Configure and Manage Durable Sessions
This document provides references and instructions for configuring, managing, and optimizing the MQTT Durable Sessions feature within EMQX, including sessions and storage configuration.
Configuration Parameters
MQTT Durable Sessions configuration is divided into two main categories:
durable_sessions: Contains settings related to MQTT clients' sessions, including how they consume data from durable storage and data retention parameters.durable_storageManages the settings of the durable storage system holding the MQTT message data.
Durable Sessions Configuration
You can configure the parameters for durable sessions in the Dashboard. Click Management -> MQTT Settings in the left menu of the Dashboard, and then select the Durable Session tab to configure the parameters.
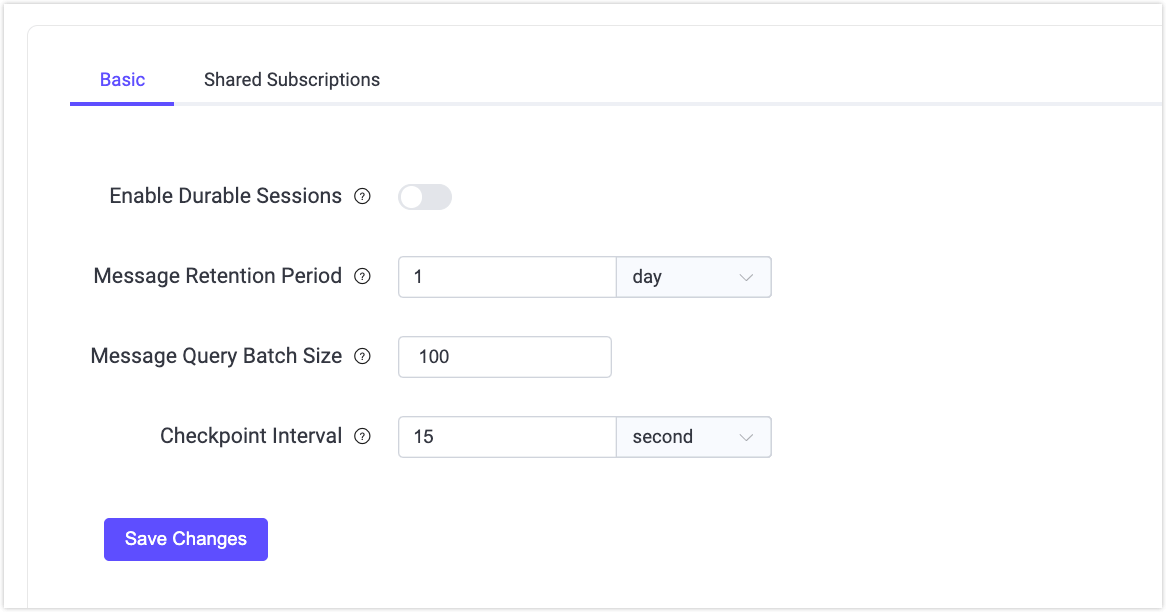
| Parameter | Dashboard UI | Description |
|---|---|---|
durable_sessions.enable | Enable Durable Sessions | Enables session durability. This configuration item cannot be modified through Dashboard, REST API, or CLI; it must be set in the configuration file. Note: Restart of the EMQX node is required for changes to take effect. |
durable_sessions.message_retention_period | Message Retention Period | Defines the retention period of MQTT messages in durable sessions. Note: this parameter is global. |
durable_sessions.batch_size | Message Query Batch Size | Controls the maximum size of message batches consumed from the storage by durable sessions. |
durable_sessions.checkpoint_interval | Session Checkpoint Interval | Specifies the interval for saving session metadata. |
The following parameters can be overridden per zone:
durable_sessions.enabledurable_sessions.batch_sizedurable_sessions.checkpoint_interval
Durable Storage Configuration
The <DS> placeholder stands for "durable storage". Currently, the available parameter for <DS> is message.
