Access IoT Devices Using the EMQX MCP Bridge
This guide describes how to use the EMQX MCP Bridge to integrate EMQX with MCP-enabled models or AI agents, enabling access to and control of IoT devices.
Prerequisites
EMQX server is installed and running, version 5.7.0 or later.
Install and Configure the MCP Bridge Plugin
Download the latest version of the MCP Bridge Plugin from https://github.com/emqx/emqx_mcp_bridge/releases
Install the plugin into the EMQX server by following the steps in Install Plugins.
Configure the plugin:
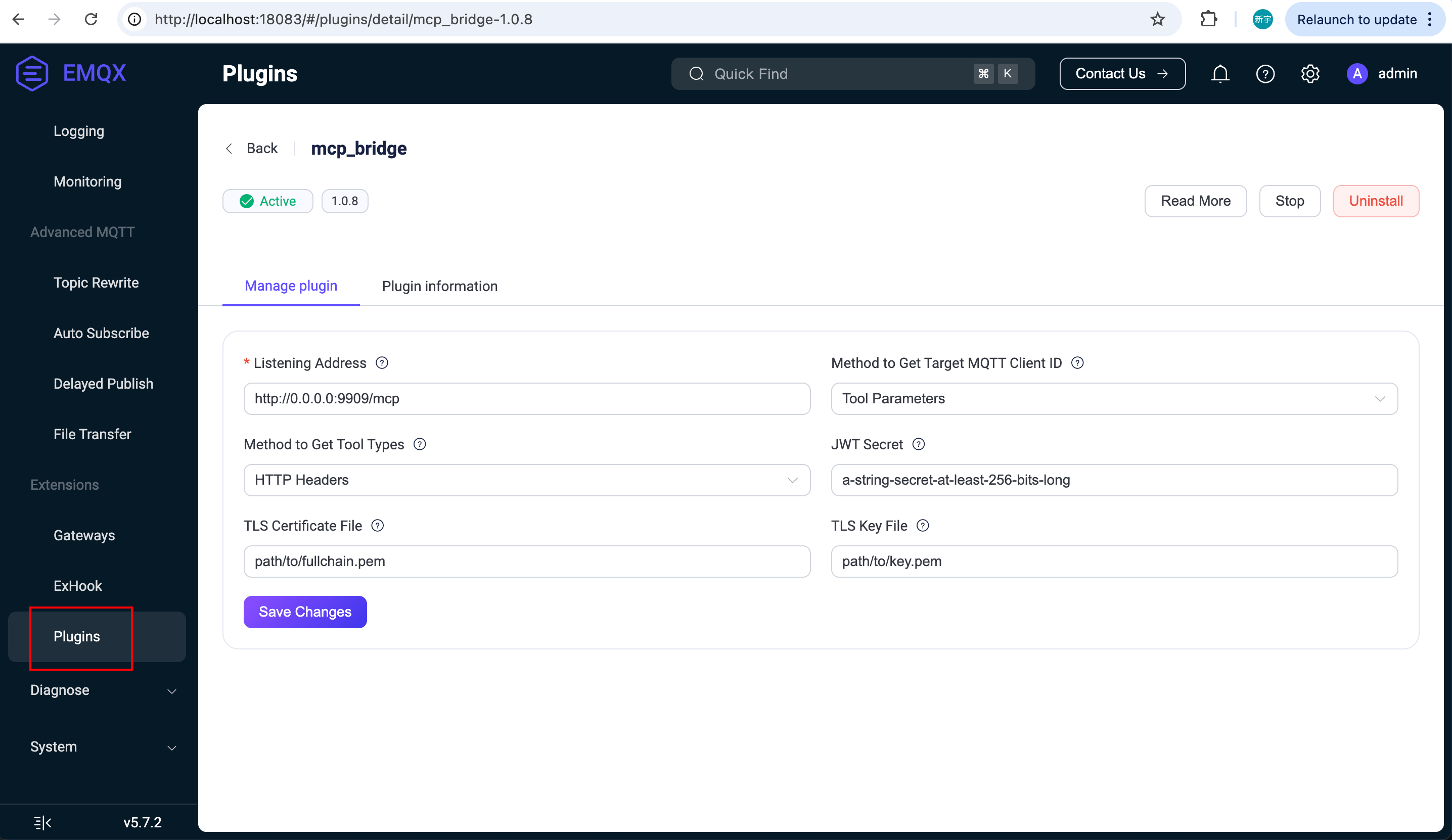
Open a browser and visit http://localhost:18083/#/plugins/. Click the MCP Bridge Plugin to enter the configuration page. Here you can modify settings such as the listening address and certificates. After clicking Save, the configuration is applied automatically, and no manual plugin restart is required.
