Quick Start: Create a Flow Using Gemini Node
This section demonstrates how to quickly create and test an LLM-based Flow in the Flow Designer through a practical use case using the Gemini Node.
This example demonstrates how to build a Flow that integrates with the Gemini LLM to process MQTT device messages containing structured sensor data while preserving the clientid for routing. The Gemini node generates a reply based on the message payload, and the Republish node sends the AI’s reply to the per-client topic devices/${clientid}/reply, ensuring each device receives its own customized reply.
Scenario Description
In an industrial monitoring scenario, each device periodically publishes structured sensor data in JSON format to the topic devices/<device_id>. Traditional rule-based alerts (e.g., threshold for temperature) may miss hidden patterns or combinations of abnormal indicators.
This Flow leverages Gemini to analyze the overall context of multiple fields, such as vibration, temperature, and pressure, and detect complex anomalies that suggest potential mechanical failures. For example, when vibration and temperature are both elevated, Gemini can infer a more severe risk (e.g., bearing overload) and output a precise, explainable alert.
- Data Processing: Extract the device readings from the payload and expose the
clientid(i.e.,device_1) for downstream use. - LLM-Based Processing: Send the full payload to Gemini for comprehensive analysis across all fields.
- Message Republish: Publish the AI-generated alert to the per-client topic
devices/<district_id>/reply.
Sample incoming message (to devices/device_1):
{
"vibration": 9.5,
"temperature": 85,
"pressure": 1.2
}Expected republished output (to devices/device_1/reply):
