CoAP Gateway
The CoAP gateway in EMQX enables you to implement publish, subscribe, and receive messages as standard with the Publish-Subscribe Broker for the CoAP protocol.
Below is the feature list supported in connection mode and connectionless mode.
| Feature | Connectionless Mode | Connection Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Message Publish | √ | √ |
| Topic Subscribe | √ | √ |
| Topic Unsubscribe | × | √ |
| Create connection | × | √ |
| Close connection | × | √ |
| Heartbeat | × | √ |
| Authentication | × | √ |
Enable the CoAP Gateway
In EMQX 5, CoAP gateway can be configured and enabled through the Dashboard, REST API, and configuration file base.hocon. This section takes the configuration via Dashboard as an example to illustrate the operating steps.
On EMQX Dashboard, click Extensions -> Gateways on the left navigation menu. On the Gateway page, all supported gateways are listed. Locate CoAP and click Setup in the Actions column. Then, you will be directed to the Initialize CoAP page.
TIP
If you are running EMQX in a cluster, the settings you made through the Dashboard or REST API will affect the whole cluster. If you only want to change the settings with one node, configure it in base.hocon.
The EMQX CoAP Gateway supports the connectionless and connection work mode. In the connectionless mode, messages are sent as a one-off transmission and it is useful for short-lived interactions such as reading sensor data or sending simple commands. In the connection mode, the client will establish a connection with the broker before the data transfer begins:
You can choose whether to enable the connection or connectionless mode by selecting false or true under Connection Requested, which is false by default.
After confirming the connection mode, you can continue with the settings. If you don't need extensive customization, you can enable the CoAP Gateway in just 3 clicks:
- Click Next in the Basic Configuration tab to accept all the default settings.
- Then you will be directed to the Listeners tab, where EMQX has pre-configured a UDP listener on port
5683. Click Next again to confirm the setting. - Then click the Enable button to activate the CoAP Gateway.
Upon completing the gateway activation process, you can return to the Gateways page and observe that the CoAP Gateway now displays an Enabled status.
The above configuration can also be configured with REST API:
Example Code:
curl -X 'PUT' 'http://127.0.0.1:18083/api/v5/gateways/coap' \
-u <your-application-key>:<your-security-key> \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name": "coap",
"enable": true,
"mountpoint": "coap/",
"connection_required": false,
"listeners": [
{
"type": "udp",
"name": "default",
"bind": "5683",
"max_conn_rate": 1000,
"max_connections": 1024000
}
]
}'For a detailed REST API description, see REST API - Gateway.
If you have some customization needs, want to add more listeners, or add authentication rules, you can continue to read the Customize Your CoAP Gateway section.
The CoAP gateway only supports UDP and DTLS type listeners, for a complete list of configurable parameters, refer to: Gateway Configuration - Listeners.
Work with CoAP Clients
Client Libraries
After establishing the CoAP gateway, you can use the CoAP client tools to test the connections and ensure everything works as expected. Below are some of the recommended CoAP client tools.
Publish/Subscribe
The CoAP gateway uses the URI path and methods defined in the Publish-Subscribe Broker for the CoAP standard.
Detailed parameters refer to Message Publish, Topic Subscribe, Topic Unsubscribe.
Customize Your CoAP Gateway
In addition to the default settings, EMQX provides a variety of configuration options to better accommodate your specific business requirements. This section offers an in-depth overview of the various fields available on the Gateways page. See the texts below the screenshot for a comprehensive explanation of each field.