Note that if the listening address is configured as
https://your-hostname:9909/mcp, the MCP plugin will start two HTTP endpoints on the specified port:/sse: for MCP connections using the SSE protocol./mcp: for MCP connections using the Streamable HTTP protocol.
If you only want to support the SSE protocol, you can set the listening address to
https://your-hostname:9909/sse.In addition, some models or AI agents may require the MCP server to be accessed over HTTPS. In this case, you must configure a valid and trusted SSL certificate for the MCP Bridge Plugin and ensure that the URL is publicly accessible.
Set the Target MQTT Client ID acquisition method to Tool Parameter. This allows the MCP client to pass the device’s MQTT Client ID as a parameter when invoking tools, instead of specifying a fixed Client ID in the HTTP headers when establishing the connection.
Simulate Devices Using the MCP over MQTT SDK
First, follow the Install MCP SDK guide to install the MCP SDK for Python:
uv init smart_light
cd smart_light
uv add git+https://github.com/emqx/mcp-python-sdk --branch main
uv add "mcp[cli]"
source .venv/bin/activateAdd a smart_light.py file to the project with the following content:
# smart_light.py
import os
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
status = "off"
# Create server
mcp = FastMCP(
"devices/light",
log_level="DEBUG",
mqtt_server_description="A simple FastMCP server that controls a light device. You can turn the light on and off, and change its brightness.",
mqtt_client_id = os.getenv("MQTT_CLIENT_ID"),
mqtt_options={
"username": "aaa",
"host": "localhost",
"port": 1883,
},
)
@mcp.tool()
def change_brightness(level: int) -> str:
"""Change the brightness of the light, level should be between 0 and 100"""
if 0 <= level <= 100:
return f"Changed brightness to {level}"
return "Invalid brightness level. Please provide a level between 0 and 100."
@mcp.tool()
def turn_on() -> str:
"""Turn the light on"""
global status
if status == "on":
return "OK, but the light is already on"
status = "on"
return "Light turned on"
@mcp.tool()
def turn_off() -> str:
"""Turn the light off"""
global status
if status == "off":
return "OK, but the light is already off"
status = "off"
return "Light turned off"The Python code above starts an MCP server using the MCP over MQTT protocol to simulate a smart light device. It exposes MCP tools for turning the light on and off and adjusting brightness. Note that the server name is specified as devices/light.
Next, in two separate terminal windows, run the following commands to start two MCP servers simulating two devices, with device IDs abc123 and abc456 respectively:
MQTT_CLIENT_ID=abc123 mcp run -t mqtt ./smart_light.py
MQTT_CLIENT_ID=abc456 mcp run -t mqtt ./smart_light.pyTest with the Cherry Studio Client
Here, we use the MCP-enabled Cherry Studio client as the MCP Client to test the EMQX MCP Bridge Plugin.