Critical Alert: Simultaneous severe vibration and high temperature detected, indicating an immediate critical equipment malfunction risk.Create the Flow
Prerequisite
Make sure you have a valid Gemini API Key.
Click the Create Flow button on the Flows page.
Add a Messages node.
- Drag a Messages node from the Source panel.
- Set the topic to
devices/+. - Click Save.
Add a Data Processing node.
Drag a Data Processing node from the Processing section.
Fill in the form with the following configurations. This setting exposes
clientidfor later use to ensure that it is accessible in downstream nodes (e.g., for${clientid}in republish topics).- Field:
clientid - Transform: Leave empty
- Alias:
clientid
- Field:
Click Save.
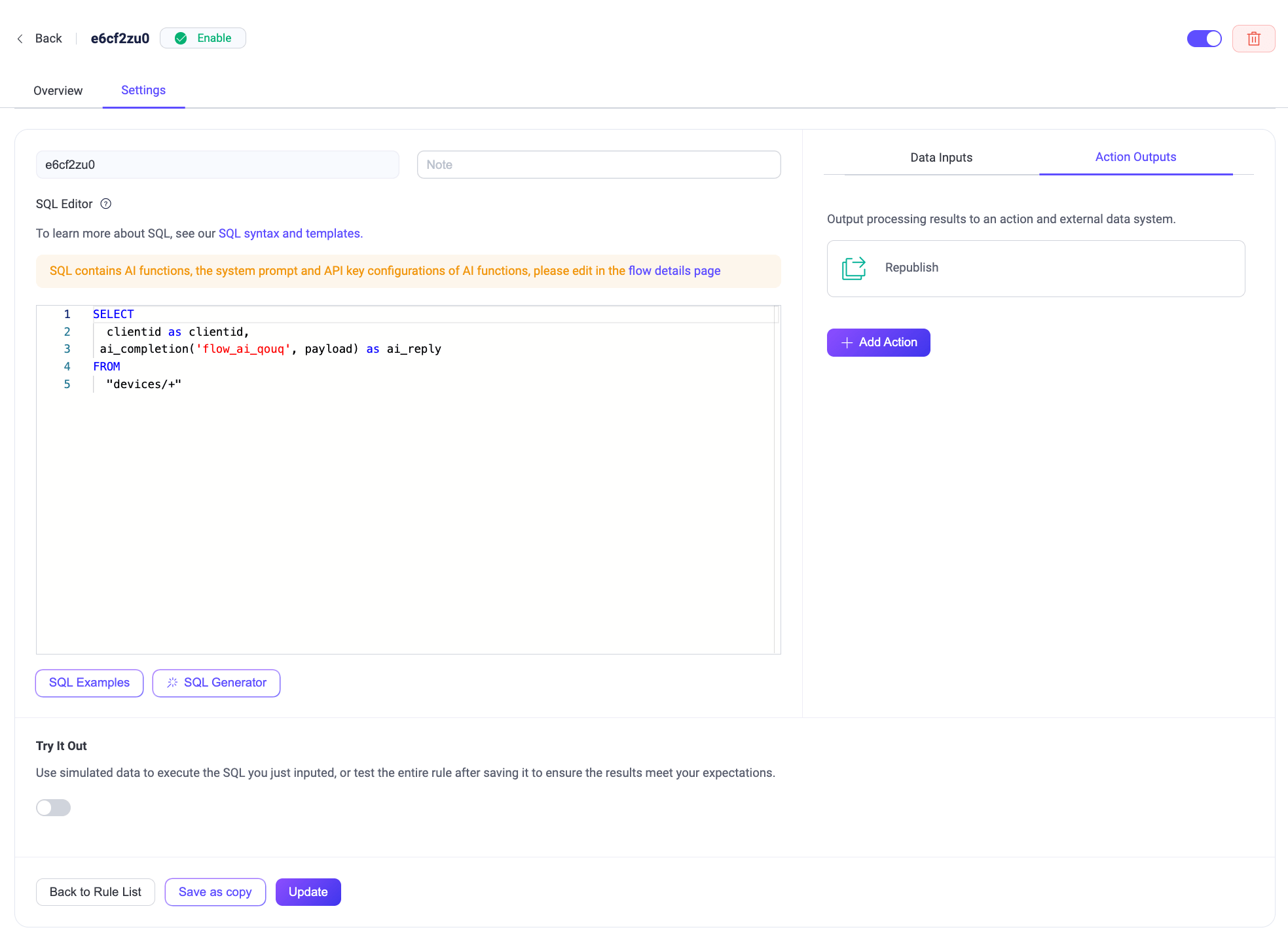
Add a Gemini node.
Drag a Gemini node from the Processing section.
Configure the node:
Input: Enter
payload.System Message: Enter the following prompt:
You are an industrial anomaly detection assistant. Analyze the incoming sensor data (vibration, temperature, pressure) as a whole. If multiple indicators exceed risk thresholds at the same time, for example, if vibration > 8 and temperature > 80 in the same reading, the combined risk is significantly higher than a single abnormal value. In such cases, generate a precise, high-priority alert. Only return a single alert sentence—no extra explanation.Model: Here you can keep the default model
gemini-2.0-flash.API Key: Enter your Gemini API key.
Base URL: Leave empty to use Gemini’s default endpoint.
Output Result Alias: Enter
ai_reply.
Click Save.
Add a Republish node.
- Drag a Republish node from the Sink section.
- Set the topic to
devices/${clientid}/reply. - Set the payload to
${ai_reply}. - Click Save.
Connect all the nodes and click Save in the upper-right corner to save the Flow.