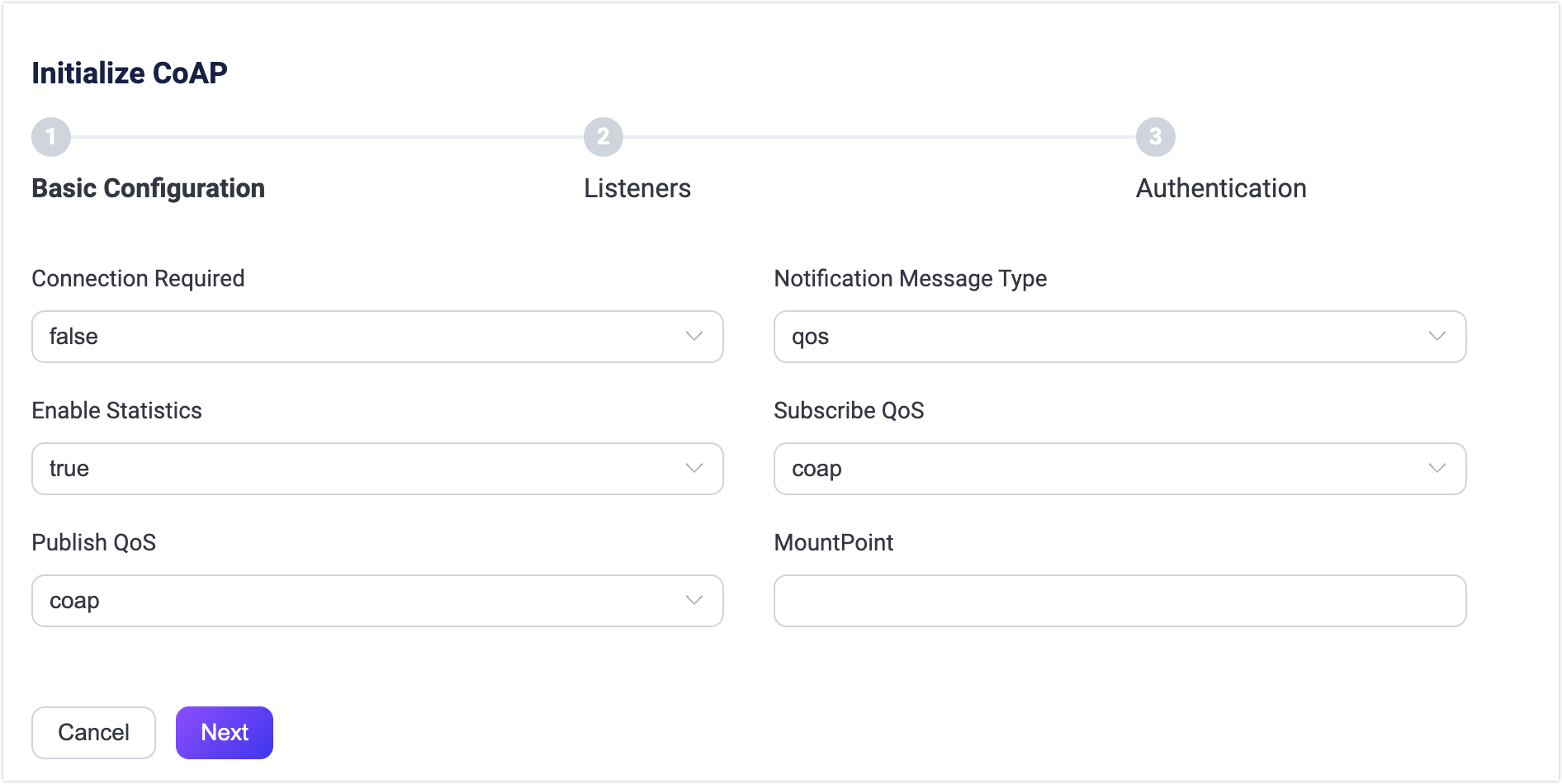
Connection Required: Set whether to enable connectionless or connection mode, default:
false(connectionless), optional values:false(connectionless),true(connection).Notification Message Type: Set the type of CoAP messages to be delivered, default:
qos; optional values:- qos: Whether the CoAP notification needs to be acknowledged depends on the QoS level of the received message.
- QoS 0, no acknowledgment is required from the client,
- QoS 1/2, acknowledgment is required from the client.
- con: The CoAP notification should be acknowledged by the client.
- non: The CoAP notification need not be acknowledged by the client.
- qos: Whether the CoAP notification needs to be acknowledged depends on the QoS level of the received message.
Heartbeat: Only needed if Connection Required is set to
true, set the minimum heartbeat interval to keep the connection alive; default: 30s.Enable Statistics: Set whether to allow the Gateway to collect and report statistics; default:
true, optional values:true,false.Subscriber QoS: Set the default QoS level for subscribe requests, default:
coap, optional values:- coap: Follow the setting in Notification Message Type to determine the QoS level
- Use QoS 0 if no acknowledgment is required.
- Use QoS 1 if acknowledgment is required.
