Enable Persistence in EMQX Cluster
Objective
Configure persistence for the set of Core nodes of an EMQX cluster through the volumeClaimTemplates field.
Configure EMQX Cluster Persistence
EMQX CRD apps.emqx.io/v2beta1 supports configuring persistence of each core node data through .spec.coreTemplate.spec.volumeClaimTemplates.
The definition and semantics of the .spec.coreTemplate.spec.volumeClaimTemplates field are consistent with those of PersistentVolumeClaimSpec defined in the Kubernetes API.
When you specify the .spec.coreTemplate.spec.volumeClaimTemplates field, EMQX Operator configures the /opt/emqx/data volume of the EMQX container to be backed by a Persistent Volume Claim (PVC), which provisions a Persistent Volume (PV) using a specified StorageClass. As a result, when an EMQX Pod is deleted, the associated PV and PVC are retained, preserving EMQX runtime data.
For more details about PVs and PVCs, refer to the Persistent Volumes documentation.
- Save the following content as a YAML file and deploy it using
kubectl apply.
apiVersion: apps.emqx.io/v2beta1
kind: EMQX
metadata:
name: emqx
spec:
image: emqx/emqx:6.1.1
config:
data: |
license {
key = "..."
}
coreTemplate:
spec:
volumeClaimTemplates:
storageClassName: standard
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Mi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
replicas: 3
listenersServiceTemplate:
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
dashboardServiceTemplate:
spec:
type: LoadBalancerTIP
Use the storageClassName field to choose the appropriate StorageClass for EMQX data. Run kubectl get storageclass to list the StorageClasses that already exist in the Kubernetes cluster, or create a StorageClass according to your needs.
- Wait for the EMQX cluster to become ready.
Check the status of the EMQX cluster with kubectl get and ensure that STATUS is Ready. This may take some time.
$ kubectl get emqx emqx
NAME STATUS AGE
emqx Ready 10mVerify Persistence
- Create a test rule in the EMQX Dashboard.
external_ip=$(kubectl get svc emqx-dashboard -o json | jq -r '.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip')- Log in to the EMQX Dashboard at
http://${external_ip}:18083. - Navigate to Data Integration → Rules to create a new rule.
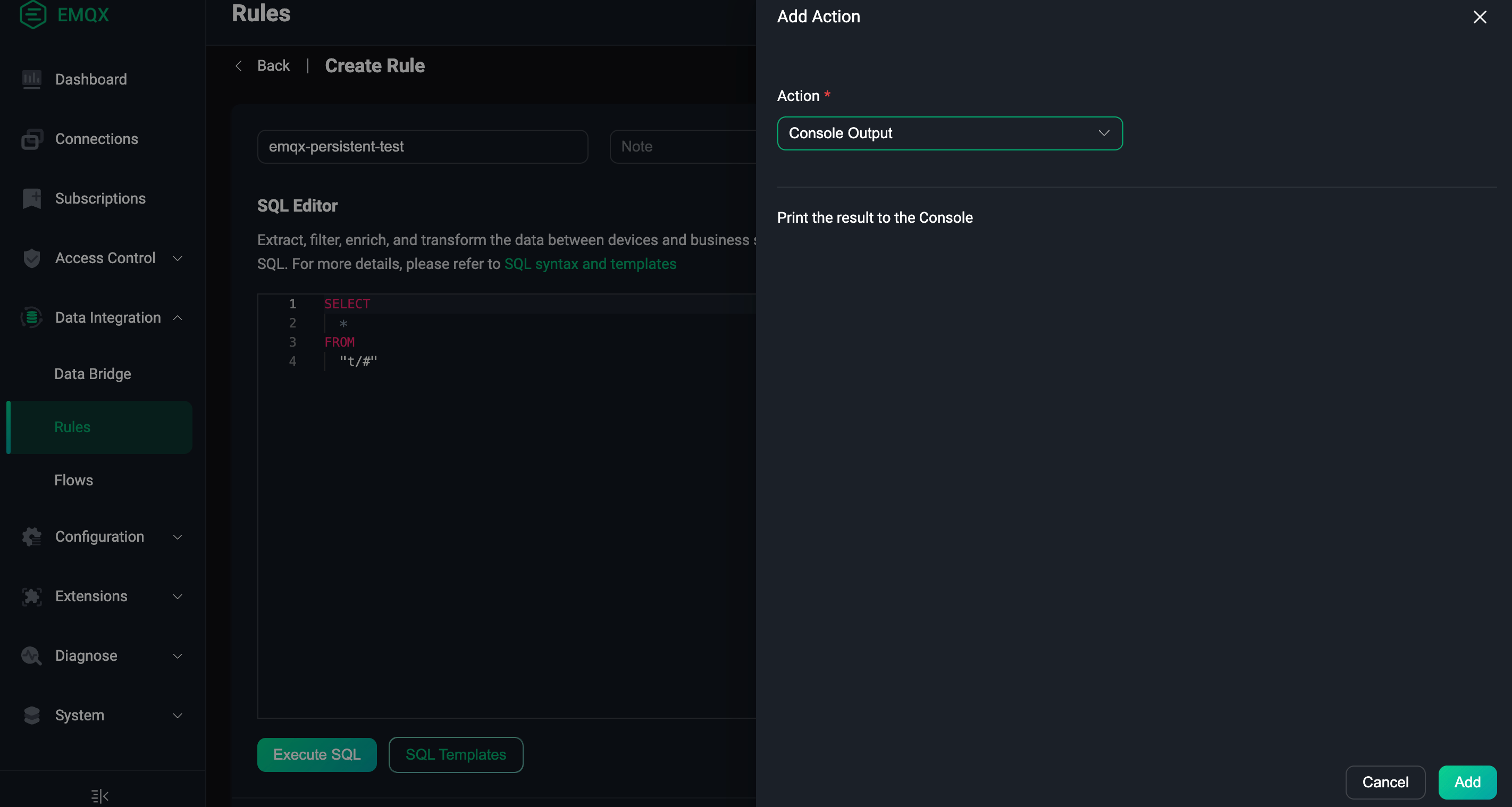
- Attach a simple action to this rule.
