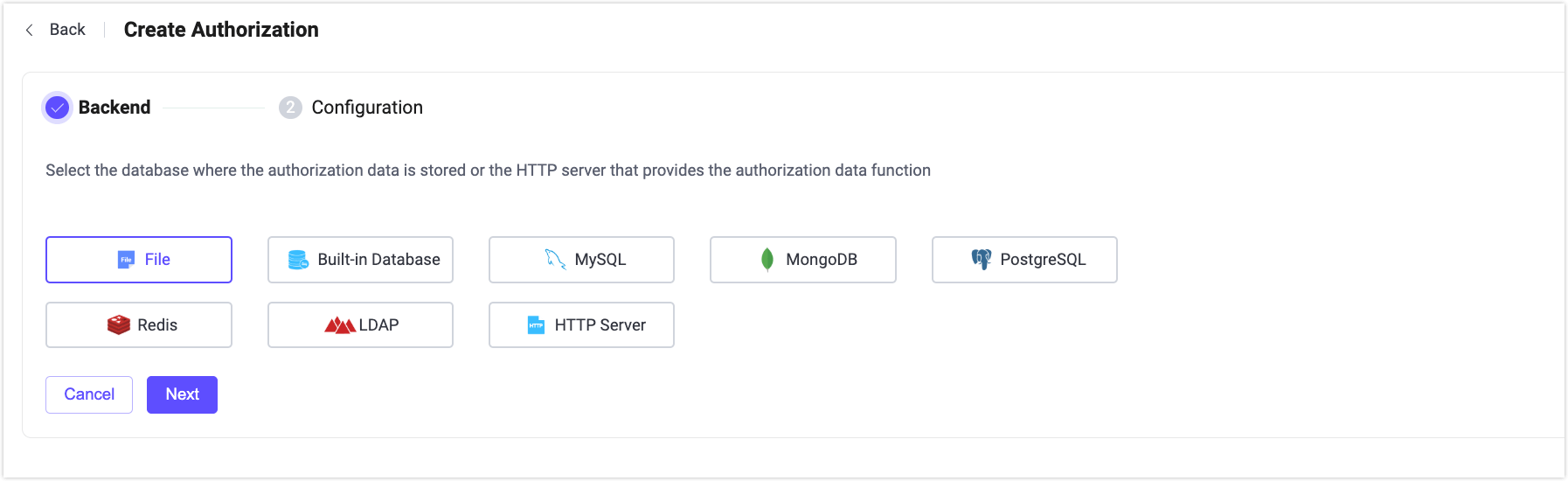
In the upper right corner on the Authorization page, click the Create button to go to the Create Authorization page. Creating an authorization requires selecting a backend to configure and store permission data.
Backend
The backend contains the option to use File, Built-in databases, external databases, or HTTP Server.
Use Access Control List (ACL) File to edit and save authorized content by scanning a set of rules defined in the file for each publishes or subscribe request to determine if the request has permission to perform the desired action.
Use the EMQX built-in database, which can also be used to configure and store authorization rules.
Use an external database to store authorization rules, supporting a selection of mainstream databases including: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Redis, etc.
Delegate authorized requests to an external HTTP server using a pre-defined HTTP service. The external HTTP service needs to include the ability to validate permissions.
Configuration
After selecting the backend it is time to create the final step of authorization and configure the selected backend. Each backend has some configuration for connection or uses that need to be configured manually by the user, or the content of the rules can be edited and saved in an ACL file. After completing the configuration, click Create to quickly complete the authorization configuration. Note: You cannot select the used authorization backend again.
File
Using the ACL file, a text edit box is provided on the configuration parameters page to edit the content of the file's authorization rules, which is a list of Erlang tuple data. (Note that each rule must be followed by a dot .) A tuple is a list wrapped in brackets, with the elements separated by commas.
For more details about how to edit the contents of file rules, refer to ACL File.
Built-in Database
For using the built-in database for authorization, there is no need to configure parameters, and just configure permission rules in the users' page after successful creation.
External Database
If you use an external database, you need to configure the address of the database you can access, the database name, the username, and the password, and fill in the SQL statements or other query statements on how to get the authorization data from the database. When publishing and subscribing, the authorization data will be queried from the database to determine whether the permission rules can be passed. Take MySQL as an example:
For more details on configuring MySQL or other external databases, refer to Integrate with MySQL or the configuration documentation for other databases.