- qos0, qos1, qos2
- coap: Follow the setting in Notification Message Type to determine the QoS level
Publish QoS: Set the default QoS level for publish requests, default:
coap, optional values:coap,qos0,qos1,qos2.MountPoint: Set a string that is prefixed to all topics when publishing or subscribing, providing a way to implement message routing isolation between different protocols, for example, CoAP.
Note: This topic prefix is managed by the gateway. CoAP clients do not need to add this prefix explicitly when publishing and subscribing.
Add Listeners
By default, one UDP listener with the name of default is already configured on port 5683, which supports up to 1,024,000 concurrent connections. You can click Settings for more customized settings, click Delete to delete the listener, or click Add Listener to add a new listener.
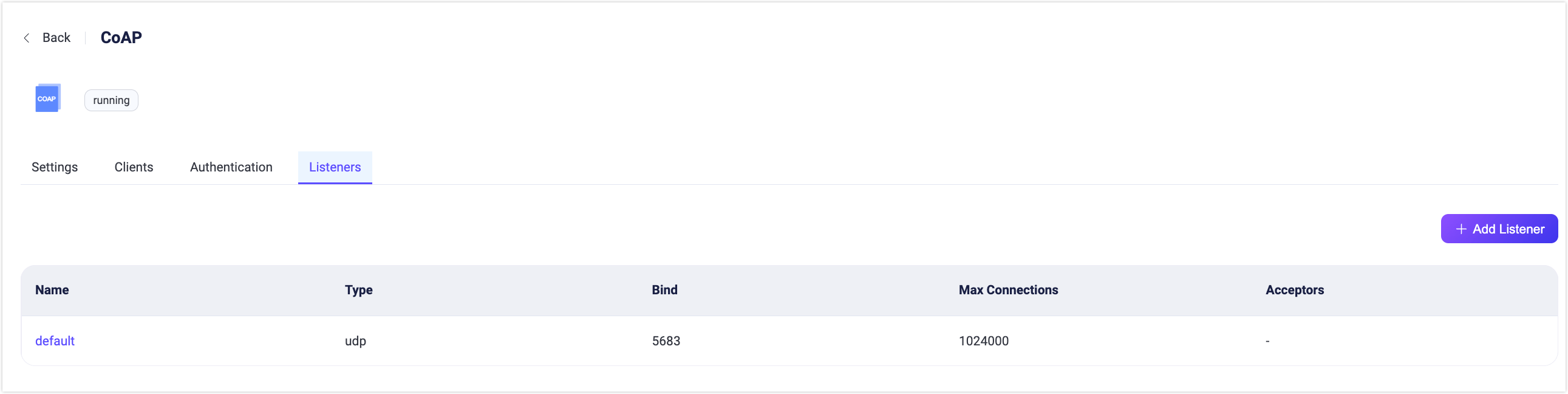
Click Add Listener to open Add Listener page, where you can continue with the following configuration fields:
Basic settings
- Name: Set a unique identifier for the listener.
- Type: Select the protocol type, for CoAP, this can be either
udpordtls. - Bind: Set the port number on which the listener accepts incoming connections.
- MountPoint (optional): Set a string that is prefixed to all topics when publishing or subscribing, providing a way to implement message routing isolation between different protocols.
Listener Settings
- Max Connections: Set the maximum number of concurrent connections that the listener can handle, default: 1024000.
- Max Connection Rate: Set the maximum rate of new connections the listener can accept per second, default: 1000.
UDP Settings
- ActiveN: Set the
{active, N}option for the socket, that is, the number of incoming packets the socket can actively process. For details, see Erlang Documentation - setopts/2. - Buffer: Set the size of the buffer used to store incoming and outgoing packets, unit: KB.
- Receive Buffer: Set the size of the receive buffer, unit: KB.
- Send Buffer: Set the size of the send buffer, unit: KB.
- SO_REUSEADDR: Set whether to allow local reuse of port numbers.
DTLS Settings (for DTLS listeners only)
You can set whether to enable the TLS Verify by setting the toggle switch. But before that, you need to configure the related TLS Cert, TLS Key, and CA Cert information, either by entering the content of the file or uploading with the Select File button. For details, see Enable SSL/TLS Connections.
