Quick Start: Create a Flow Using Gemini Node
This section demonstrates how to quickly create and test an LLM-based Flow in the Flow Designer through a practical use case using the Gemini Node.
This example demonstrates how to build a Flow that integrates with the Gemini LLM to process MQTT device messages using dynamic input context, such as clientid and payload.type, by constructing a natural language prompt from multiple parameters. It breaks the limitation of single-field LLM input, enabling more flexible and context-aware AI processing. The workflow receives command-type messages from devices, generates a formatted response via the LLM, and republishes the result to a client-specific topic for further handling.
Scenario Description
Assume a device reports a command request to the MQTT topic commands/inbox/<clientid>. Each message includes a command type, such as restart, in JSON format. The EMQX Flow will perform the following steps:
- Data Processing: Build a prompt that includes the client ID and requested command type contained in the message payload.
- LLM-Based Processing: Use a Gemini-compatible model to generate an action instruction based on the request.
- Message Republish: Publish the AI-generated result to a topic such as
device/<clientid>/command.
Sample message:
{
"type": "restart"
}Expected output (AI-generated):
action:restart;client:clientidCreate the Flow
Prerequisite
Make sure you have a valid Gemini API Key.
Click the Create Flow button on the Flows page.
Add a Messages node.
- Drag a Messages node from the Source panel.
- Set the topic to
commands/inbox/+. - Click Save.
Add a Data Processing node.
