Access EMQX Cluster through LoadBalancer
Objective
Access the EMQX cluster through a Service of type LoadBalancer.
Configure EMQX Cluster
EMQX CRD apps.emqx.io/v2 supports:
- Configuring the EMQX Dashboard Service through
.spec.dashboardServiceTemplate. - Configuring the EMQX cluster listener Service through
.spec.listenersServiceTemplate.
Refer to the respective documentation for more details.
Save the following as a YAML file and deploy it using
kubectl apply.yamlapiVersion: apps.emqx.io/v2 kind: EMQX metadata: name: emqx spec: image: emqx/emqx:6.1.1 config: data: | license { key = "..." } listenersServiceTemplate: spec: type: LoadBalancer dashboardServiceTemplate: spec: type: LoadBalancerTIP
By default, EMQX starts an MQTT TCP listener
tcp-defaulton port 1883 and a Dashboard HTTP listener on port 18083.Users can configure new or existing listeners through
.spec.config.data, or manage them through the EMQX Dashboard.EMQX Operator automatically reflects the default listener information in the Service resources. When there is a conflict between the Service configured by the user and the listener configured by EMQX (name or port fields are repeated), EMQX Operator prioritizes the user configuration.
Wait for the EMQX cluster to become ready.
Check the status of the EMQX cluster with