Configure Authentication
The client ID, username, and password are provided by the client's Create Connection request. The CoAP gateway supports the following authenticator types:
- Built-in Database Authentication
- MySQL Authentication
- MongoDB Authentication
- PostgreSQL Authentication
- Redis Authentication
- HTTP Server Authentication
- JWT Authentication
- LDAP Authentication
This part takes the Dashboard as an example to illustrate how to do the authentication configuration.
On the Gateways page, locate CoAP and click Setup in the Actions column and click Authentication to enter the Authentication tab.
Click Create Authentication, choose Password-Based or JWT as the Mechanism, and select the Backend as needed.
For a detailed explanation of how to configure the authenticators, you may refer to the pages listed at the beginning of this section.
Besides the Dashboard, you can also use REST API to configure the authenticator. For example, to create a built-in database authentication for CoAP gateway, you can use the code below:
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://127.0.0.1:18083/api/v5/gateway/coap/authentication' \
-u <your-application-key>:<your-security-key> \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"backend": "built_in_database",
"mechanism": "password_based",
"password_hash_algorithm": {
"name": "sha256",
"salt_position": "suffix"
},
"user_id_type": "username"
}'TIP
Unlike the MQTT protocol, the gateway only supports the creation of an authenticator, not a list of authenticators (or an authentication chain). If no authenticator is enabled, all CoAP clients are allowed to log in.
Reference: CoAP Client Guide
Create Connection
Only available in Connection Mode.
This interface is used to create a client connection to the CoAP gateway. When the authentication of the CoAP gateway is enabled, the gateway will verify the clientid, username, and password provided by this request to prevent illegal users.
Request Parameters:
- Method:
POST - URI:
mqtt/connection{?QueryString*}, theQueryStringis:clientid: required parameter, UTF-8 string. The gateway uses this string as a unique identifier for the connectionusername: optional parameter, UTF-8 string. Used for connection authentication.password: optional parameter, UTF-8 string. Used for connection authentication.
- Payload: empty
Response:
- Return Code:
2.01: Connection created successfully. The token string for this connection will be returned in the message body.4.00: Bad request. Detailed error information will be returned in the message body.4.01: Not authorized. The request format is validated, but authorization failed.
- Payload: When the return code is
2.01, the message body isToken, otherwise it isErrorMessage.Token: The token string to be used for subsequent requests.ErrorMessage: the error description messages.
Take libcoap as an example:
# Initiate a connection request with clientid 123 and username and password admin/public.
# Returned token is 3404490787
coap-client -m post -e "" "coap://127.0.0.1/mqtt/connection?clientid=123&username=admin&password=public"
3404490787TIP
After the connection is successfully created, you can use Dashboard, REST API or CLI to check the client list in the CoAP gateway.
Close Connection
Only available in Connection Mode.
This interface is used to close the CoAP connection.
Request Parameters:
- Method:
DELETE - URI:
mqtt/connection{?QueryString*}, theQueryStringis:clientid: required parameter, UTF-8 string. The gateway uses this string as a unique identifier for the connectiontoken: required parameter, using the token string returned by the "Create Connection" request
- Payload: empty
Response:
- Return Code:
2.01: Close connection successfully.4.00: Bad request. Detailed error information will be returned in the message body.4.01: Not authorized. The request format is validated, but authorization failed.
- Payload: When the return code is
2.01, the message body isToken, otherwise it isErrorMessage.
For example:
coap-client -m delete -e "" "coap://127.0.0.1/mqtt/connection?clientid=123&token=3404490787"Heartbeat
Only available in Connection Mode.
This interface is used to maintain the connection between the CoAP client and the gateway. When the heartbeat expires, the gateway deletes the session and subscription, and releases all resources for that client.
Request Parameters:
- Method:
PUT - URI:
mqtt/connection{?QueryString*}, theQueryStringis:clientid: required parameter, UTF-8 string. The gateway uses this string as a unique identifier for the connectiontoken: required parameter, using the token string returned by the "Create Connection" request
- Payload: empty
Response:
- Return Code:
2.01: Close connection successfully.4.00: Bad request. Detailed error information will be returned in the message body.4.01: Not authorized. The request format is validated, but authorization failed.
- Payload: When the return code is
2.01, the message body isToken, otherwise it isErrorMessage.