HTTP Server
To use the HTTP Server, you need to first have an HTTP server that is preconfigured to support authorization data matching. When subscribing and publishing, EMQX forwards the data to the HTTP service and determines, by the results returned by HTTP, whether the operation can pass the permission rules.
You need to configure the address and method of requesting the service including the POST or GET method, request the Headers of the service, and configure the authorization information needed for publishing the subscription into the Body field, e.g. username, topic and action into the JSON data.
For more details about how to configure HTTP Server authorization, refer to Use HTTP Service.
Authorization List
Once the authorization configuration is completed, you can view and manage it in the authorization list. In this list, you can see the backend and its status. For instance, if an external database is not deployed or connected successfully, the status of the backend will appear as Disconnected. Hovering over this field allows you to check the connection status of this data source across all nodes in the EMQX cluster. You can quickly enable or disable the authorization configuration by clicking the Enable switch.
Similar to the authentication list, each row in the authorization list can be dragged to adjust the order using the mouse or rearranged through the action column. EMQX allows the creation of multiple authorization mechanisms. When a client performs publish or subscribe operations, EMQX checks them sequentially. For example, if an authorization configuration finds a matching ACL for the client, it applies the corresponding rule, either allowing or denying the action. If no applicable rule is found for the client, EMQX continues to check the next authorization configuration in the authorization chain.
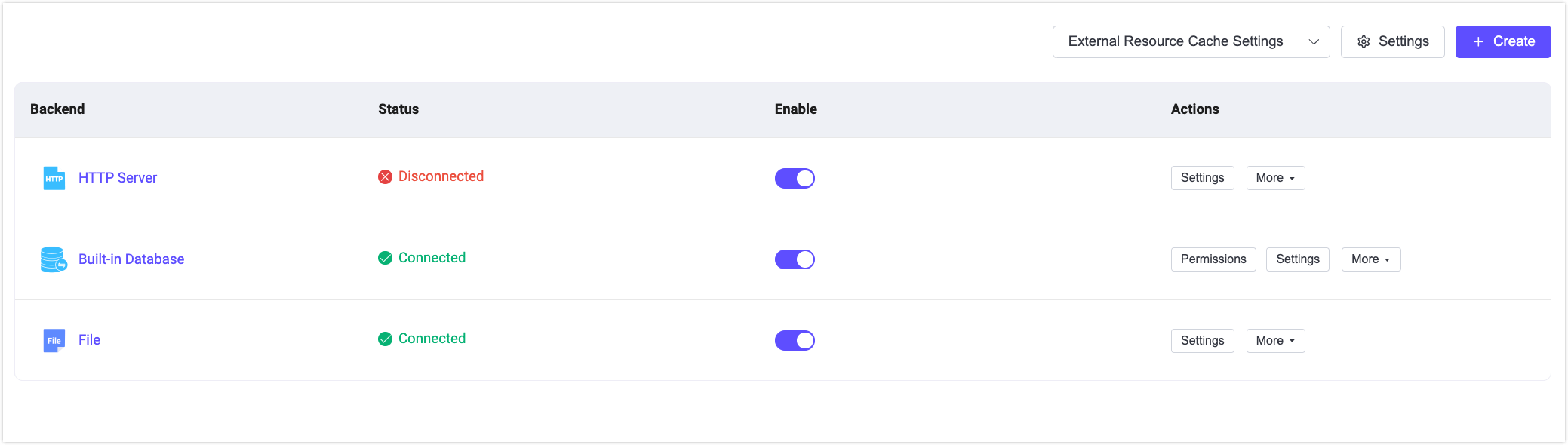
In the Actions column, you can also set up, adjust the order of the authorizer or delete the authorizer.
Note
Disabled the authorization will affect the operation of permissions when the client publishes/subscribes. Please proceed with caution.