Drag a Data Processing node from the Processing section.
Fill in the transformation form with the following configurations. These transformations construct a readable natural language prompt that includes the MQTT client ID and the requested action type that will be contained in the message payload. This prompt will be sent to the Gemini LLM for processing.
Concatenate
Clientandclientidinto a base string. Creates the beginning of the prompt by identifying the client.- Field:
clientid - Transform: Select
String Functions->concat - Alias:
base - String1:
Client(include a space after the word) - String2:
clientid
- Field:
Concatenate
baseandrequestedintobase2. Adds the verb to indicate the action being requested.- Field:
base - Transform:
concat - Alias:
base2 - String1:
base - String2:
requested(include a space before and after the word)
- Field:
Concatenate
base2andpayload.typeintoprompt. Completes the full sentence for the LLM prompt.Field:
base2Transform:
concatAlias:
promptString1:
base2String2:
payload.type
Example prompt result
If a client with ID
device123sends a message with payload{ "type": "restart" }, the resulting prompt will be:Client device123 requested restartExpose
clientidfor later use to ensures that it is accessible in downstream nodes (e.g., for${clientid}in republish topics).Field:
clientidTransform: Leave empty
Alias:
clientid
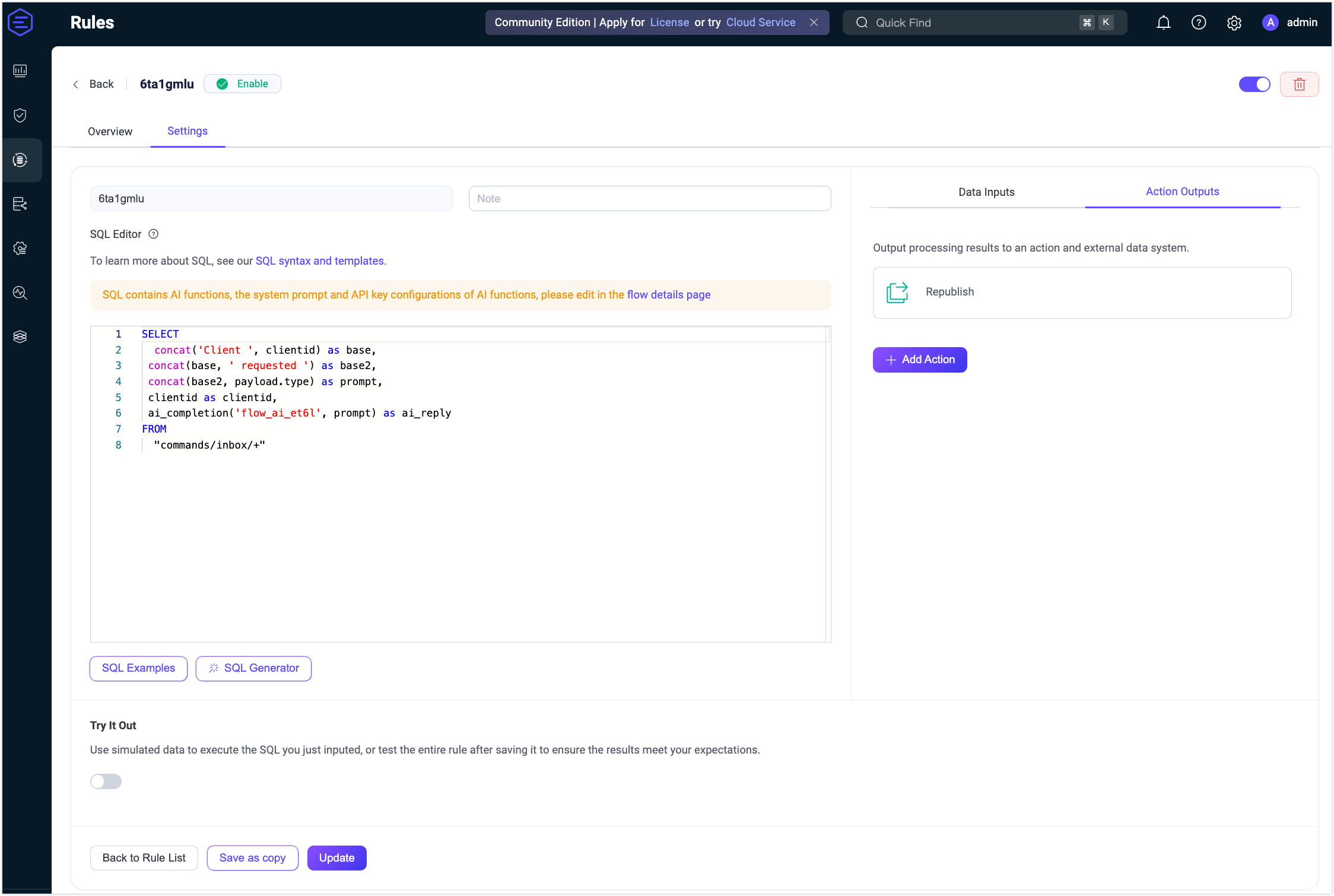
Click Switch to SQL. You should see a SQL expression similar to:
sqlconcat('Client ', clientid) as base, concat(base, ' requested ') as base2, concat(base2, payload.type) as prompt, clientid as clientidTIP
The