For example:
coap-client -m put -e "" "coap://127.0.0.1/mqtt/connection?clientid=123&token=3404490787"TIP
The heartbeat interval is determined by the heartbeat option of CoAP gateway, default: 30 seconds.
Message Publish
This interface is used by the CoAP client to send messages to the specified topic. Additional identity information needs to be carried if the Connection Mode is enabled.
Request Parameters:
Method:
POSTURI:
ps/{+topic}{?QueryString*}{+topic}is the topic of publish messages, i.e. the URI isps/coap/testif publish message tocoap/test.{?QueryString}is request parameters:clientid: required inConnection Modeand optional inConnectionless Mode.token:Connection Modeonly, required parameter.retain(optional): Whether to publish as a retained message. It is a boolean, default:false.qos: Message QoS, which identifies the QoS level of the message and affects only how the MQTT client receives the message. Enum with0,1,2.expiry: Message expiry interval in seconds, default is 0 which means never expire
Payload: Message payload
Response:
- Return Code:
2.04: Publish successfully4.00: Bad request. Detailed error information will be returned in the message body.4.01: Not authorized. The request format is validated, but authorization failed.
- Payload: When the return code is
2.04, the message body is empty, otherwise it isErrorMessage.
For example, publish a message in Connectionless Mode:
coap-client -m post -e "Hi, this is libcoap" "coap://127.0.0.1/ps/coap/test"Or carry clientid and token in Connection Mode:
coap-client -m post -e "Hi, this is libcoap" "coap://127.0.0.1/ps/coap/test?clientid=123&token=3404490787"Topic Subscribe
This interface is used by the CoAP client to subscribe a topic. Additional identity information needs to be carried if the Connection Mode enabled.
Request Parameters:
Method:
GETOptions: Set
observerto0URI:
ps/{+topic}{?QueryString*}{+topic}is the topic to subscribe, i.e. the URI isps/coap/testif to subscribecoap/test.{?QueryString}is request parameters:clientid: required inConnection Modeand optional inConnectionless Mode.token:Connection Modeonly, required parameter.qos: Subscription QoS to indicate which MessageType (CONorNON) is used by the gateway to deliver messages to CoAP client. Enumerated with:0: UsingNONmessage to delivery1or2: UsingCONmessage to delivery
Payload: empty
Response:
- Return Code:
2.05: Subscribe successfully4.00: Bad request. Detailed error information will be returned in the message body.4.01: Not authorized. The request format is validated, but authorization failed.
- Payload: When the return code is
2.05, the message body is empty, otherwise it isErrorMessage.
For example, subscribe to coap/test in Connectionless Mode:
coap-client -m get -s 60 -O 6,0x00 -o - -T "obstoken" "coap://127.0.0.1/ps/coap/test"Or, carry clientid and token to subscribe in Connection Mode:
coap-client -m get -s 60 -O 6,0x00 -o - -T "obstoken" "coap://127.0.0.1/ps/coap/test?clientid=123&token=3404490787"Topic Unsubscribe
This interface is used by the CoAP client to unsubscribe from a topic.
In the current implementation, the unsubscribing operation is only available in Connection Mode.
Request Parameters:
Method:
GETURI:
ps/{+topic}{?QueryString*}{+topic}is the topic to unsubscribe, i.e. the URI isps/coap/testif subscribe tocoap/test.{?QueryString}is request parameters:clientid: required inConnection Modeand optional inConnectionless Mode.token:Connection Modeonly, required parameter.
Payload: empty
Response:
- Return Code:
2.07: Unsubscribe successfully4.00: Bad request. Detailed error information will be returned in the message body.4.01: Not authorized. The request format is validated, but authorization failed.
- Payload: When the return code is
2.07, the message body is empty, otherwise it isErrorMessage.
For example, unsubscribe to coap/test in Connection Mode:
coap-client -m get -O 6,0x01 "coap://127.0.0.1/ps/coap/test?clientid=123&token=3404490787"Short Parameter Names
To reduce message size, the CoAP gateway supports short parameter names. For example, the parameter clientid=barx can be written as c=bar. Therefore, the supported short parameter names are listed in the following table:
| Parameter Name | Short Name |
|---|---|
clientid | c |
username | u |
password | p |
token | t |
qos | q |
retain | r |