Global Settings
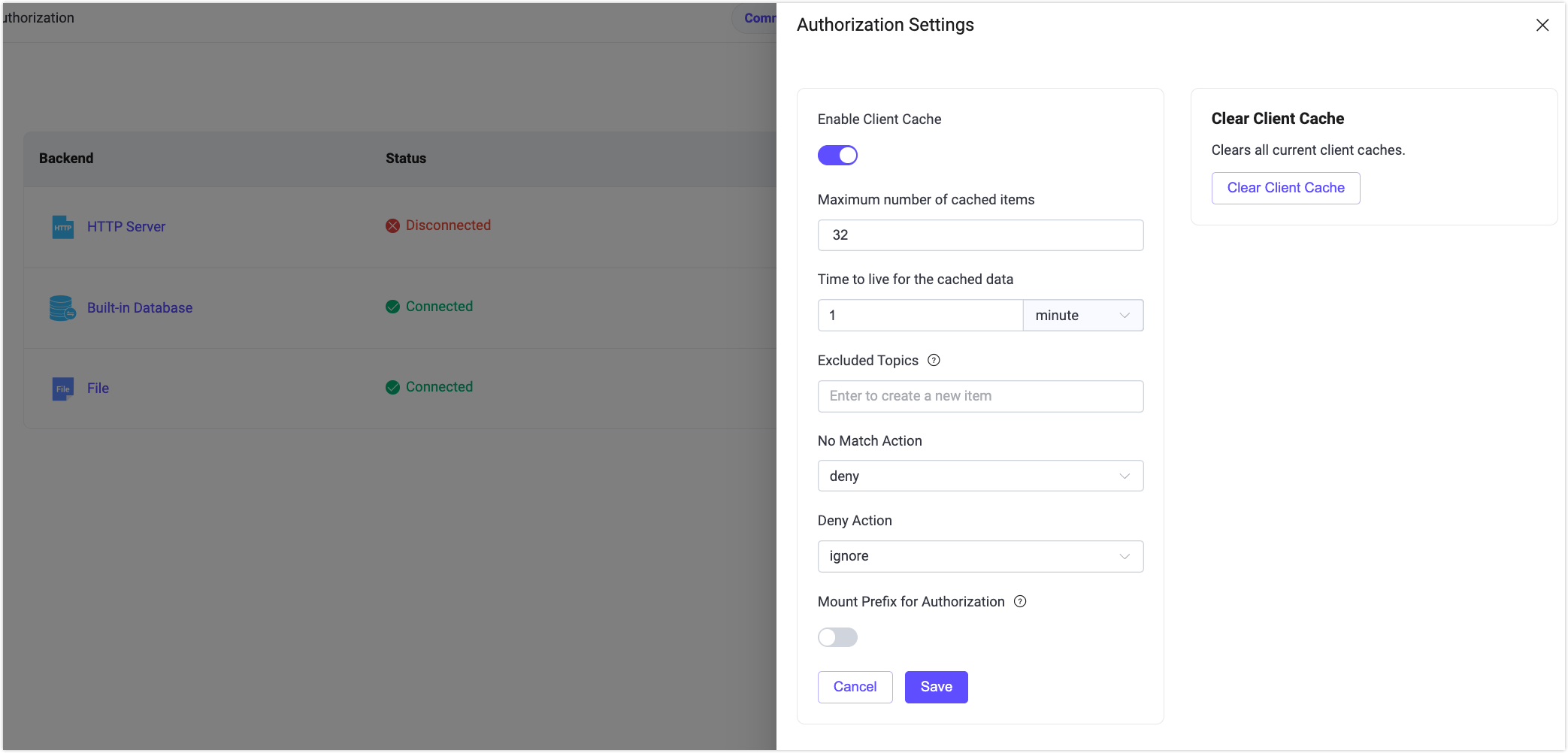
Clicking the Settings button in the top right corner of the list page allows you to configure global settings for authorization.
You can set actions when authorization rules do not match, whether to allow or deny, and decide whether to ignore messages or disconnect clients after denying access. Enabling authorization data caching reduces backend access pressure. Click Clear Cache on the right to quickly clear all current authorization result caches.