Install the Cherry Studio client by referring to the Cherry Studio documentation: https://docs.cherry-ai.com/
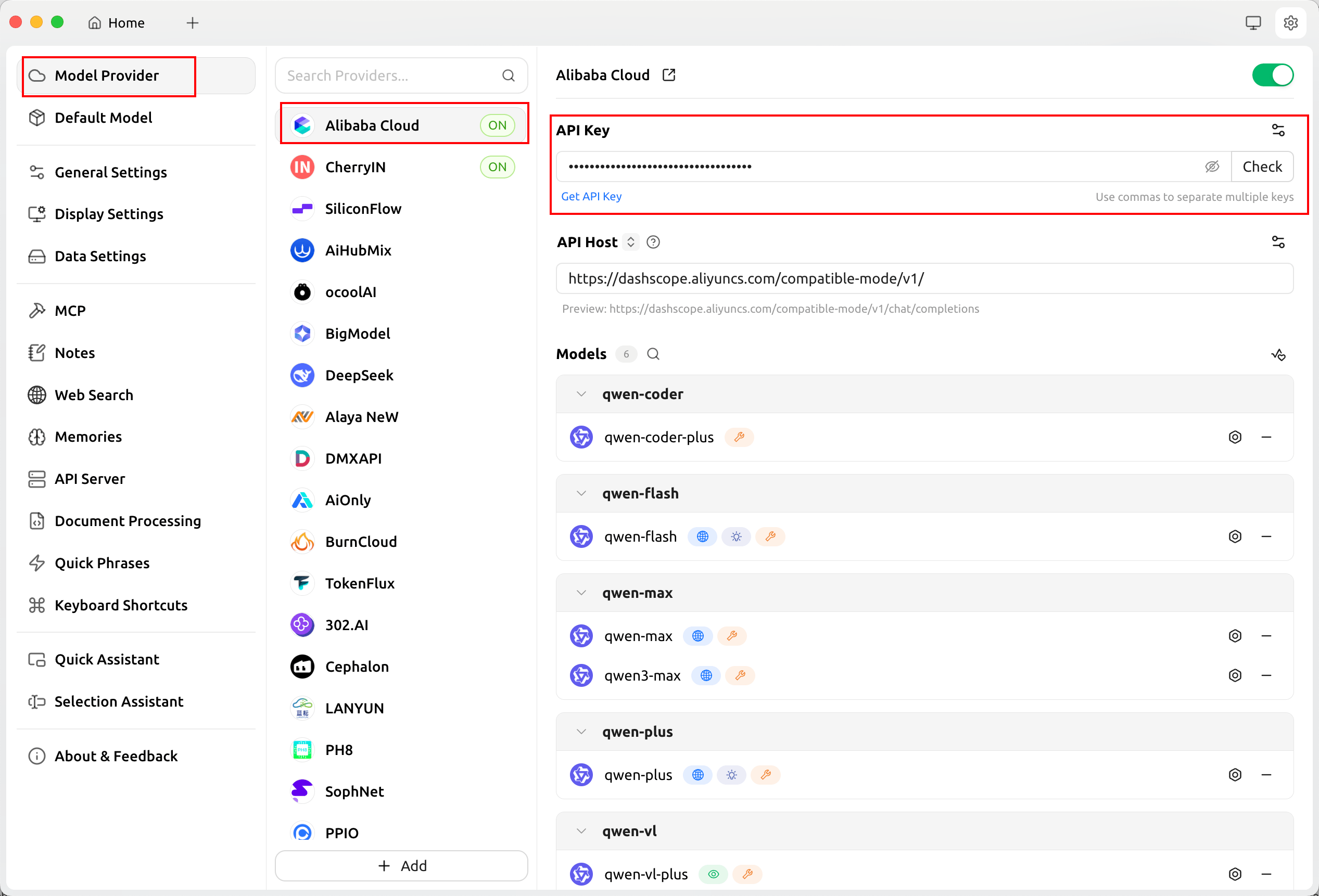
On the Model Provider page, add an LLM provider and configure the model endpoint, API key, and other required information.
