Enable Core + Replicant Cluster
Objective
- Configure EMQX cluster Core nodes through the
coreTemplatefield. - Configure EMQX cluster Replicant nodes through the
replicantTemplatefield.
Core and Replicant Nodes
Nodes in the EMQX cluster can have one of two roles: Core node and Replicant node.
- Core nodes are responsible for data persistence in the cluster and serve as the authoritative source for shared cluster state such as routing tables, MQTT client channels, retained messages, cluster configuration, alarms, Dashboard user credentials, etc.
- Replicant nodes are designed to be stateless and do not participate in database operations. Adding or deleting Replicant nodes will not affect the redundancy of the cluster data.
Communication between Core and Replicant nodes in a typical EMQX cluster is illustrated in the following diagram:
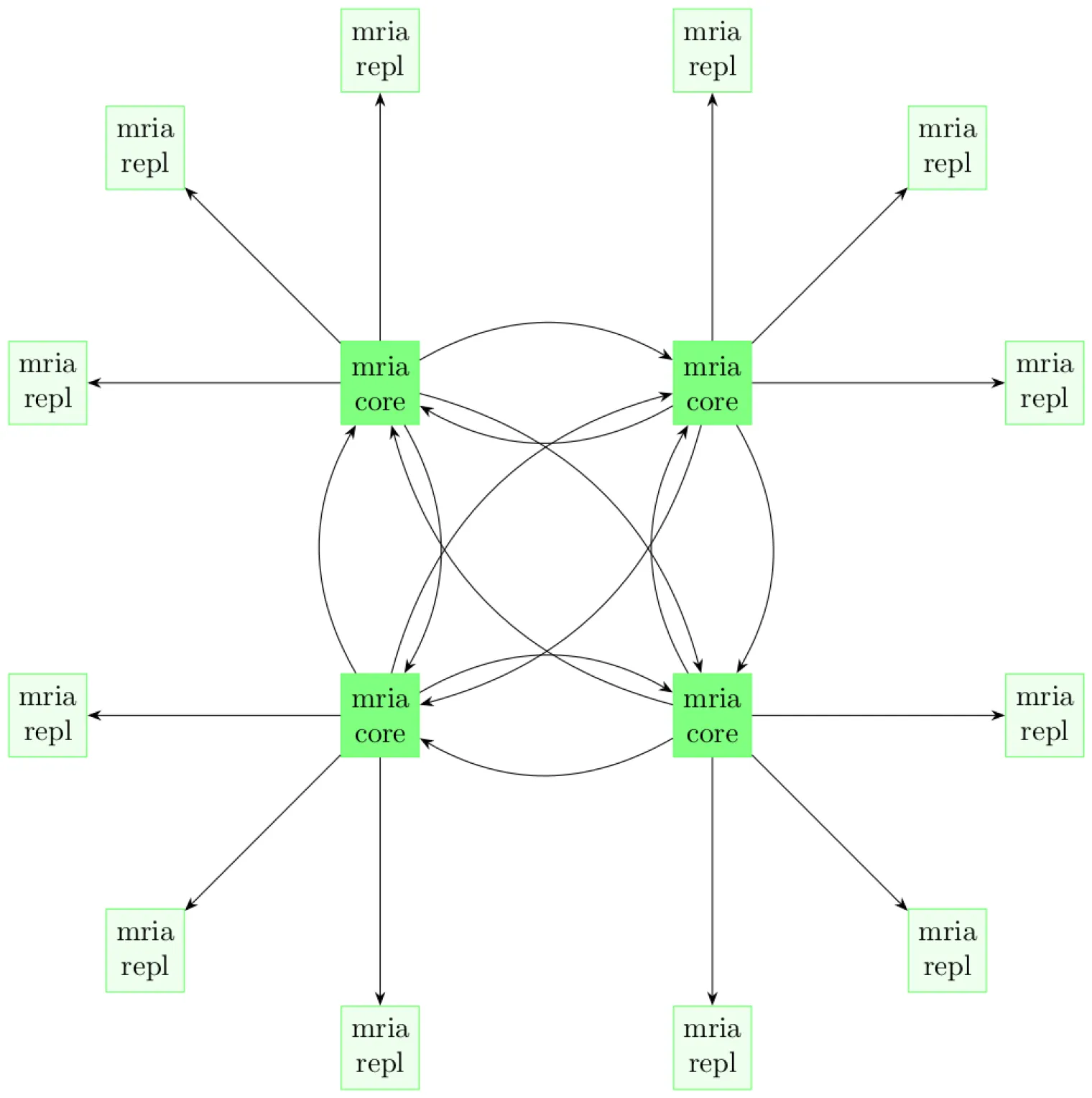
For more information about the EMQX Core-Replicant architecture, refer to the Cluster Architecture documentation.