Overview
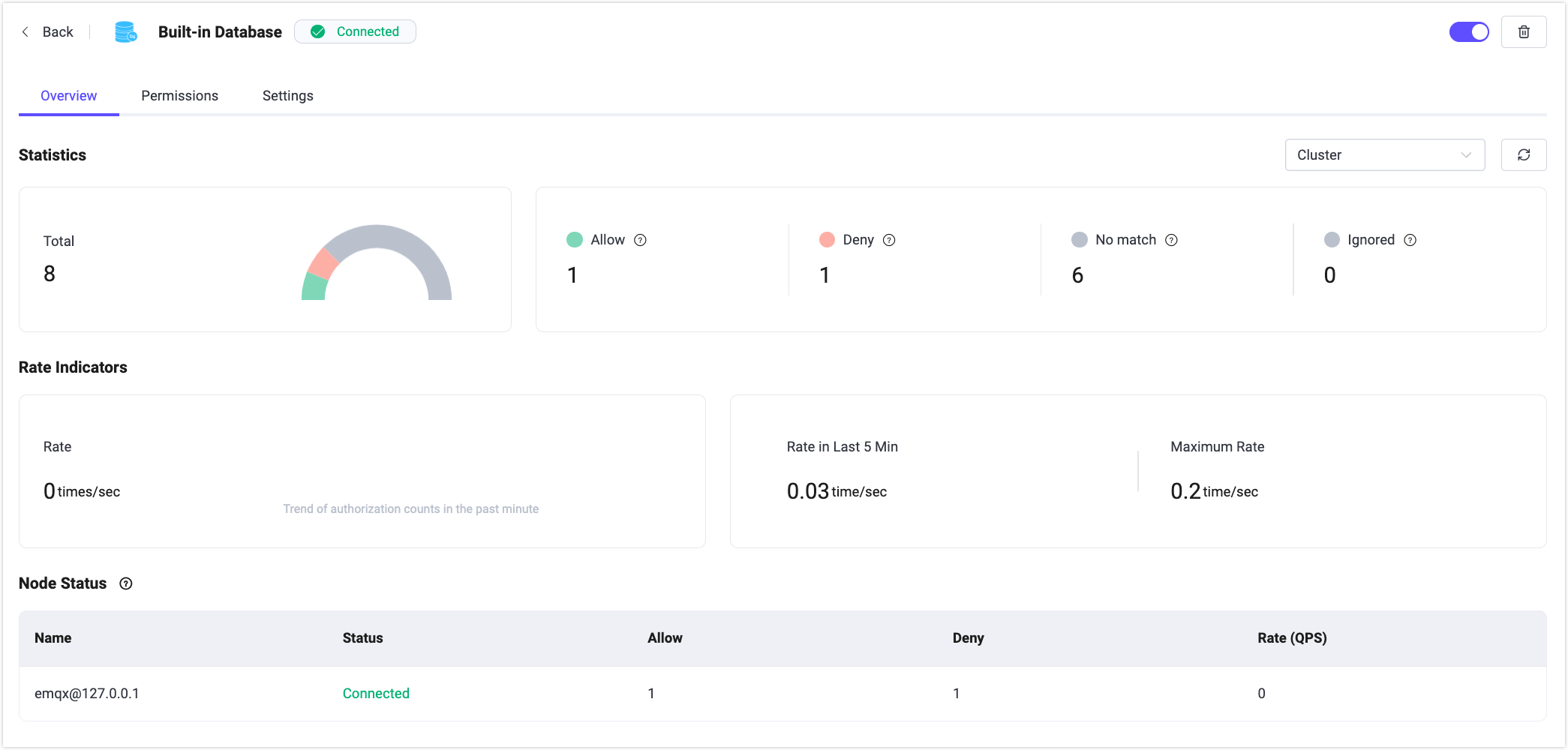
Clicking the name of an authorizer in the Backend column on the list page takes you to an overview of that authorization configuration. This page provides various metrics related to authorization in the EMQX cluster, such as the number of successful and failed authorizations, mismatches, and current rates.
At the bottom of the page, the node status allows you to view authorization metrics data for each node listed.
Permissions
If you are using the built-in database, in the Actions column of the list page, clicking Permissions allows you to manage and configure authorization rules. You can differentiate clients by Client ID or username, or add authorization rules for all users.
To configure an authorization rule, enter a topic that needs authorization configuration, select whether the permission applies when subscribing to or publishing messages to that topic, and set whether the permission should be allow or deny.