clientidandpayload.typeshould not be wrapped in quotes or treated as string literals. They are field references, and quoting them would cause the rule to treat them as plain text instead of extracting their actual values from the message.Click Save.
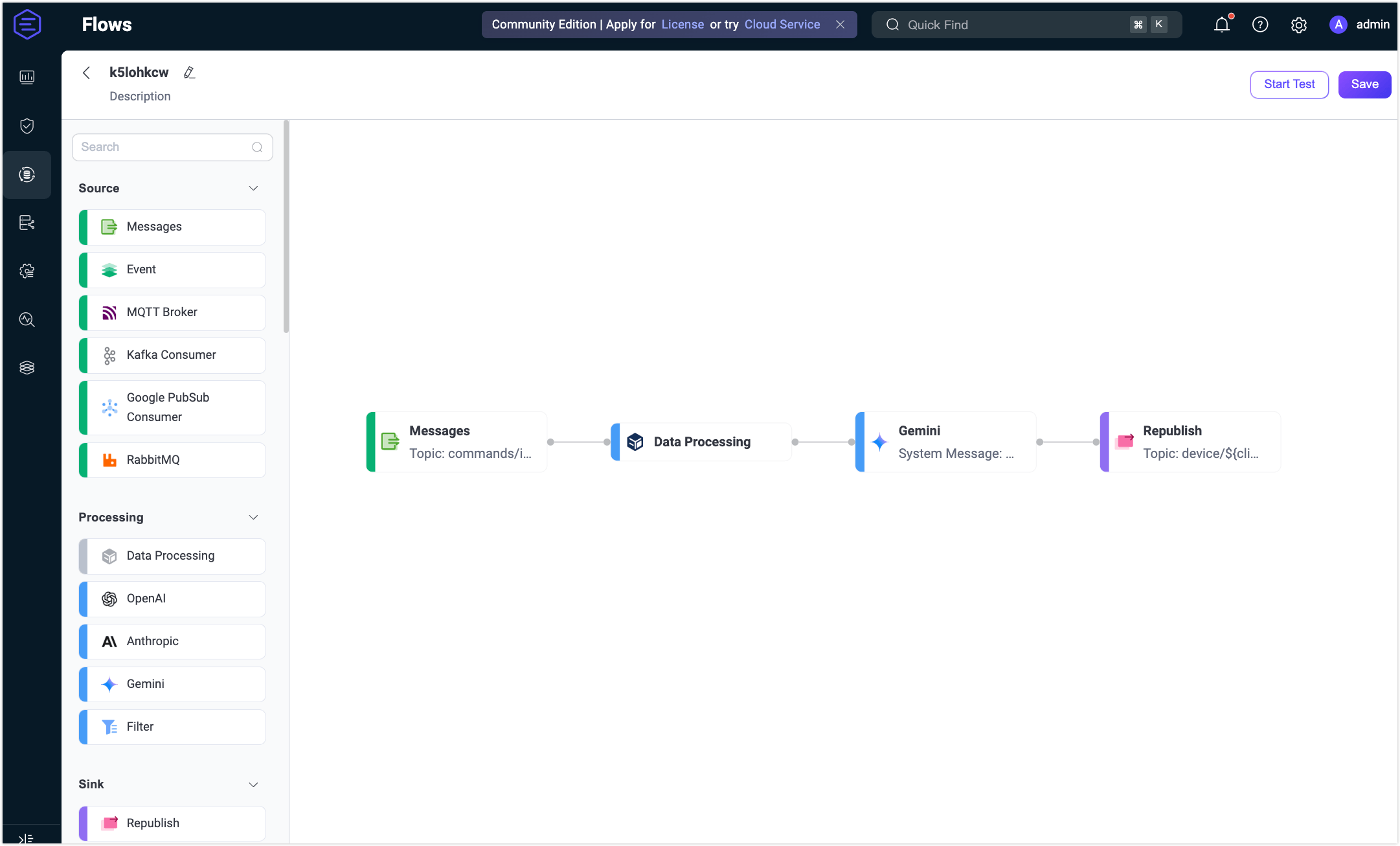
Add a Gemini node.
Drag a Gemini node from the Processing section and connect it to the Data Processing node.
Configure the node:
Input: Enter
prompt.System Message: Enter the following message:
You are a device command formatter. Generate a short command in this format: action:<type>;client:<clientid> Only return a single line, no Markdown or extra formatting.Model: Here you can keep the default model
gemini-2.0-flash.API Key: Enter your Gemini API key.
Base URL: Leave empty to use Gemini’s default endpoint.
Output Result Alias: Enter
ai_reply.
Click Save.
Add a Republish node.
- Drag a Republish node from the Sink section and connect it to the Gemini node.
- Set the topic to
device/${clientid}/command. - Set the payload to
${ai_reply}. - Click Save.
Connect all the nodes and click Save in the upper-right corner to save the Flow.
Flows and form rules are interoperable. You can also view the SQL and related rule configurations on the Rule page.
Test the Flow
Connect an MQTT client to EMQX.
To quickly test the flow, you can use the Diagnostic Tools -> WebSocket Client on the Dashboard to simulate an MQTT client. Alternatively, you can also use the MQTTX tool or a real MQTT client:
- Connect to your EMQX server.
- Subscribe to the topic, for example
device/c_emqx/command.
Start Testing.
In the Flow Designer, click any node to open the Edit panel.
Click Edit, then click Start Test to open the test panel at the bottom.