TIP
There must be at least one Core node in the EMQX cluster. For the purpose of high availability, EMQX Operator recommends that the EMQX cluster have at least three Core nodes.
Configure EMQX Cluster
EMQX CRD apps.emqx.io/v2 supports configuring Core nodes of the EMQX cluster through the .spec.coreTemplate field, and configuring Replicant nodes of the EMQX cluster through the .spec.replicantTemplate field.
Save the following content as a YAML file and deploy using
kubectl apply.yamlapiVersion: apps.emqx.io/v2 kind: EMQX metadata: name: emqx spec: image: emqx/emqx:6.1.1 config: data: | license { key = "..." } coreTemplate: spec: replicas: 2 resources: requests: cpu: 250m memory: 512Mi replicantTemplate: spec: replicas: 3 resources: requests: cpu: 250m memory: 1Gi dashboardServiceTemplate: spec: type: LoadBalancerIn the example above, the EMQX CR defines an EMQX cluster consisting of two Core nodes and three Replicant nodes.
Core nodes require a minimum of 512Mi of memory, and Replicant nodes require a minimum of 1Gi of memory. You can adjust these constraints according to the actual business load. Typically, Replicant nodes accept all client requests, so the resources required by Replicant nodes may be higher to accommodate many concurrent connections.
Wait for the EMQX cluster to become ready. Check the status of the EMQX cluster with
kubectl get, ensuring thatSTATUSisReady. This may take some time.bash$ kubectl get emqx emqx NAME STATUS AGE emqx Ready 10m
Verify EMQX Cluster
You can view information about all nodes in the cluster by checking the .status field of the EMQX CR.
$ kubectl get emqx emqx -o json | jq .status.coreNodes
[
{
"name": "emqx@emqx-core-adcdef012-0.emqx-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"podName": "emqx-core-adcdef012-0",
"status": "running",
"otpRelease": "27.3.4.2-6/15.2.7.1",
"role": "core",
"version": "6.1.1",
"sessions": 0,
"connections": 0
},
{
"name": "emqx@emqx-core-adcdef012-1.emqx-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"podName": "emqx-core-adcdef012-1",
"status": "running",
"otpRelease": "27.3.4.2-6/15.2.7.1",
"role": "core",
"version": "6.1.1",
"sessions": 0,
"connections": 0
}
]$ kubectl get emqx emqx -o json | jq .status.replicantNodes
[
{
"name": "emqx@10.244.4.56",
"podName": "emqx-replicant-adcdef012-0",
"status": "running",
"otpRelease": "27.3.4.2-6/15.2.7.1",
"role": "replicant",
"version": "6.1.1",
"sessions": 42,
"connections": 42
},
{
"name": "emqx@10.244.4.57",
"podName": "emqx-replicant-adcdef012-1",
"status": "running",
"otpRelease": "27.3.4.2-6/15.2.7.1",
"role": "replicant",
"version": "6.1.1",
"sessions": 11,
"connections": 11
},
{
"name": "emqx@10.244.4.58",
"podName": "emqx-replicant-adcdef012-2",
"status": "running",
"otpRelease": "27.3.4.2-6/15.2.7.1",
"role": "replicant",
"version": "6.1.1",
"sessions": 13,
"connections": 13
}
]