- Click Create to generate a rule, as shown in the following figure:
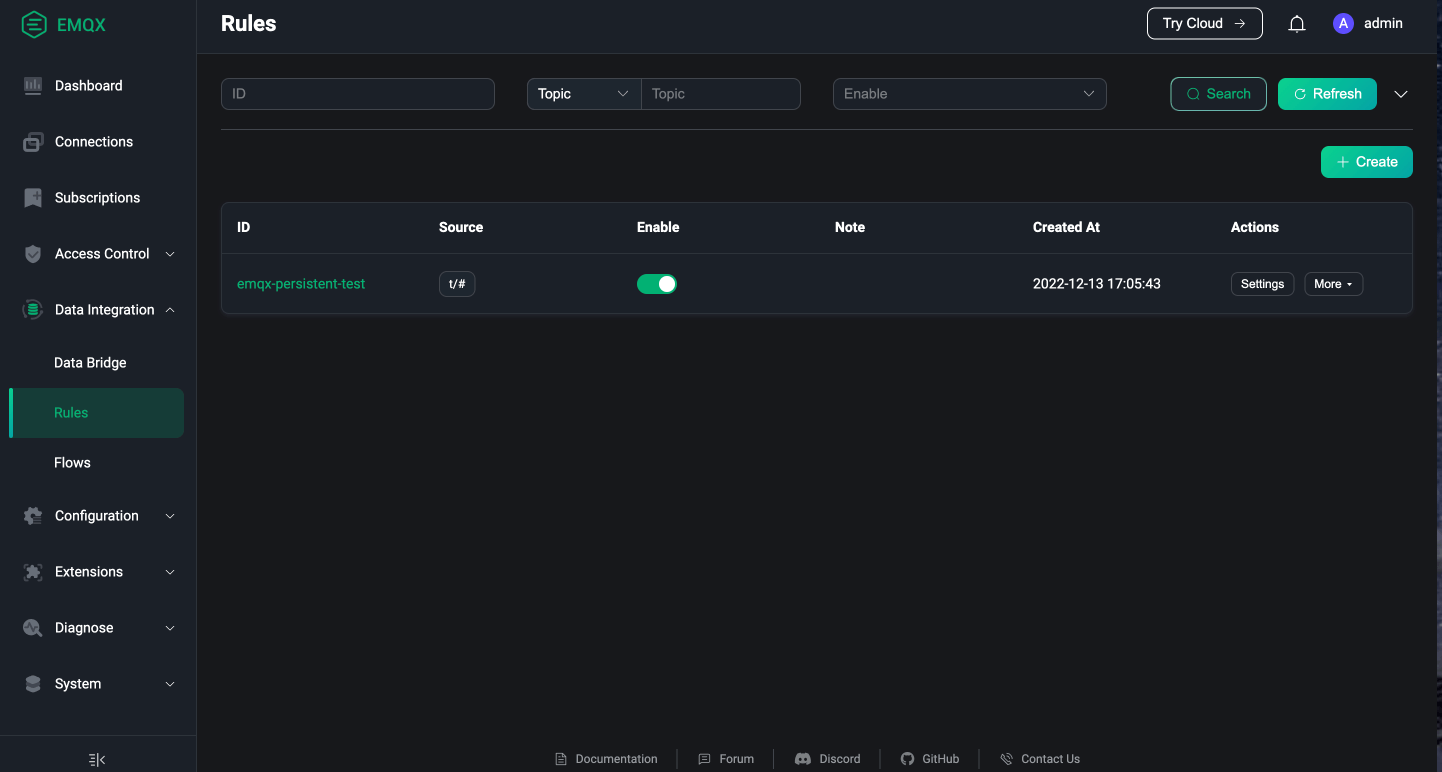
Once the rule is created successfully, a corresponding record with emqx-persistent-test ID will appear on the page, as shown in the figure below:
- Delete the old EMQX cluster.