Core Durable Storage Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
durable_storage.n_sites | Number of sites. |
durable_storage.<DS>.data_dir | Directory in the file system where EMQX stores the data. |
durable_storage.<DS>.n_shards | Number of shards. |
durable_storage.<DS>.replication_factor | Replication factor determines the number of replicas for each shard. |
durable_storage.<DS>.transaction | Contains parameters related to message buffering. See Buffering. |
durable_storage.<DS>.layout | Contains parameters that control how EMQX lays out data on disk. See Storage Layout Configuration. |
Database Groups Configuration
Starting from EMQX 6.0.2, Durable Storage introduces database groups to support node-level resource governance. Database groups enable multiple durable storage databases to be managed together with shared resource limits, without modifying their logical data models.
By default, each durable storage database belongs to a database group named after the database itself, and each such group contains only that single database, preserving the behavior of earlier releases.
Database groups are configured under the durable_storage.db_groups namespace.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
durable_storage.db_groups.<group>.storage_quota | Soft quota for total SST file disk usage of the group. |
durable_storage.db_groups.<group>.write_buffer_size | Maximum combined RocksDB memtable size for the group. |
durable_storage.db_groups.<group>.rocksdb_nthreads_high | Number of high-priority RocksDB background threads. |
durable_storage.db_groups.<group>.rocksdb_nthreads_low | Number of low-priority RocksDB background threads. |
Buffering
EMQX writes MQTT messages from clients to the durable storage in batches to maximize the throughput. Batching is configured using the following parameters under durable_storage.<DS>.transaction configuration sub-tree:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
max_pending | Flushes the buffer once it accumulates this specified number of messages. |
flush_interval | Flushes the buffer at this time interval if it contains at least one message. |
idle_flush_interval | Flushes the buffer early if no new messages arrive within this interval. |
Storage Layout Configuration
Storage layout determines how EMQX organizes data on disk. Setting durable_storage.<DS>.layout.type parameter can change the layout used by the new generations. This change does not affect existing generations. The configuration of each layout type varies and is contained under the durable_storage.<DS>.layout sub-tree. Currently, the wildcard_optimized layout type is available.
Configuration of wildcard_optimized Layout Type
The wildcard_optimized layout is aimed at optimizing wildcard subscriptions matching a large number of MQTT topics. It achieves this by autonomously accumulating knowledge about topic structures over time. Leveraging a lightweight machine learning algorithm, it predicts the wildcard topic filters that clients are likely to subscribe to. Subsequently, it organizes these topics into a unified stream, allowing efficient consumption in a single sweep.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
bytes_per_topic_level | Determines the size of the topic-level hash. |
topic_index_bytes | Specifies the size of the stream identifier in bytes. |
CLI Commands
The following CLI commands are available for managing the durable storage:
emqx ctl ds info
Displays an overview of the durable storage state.
Example:
$ emqx ctl ds info
THIS SITE:
D8894F95DC86DFDB
SITES:
.------------------.-------------------.----------.
: Site : Node : Status :
:------------------:-------------------:----------:
: 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : 'emqx@n2.local' : up :
: D8894F95DC86DFDB : 'emqx@n1.local' : up :
: F4E92DEA197C8EBC : 'emqx@n3.local' : (x) down :
`------------------`-------------------`----------`
SHARDS:
.-------------.------------------.-------------.
: DB/Shard : Replicas : Transitions :
:-------------:------------------:-------------:
:-messages/0--:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/1--:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/10-:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/11-:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/12-:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/2--:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/3--:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/4--:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/5--:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/6--:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/7--:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/8--:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
:-messages/9--:------------------:-------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : :
`-------------`------------------`-------------`This command output includes:
THIS SITE: ID of the site claimed by the local EMQX node.SITES: List of all known sites, including EMQX node names and their statuses.SHARDS: List of durable storage shards and site IDs where their replicas are located.
emqx ctl ds set-replicas all <site1> <site2> ...
This command allows to set the list of sites containing replicas of the durable storage in the cluster. Once executed, it creates a plan of operations that leads to fair allocation of the shards between the sites, and then continues to execute it in the background.