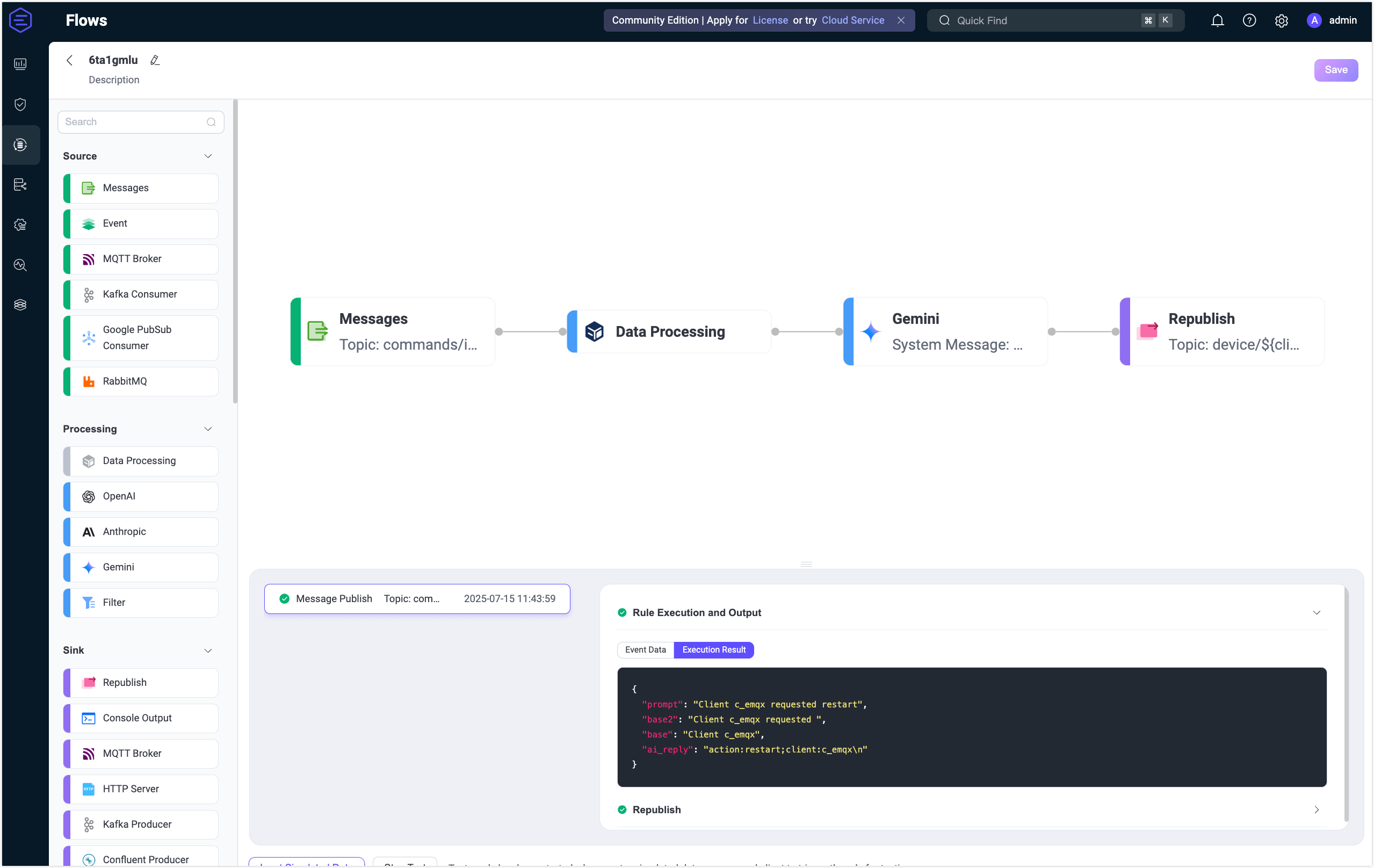
Click Input Simulated Data and publish this message to topic
commands/inbox/c_emqxby clicking Submit Test:json{ "type": "restart" }
Review results.
You can see the successful execution result of the flow.
Return to the WebSocket Client page and you should receive an AI-generated summary like:
“action:restart;client:c_emqx”
If the test results are unsuccessful, error messages will be displayed accordingly.