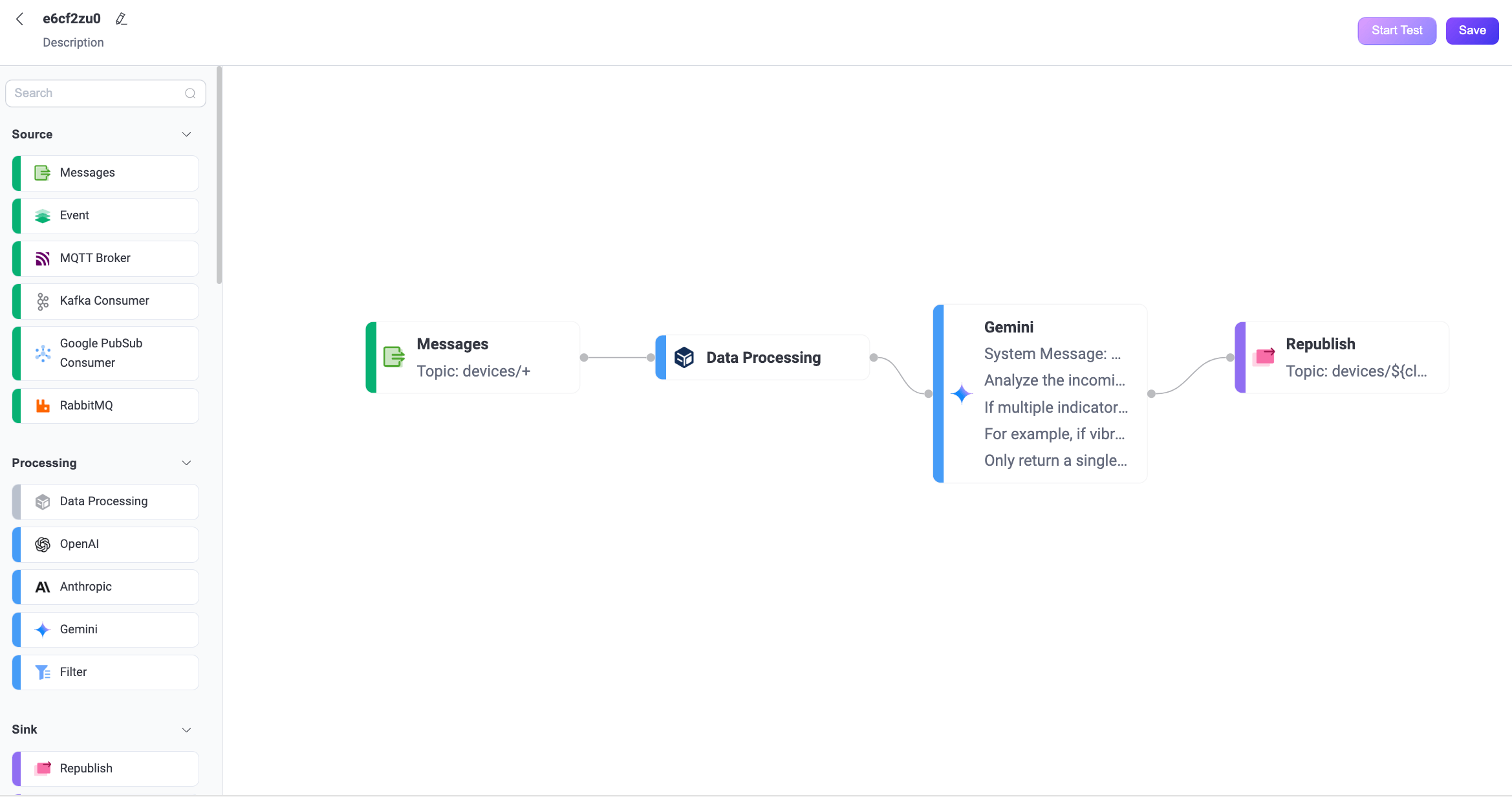
Flows and form rules are interoperable. You can also view the SQL and related rule configurations on the Rule page.
Test the Flow
Connect an MQTT client to EMQX.
To quickly test the flow, you can use the Diagnostic Tools -> WebSocket Client on the Dashboard to simulate an MQTT client. Alternatively, you can also use the MQTTX tool or a real MQTT client:
- Connect to your EMQX server.
- Subscribe to the topic, for example
devices/device_1/reply.
Start Testing.
In the Flow Designer, click any node to open the Edit panel.
Click Edit, then click Start Test to open the test panel at the bottom.
Click Input Simulated Data and publish the following message to topic
devices/device_1by clicking Submit Test:json{ "vibration": 9.5, "temperature": 85, "pressure": 1.2 }
Review results.
You can see the successful execution result of the flow.