Important Notice
Updating the list of durable storage replicas can be costly as it may involve copying large volumes of data between sites.
Example:
$ emqx ctl ds set-replicas all 5C6028D6CE9459C7 D8894F95DC86DFDB F4E92DEA197C8EBC
okAfter executing this command, the output of ds info may look like this:
$ emqx ctl ds info
THIS SITE:
D8894F95DC86DFDB
SITES:
.------------------.-------------------.----------.
: Site : Node : Status :
:------------------:-------------------:----------:
: 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : 'emqx@n2.local' : up :
: D8894F95DC86DFDB : 'emqx@n1.local' : up :
: F4E92DEA197C8EBC : 'emqx@n3.local' : up :
`------------------`-------------------`----------`
SHARDS:
.-------------.------------------.--------------------.
: DB/Shard : Replicas : Transitions :
:-------------:------------------:--------------------:
:-messages/0--:------------------:--------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : D8894F95DC86DFDB : :
:-messages/1--:------------------:--------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : D8894F95DC86DFDB : :
:-messages/10-:------------------:--------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : : + D8894F95DC86DFDB :
:-messages/11-:------------------:-------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : D8894F95DC86DFDB : :
:-messages/2--:------------------:--------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : D8894F95DC86DFDB : :
:-messages/3--:------------------:--------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : : + D8894F95DC86DFDB :
:-messages/4--:------------------:-------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : D8894F95DC86DFDB : :
:-messages/5--:------------------:--------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : D8894F95DC86DFDB : :
:-messages/6--:------------------:--------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : : + D8894F95DC86DFDB :
:-messages/7--:------------------:-------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : D8894F95DC86DFDB : :
:-messages/8--:------------------:--------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : D8894F95DC86DFDB : :
:-messages/9--:------------------:--------------------:
: : 5C6028D6CE9459C7 : + F4E92DEA197C8EBC :
: : : + D8894F95DC86DFDB :
`-------------`------------------`--------------------`The new section REPLICA TRANSITIONS lists pending operations. Once all operations are complete, this list will be empty.
emqx ctl ds join all <site> / emqx ctl ds leave all <Site>
These commands add or remove a site from the list of replicas of the durable storage. They are similar to the set_replicas command but update one site at a time.
Example:
$ emqx ctl ds join all B2A7DBB2413CD6EE
okFor more detailed information, see Add Sites and Remove Sites.
REST API
The following REST API endpoints are available for managing and monitoring the built-in durable sessions:
/ds/sites: Lists known sites./ds/sites/:site: Provides information about a site (status, current EMQX node name managing the site, etc.)./ds/storages: Lists durable storage./ds/storages/:ds: Provides information about the durable storage and its shards./ds/storages/:ds/replicas: Lists or updates sites containing replicas of durable storage./ds/storages/:ds/replicas/:site: Adds or removes a replica of the durable storage on a site.
See EMQX OpenAPI schema for more information.
Metrics
The following Prometheus metrics are relevant to durable sessions:
emqx_ds_egress_batches
Increments each time a batch of messages is successfully written to durable storage.
emqx_ds_egress_messages
Counts messages successfully written to durable storage.
emqx_ds_egress_bytes
Counts the total volume of payload data successfully written to durable storage. Note: This metric only considers message payloads, so the actual volume of data written may be larger.
emqx_ds_egress_batches_failed
Increments each time writing data to durable storage fails for any reason.
emqx_ds_egress_flush_time
A rolling average of time (in μs) spent writing batches to durable storage. It's a key indicator of replication speed.
emqx_ds_store_batch_time
A rolling average of time (in μs) spent writing batches to the local RocksDB storage. Unlike emqx_ds_egress_flush_time, it excludes network replication costs, making it a key indicator of disk I/O efficiency.
emqx_ds_builtin_next_time
A rolling average of time (in μs) spent consuming a batch of messages from durable storage.
emqx_ds_storage_bitfield_lts_counter_seek and emqx_ds_storage_bitfield_lts_counter_next
These counters are specific to the "wildcard optimized" storage layout. They measure the efficiency of consuming data from local storage. The seek primitive is generally slower, so the rate of emqx_ds_storage_bitfield_lts_counter_next should ideally grow faster than seek.