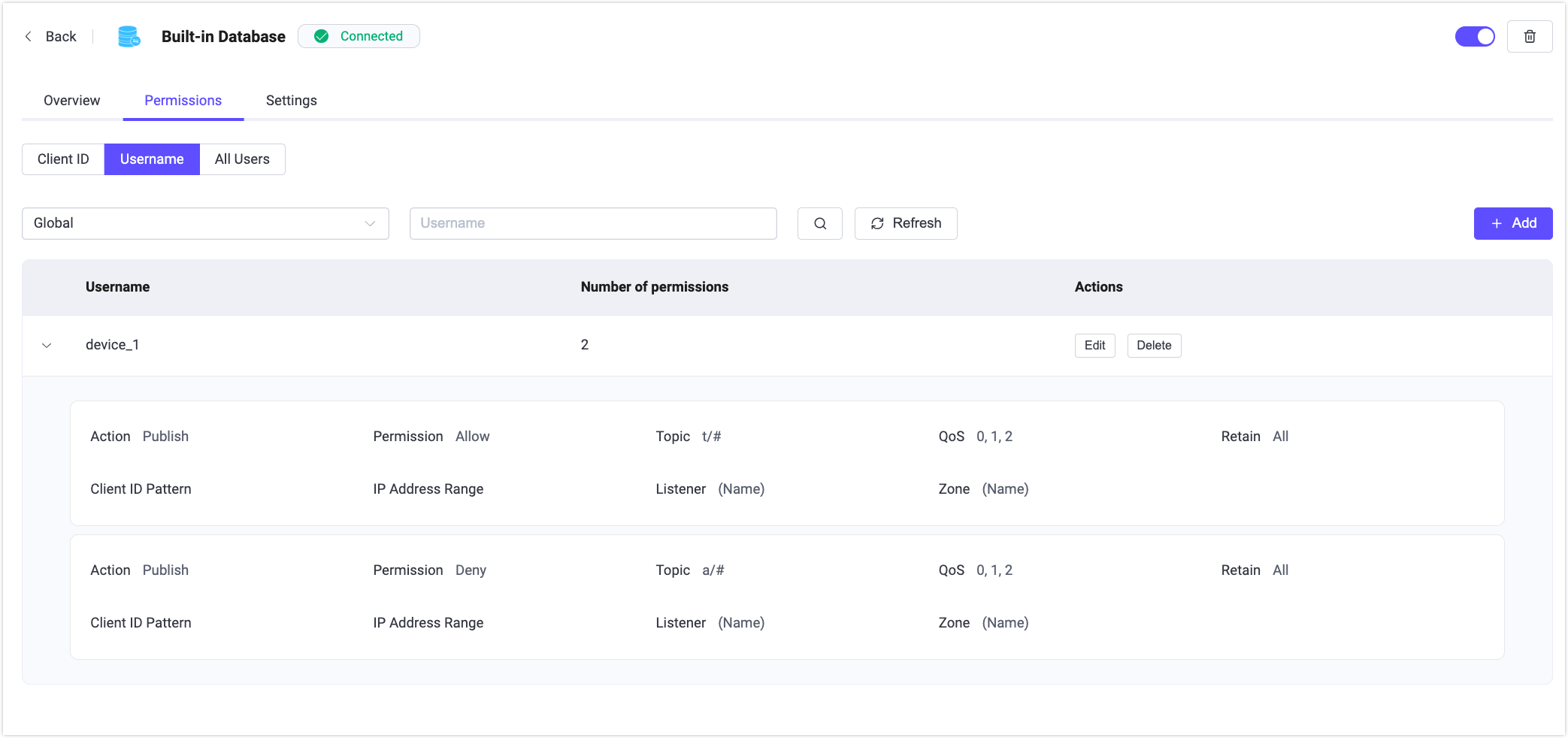
For more details about how to configure the authorization of the built-in database, refer to Use Built-in Database.
Note
Disabling authorization will affect client operations for publishing/subscribing permissions. Please proceed with caution.
Settings
When you need to modify the backend of authorization, you can click Settings in the Actions column on the list page, and you can modify the configuration on the settings page, such as when you need to modify the content of the permission rules of the ACL file, or when some connection information of the external database occurs or the query statement is changed.
For example, when you need to modify the backend of an authorization configuration, change ACL permission rules, or when there are changes in connection information or query statements for an external database, you can click Settings in the Actions column of the list page. This will allow you to modify the configuration information on the settings page.
More Information
For more details about Authorization, please visit Authorization Introduction.