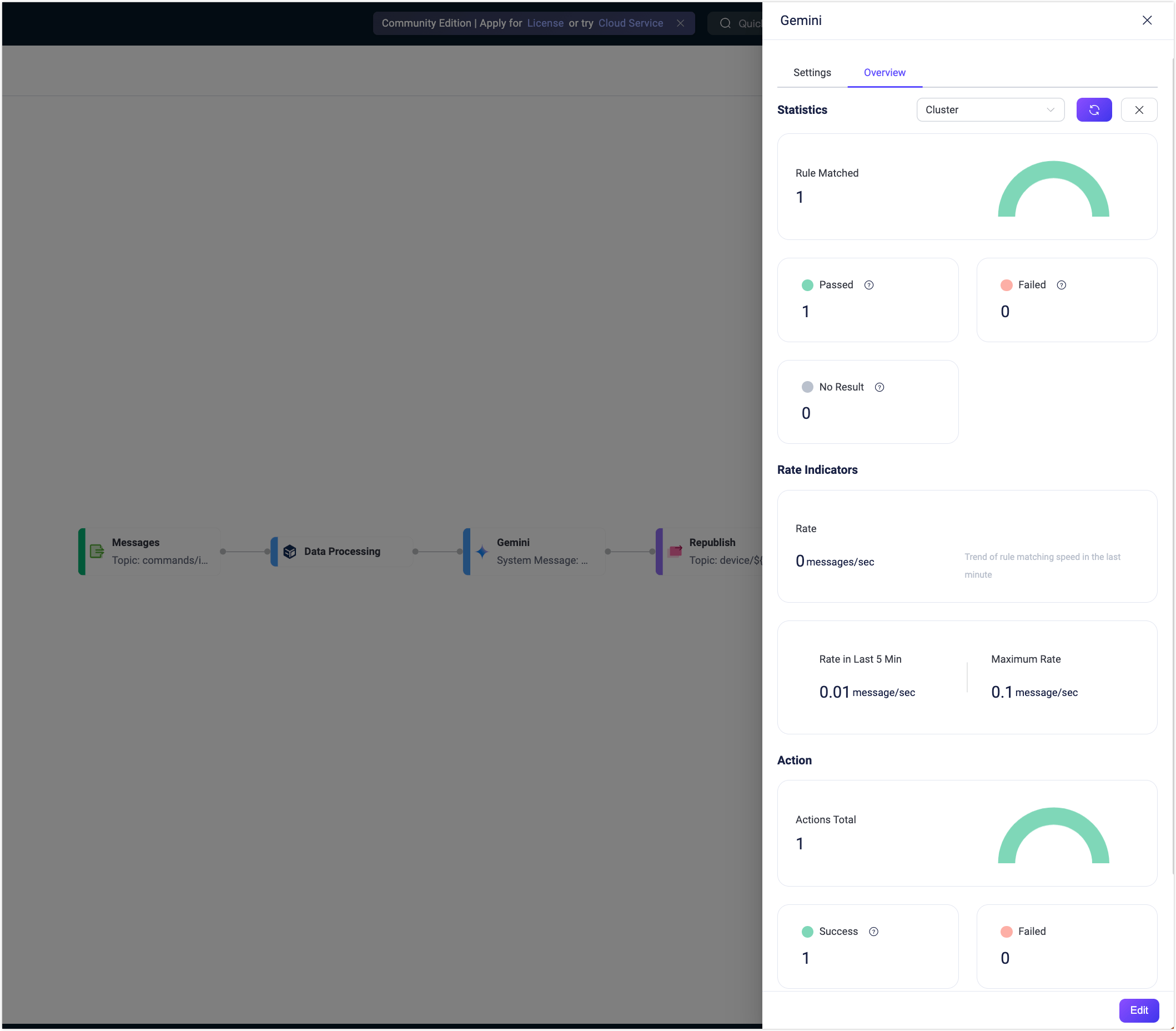
To view the running statistics and metrics of the Gemini node, exit the editing page, click the node to open the Edit panel and click the Overview tab.