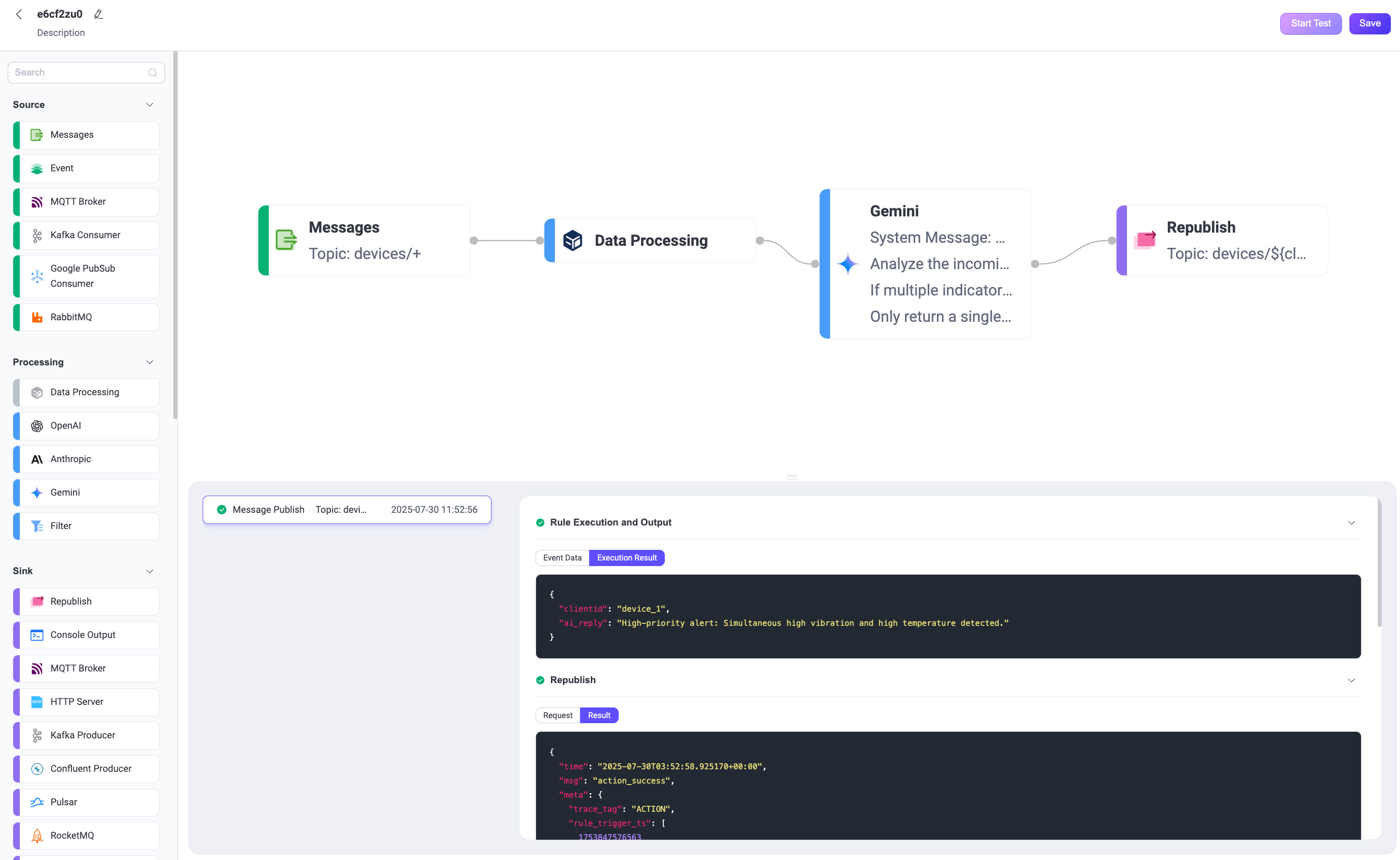
Return to the WebSocket Client page and you should receive an AI-generated summary like:
“High-priority alert: Simultaneous high vibration and high temperature detected.”
If the test results are unsuccessful, error messages will be displayed accordingly.
