Perform Blue-Green Upgrade of EMQX Cluster
Objective
Perform a graceful upgrade of the EMQX cluster through blue-green deployment.
Background
In traditional EMQX cluster deployment, StatefulSet's default rolling upgrade strategy is usually used to update EMQX Pods. However, this approach has the following two problems:
- During the rolling update, both new and old Pods are selected by the corresponding Service. This may cause MQTT clients to connect to old Pods that are being terminated, resulting in frequent disconnections and reconnections.
- During the rolling update process, only N - 1 Pods can provide services at any given time because it takes some time for new Pods to start up and become ready. This may lead to a decrease in service availability.
Solution
EMQX Operator performs blue-green deployment by default. When an EMQX cluster is updated through the corresponding EMQX CR, EMQX Operator initiates an upgrade.
The entire upgrade process is roughly divided into the following steps:
- Create a set of new EMQX nodes with updated specifications.
- Redirect the Service resources to the new set of nodes once they are ready, ensuring that no new connections are routed to the old set.
- Safely migrate existing MQTT connections from the old set of nodes to the new set of nodes at a controlled rate to avoid reconnect storms.
- Gradually scale down the old set of EMQX nodes.
- Complete the upgrade.
Procedure
Configure the Update Strategy
- Create an
apps.emqx.io/v2beta1EMQX CR and configure the update strategy.
apiVersion: apps.emqx.io/v2beta1
kind: EMQX
metadata:
name: emqx-ee
spec:
image: emqx/emqx:6.1.1
config:
data: |
license {
key = "..."
}
updateStrategy:
evacuationStrategy:
# MQTT client evacuation rate, connections per second:
connEvictRate: 1000
# MQTT Session evacuation rate, sessions per second:
sessEvictRate: 1000
# Time to wait before deleting a Pod:
waitTakeover: 10
# Time to wait before starting the upgrade once all nodes are ready:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
type: Recreate- Save the above content as
emqx-update.yamland deploy it usingkubectl apply:
$ kubectl apply -f emqx-update.yaml
emqx.apps.emqx.io/emqx-ee created- Check the status of the EMQX cluster.
Make sure that STATUS is Ready. This may take a while.
$ kubectl get emqx
NAME STATUS AGE
emqx-ee Ready 8m33sConnect to EMQX Cluster
MQTTX is an open-source MQTT 5.0 compatible command line client tool that supports automatic reconnection, designed to help in development and debugging of MQTT services and applications.
Use MQTTX to connect to the EMQX cluster:
mqttx bench conn -h ${IP} -p ${PORT} -c 3000
[10:05:21 AM] › ℹ Start the connect benchmarking, connections: 3000, req interval: 10ms
✔ success [3000/3000] - Connected
[10:06:13 AM] › ℹ Done, total time: 31.113sTrigger the upgrade
- Any modifications made to the Pod template will trigger the upgrade strategy of EMQX Operator.
In this example, we trigger the upgrade by modifying the Pod's ImagePullPolicy.
$ kubectl patch emqx emqx-ee --type=merge -p '{"spec": {"imagePullPolicy": "Never"}}'
emqx.apps.emqx.io/emqx-ee patched- Check the status of the upgrade process.
$ kubectl get emqx emqx-ee -o json | jq ".status.nodeEvacuationsStatus"
[
{
"connection_eviction_rate": 200,
"node": "emqx-ee@emqx-ee-54fc496fb4-2.emqx-ee-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"session_eviction_rate": 200,
"session_goal": 0,
"connection_goal": 22,
"session_recipients": [
"emqx-ee@emqx-ee-5d87d4c6bd-2.emqx-ee-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"emqx-ee@emqx-ee-5d87d4c6bd-1.emqx-ee-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"emqx-ee@emqx-ee-5d87d4c6bd-0.emqx-ee-headless.default.svc.cluster.local"
],
"state": "waiting_takeover",
"stats": {
"current_connected": 0,
"current_sessions": 0,
"initial_connected": 33,
"initial_sessions": 0
}
}
]| Field | Description |
|---|---|
node | The node currently being evacuated. |
state | Node evacuation phase. |
session_recipients | MQTT session recipients. |
session_eviction_rate | MQTT session eviction rate on this node (sessions per second). |
connection_eviction_rate | MQTT connection eviction rate on this node (connections per second). |
initial_sessions | Initial number of sessions on this node. |
initial_connected | Initial number of connections on this node. |
current_sessions | Current number of sessions on this node. |
current_connected | Current number of connections on this node. |
- Wait for the upgrade to complete.
$ kubectl get emqx
NAME STATUS AGE
emqx-ee Ready 8m33sMake sure that the STATUS is Ready. Depending on the number of MQTT clients and sessions, the upgrade process may take a while.
After the upgrade is completed, you can verify that the old EMQX nodes have been deleted using kubectl get pods.
Grafana Monitoring
The following monitoring graph shows the number of connections during the upgrade process, using 10,000 connections as an example.
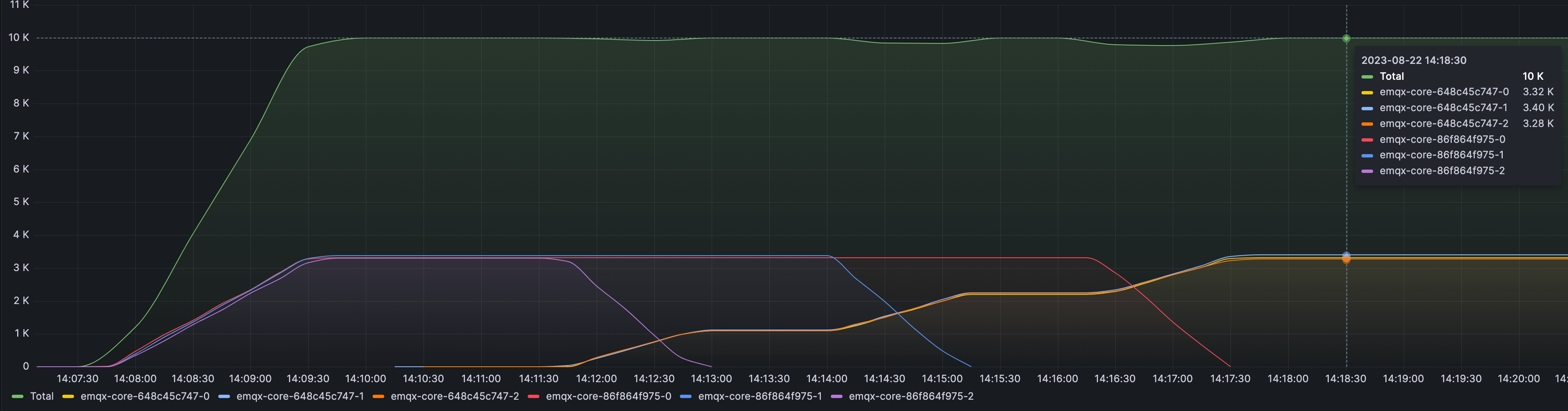
| Label/Prefix | Description |
|---|---|
| Total | Total number of connections; shown as the top line in the graph. |
emqx-ee-86f864f975 | Name prefix for the set of 3 old EMQX nodes. |
emqx-ee-648c45c747 | Name prefix for the set of 3 upgraded EMQX nodes. |
This timeline illustrates how EMQX Operator performs a smooth blue-green upgrade. Throughout the process, the total number of connections remained stable (subject to factors such as migration rate, server capacity, and client reconnection strategy). This approach ensures minimal disruption, prevents server overload, and enhances overall service stability.