Run the following command to delete the EMQX cluster, where emqx.yaml is the file you used to deploy the cluster earlier:
$ kubectl delete -f emqx.yaml
emqx.apps.emqx.io "emqx" deleted- Re-deploy the EMQX cluster.
Run the following command to re-deploy the EMQX cluster:
$ kubectl apply -f emqx.yaml
emqx.apps.emqx.io/emqx createdWait for the EMQX cluster to be ready. Access the EMQX Dashboard through your browser to verify that the previously created rule still exists, as shown in the following figure:
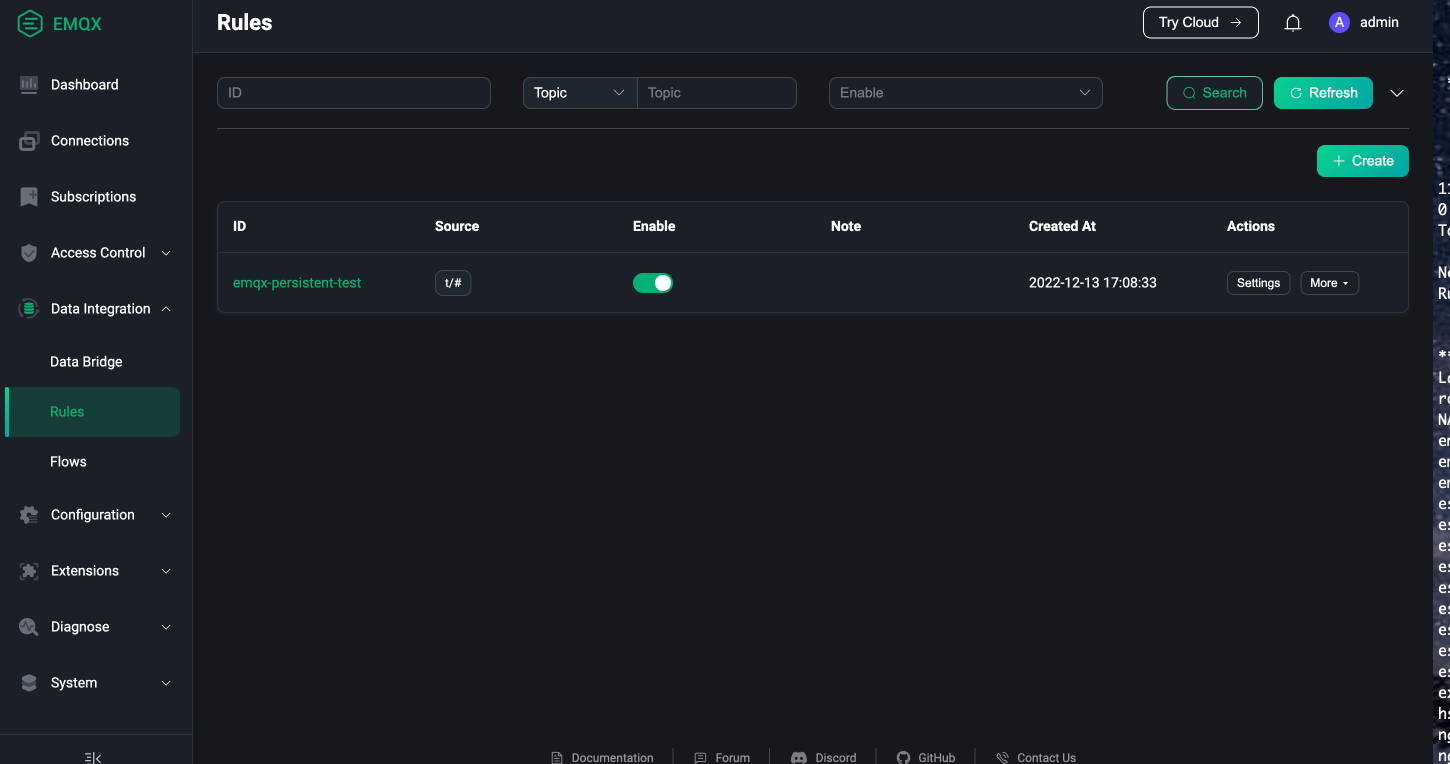
The emqx-persistent-test rule created in the old cluster still exists in the new cluster, which confirms that the persistence configuration is working correctly.