Increasing the durable_storage.messages.layout.epoch_bits parameter can help improve this ratio.
emqx_ds_raft_db_shards_num
The number of shards the DB is split into.
emqx_ds_raft_db_sites_num
This gauge tracks the number of current and assigned sites a DS DB is replicated across.
Most of the time, the number of current sites is equal to the number of assigned sites. If the current stays different from the assigned for a long time, something is likely wrong with the replica transfers.
emqx_ds_raft_shard_replication_factor
Tracks the number of replicas in the replica set of a DS DB shard.
If this number falls below the configured and expected replication factor, durability is at risk. Consider rebalancing replicas across more sites.
emqx_ds_raft_db_shards_online_num
Tracks the number of DS DB shards actively managed on this node.
This number should be equal to the number of shards currently assigned to this node. If this is not the case, availability might be compromised. Check the logs for details.
emqx_ds_raft_shard_transition_queue_len
Tracks the number of pending replica set transitions for a DS DB shard.
If this number stays non-zero for a long time, something is wrong with the replica transfers.
emqx_ds_raft_shard_transitions
Counts the number of started / completed / skipped / crashed replica set transitions of a DB shard.
Crashed transitions should always be zero. If this is not the case, consider checking the logs for errors.
emqx_ds_raft_shard_transition_errors
Counts the number of transient errors that occurred during the orchestration of replica set transitions of a DB shard.
If this counter grows, something is wrong with the replica transfers. Consider checking the logs for errors.
emqx_ds_raft_snapshot_reads
Counts the number of started / completed snapshot reads for a DS DB shard, when a shard was the source of snapshot replication.
emqx_ds_raft_snapshot_read_errors
Counts the number of errors that occurred during reading the snapshot on the source DS DB shard, which caused snapshot replication to be aborted.
Errors are not expected to happen. Look for possible reasons in the logs.
emqx_ds_raft_snapshot_read_chunks
Counts the number of individual chunks read on the DS DB shard acting as a source of snapshot transfer, and later transferred to the recipient.
emqx_ds_raft_snapshot_read_chunk_bytes
Counts the number of bytes read as chunks on the source DS DB shard.
emqx_ds_raft_snapshot_writes
Counts the number of started / completed snapshot writes for a DS DB shard when a shard was the recipient of snapshot replication.
emqx_ds_raft_snapshot_write_errors
Counts the number of errors that occurred during writing the snapshot to the recipient DS DB shard, which caused snapshot replication to be aborted.
This is also not expected to grow. Consider checking the logs for details.
emqx_ds_raft_snapshot_write_chunks
Counts the number of individual chunks received from the source DS DB shard and written to the recipient.
emqx_ds_raft_snapshot_write_chunk_bytes
Counts the number of bytes written as chunks on the recipient DS DB shard.
emqx_ds_raft_current_timestamp_us
Tracks the latest operation timestamp currently replicated by a shard server (in microseconds).
Normally, each replica should always have the same timestamp. If this is not the case, something is wrong with the replication.
emqx_ds_raft_rasrv_state_changes
Counts the number of times the Raft server turned into a candidate / follower / leader.
Frequent state changes are a sign of instability. Consider checking the logs for details.
Database Group Metrics
The following Prometheus metrics provide node-level visibility into durable storage database groups:
emqx_ds_disk_usage
Total size of SST files used by all databases in the group.
emqx_ds_write_buffer_memory_usage
Total RocksDB memtable memory used by the group.
emqx_ds_total_trash_size
Disk usage of obsolete SST files pending deletion.
These metrics are reported per node and per database group. In clustered deployments, operators may aggregate metrics externally to assess cluster-wide capacity.