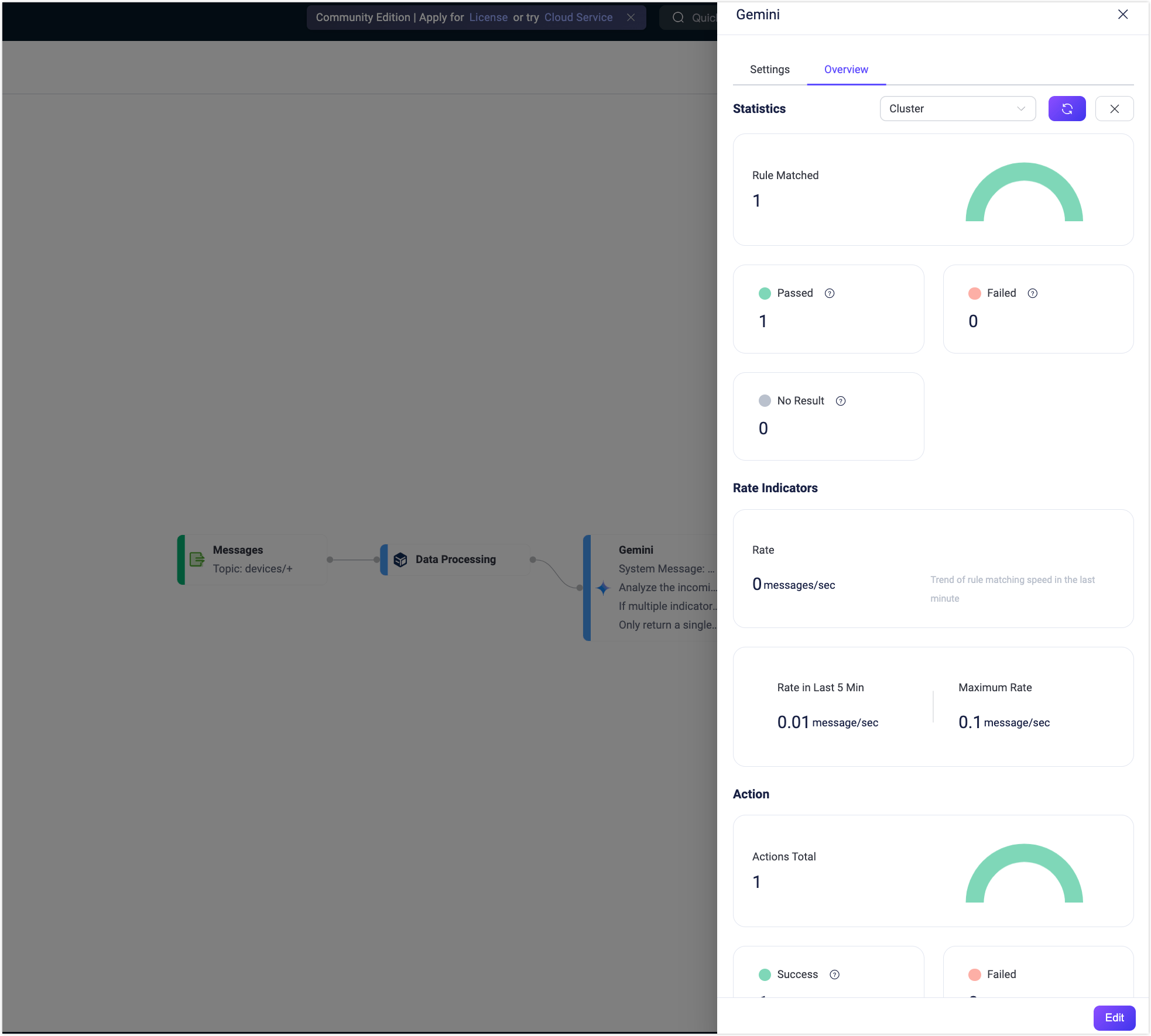
To view the running statistics and metrics of the Gemini node, exit the editing page, click the node to open the Edit panel and click the Overview tab.