kubectl getand make sure thatSTATUSisReady. This may take some time.bash$ kubectl get emqx emqx NAME STATUS AGE emqx Ready 10m
Add New Listener through EMQX Dashboard
Add a new listener.
Open the EMQX Dashboard and navigate to Management -> Listeners.
Click the Add Listener to add a new listener with the name
testand port1884, as shown in the following figure: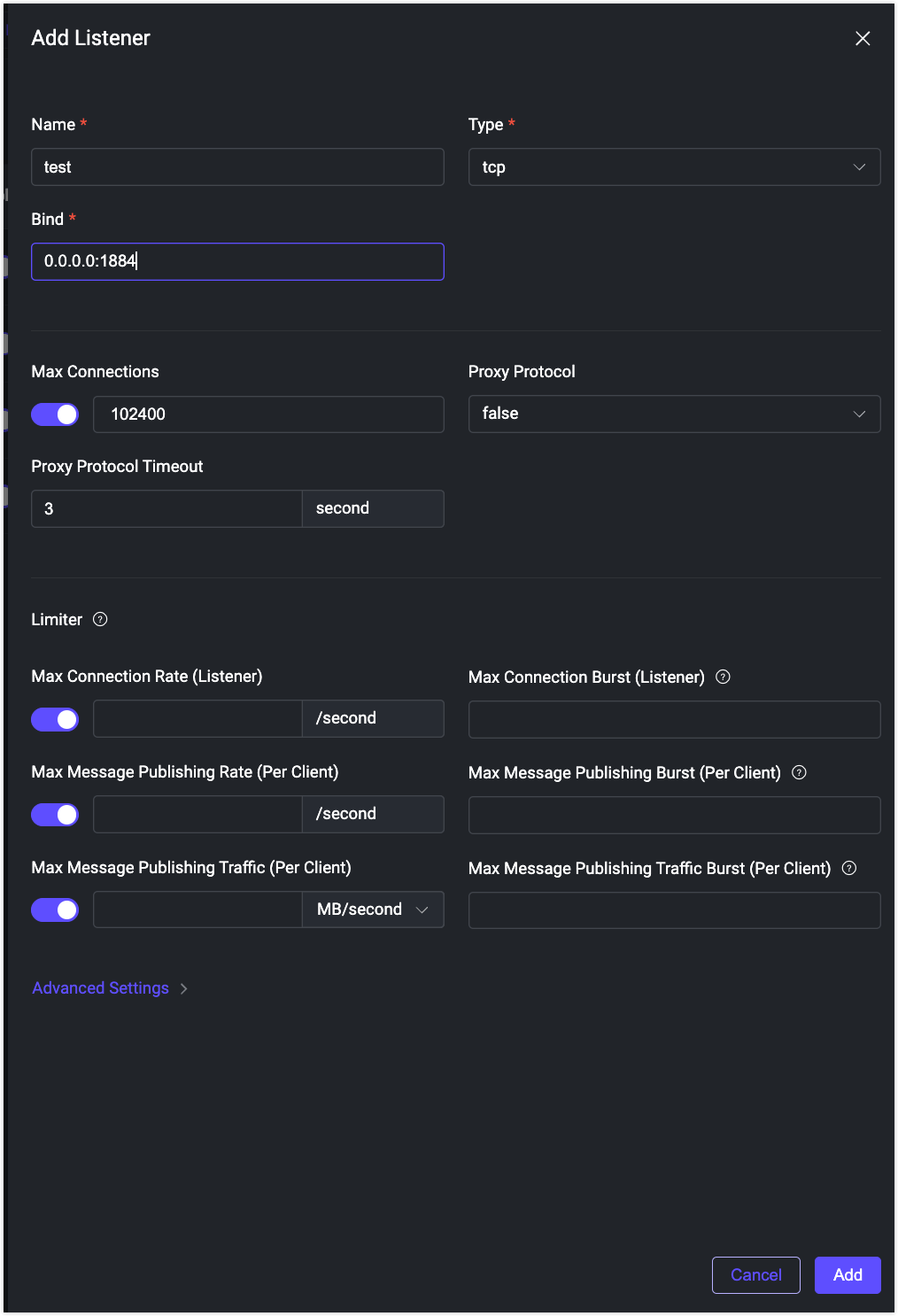
Click Add to create the listener. As shown in the following figure, the new listener has been created.
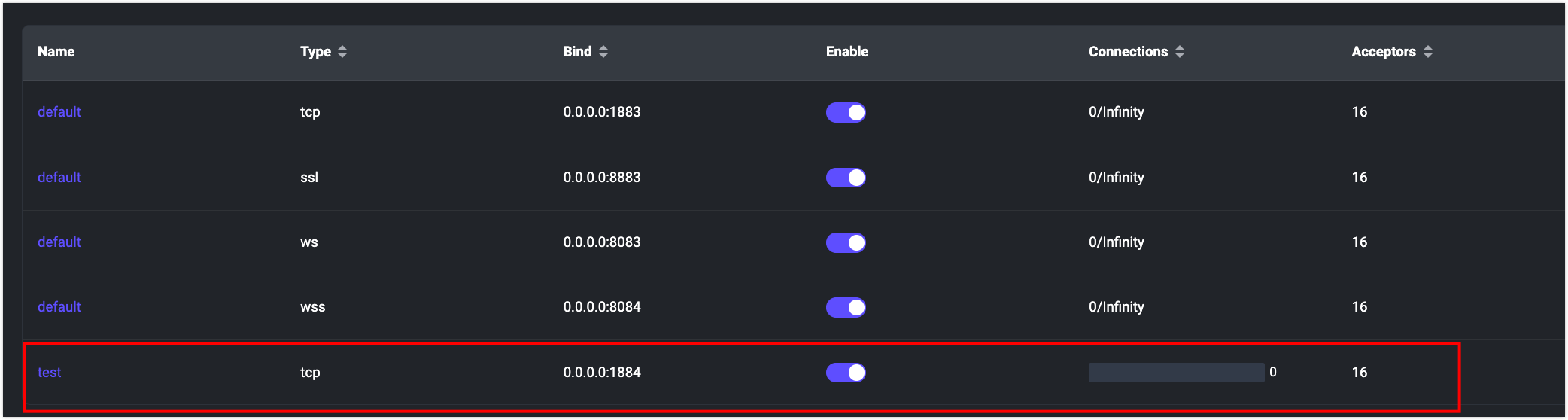
Check if the new listener is reflected in the Service.
bashkubectl get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE emqx-dashboard NodePort 10.105.110.235 <none> 18083:32012/TCP 13m emqx-listeners NodePort 10.106.1.58 <none> 1883:32010/TCP,1884:30763/TCP 12mThis output shows that the newly added listener on port 1884 has been reflected in the
emqx-listenersService resource.
Connect to the New Listener Using MQTTX
Obtain the external IP of the EMQX listeners service.
bashexternal_ip=$(kubectl get svc emqx-listeners -o json | jq -r '.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip')Connect to the new listener using MQTTX CLI.
bash$ mqttx conn -h ${external_ip} -p 1884 [4/17/2023] [5:17:31 PM] › … Connecting... [4/17/2023] [5:17:31 PM] › ✔ Connected