On the MCP page, add an MCP server with the following configuration:
Name:
MQTT MCP ToolsType: SSE or Streamable HTTP (Streamable HTTP is used in this example)
URL: Use the Streamable HTTP endpoint provided by the MCP Bridge:
http://localhost:9909/mcpHeaders: To avoid exposing too many irrelevant tools to the model, only load tools of the
devices/lighttype by adding the following header:Tool-Types=devices/light
Here,
devices/lightis the MCP server name specified in the Python device-side code above.Cherry Studio supports both HTTP and SSE protocols. For local testing, you can use
http://localhost:9909/mcp.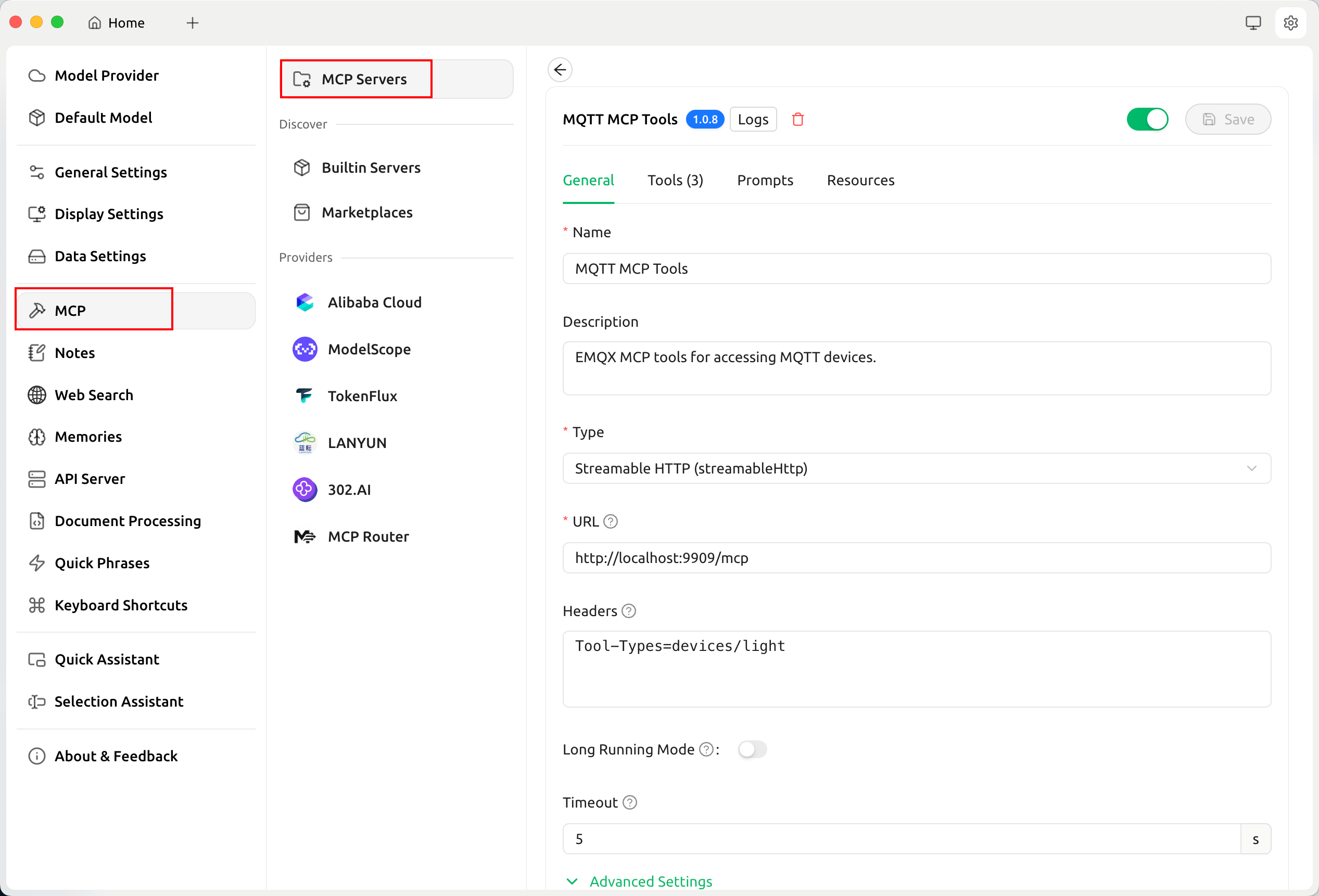
Create a new assistant named “Device Assistant”, and within it create a new conversation topic named “MQTT Device Control”. Then set the system prompts for the assistant and the conversation topic as follows:
Assistant system prompt:
You are a device assistant. You may only answer questions related to device access and control. For any other questions, reply directly: “I am only a device assistant and cannot answer other questions.”Conversation system prompt:
I have the following devices: - Living room light, device ID: abc123 - Bedroom light, device ID: abc456In the conversation settings, enable the MCP tool: the
MQTT MCP Toolsserver.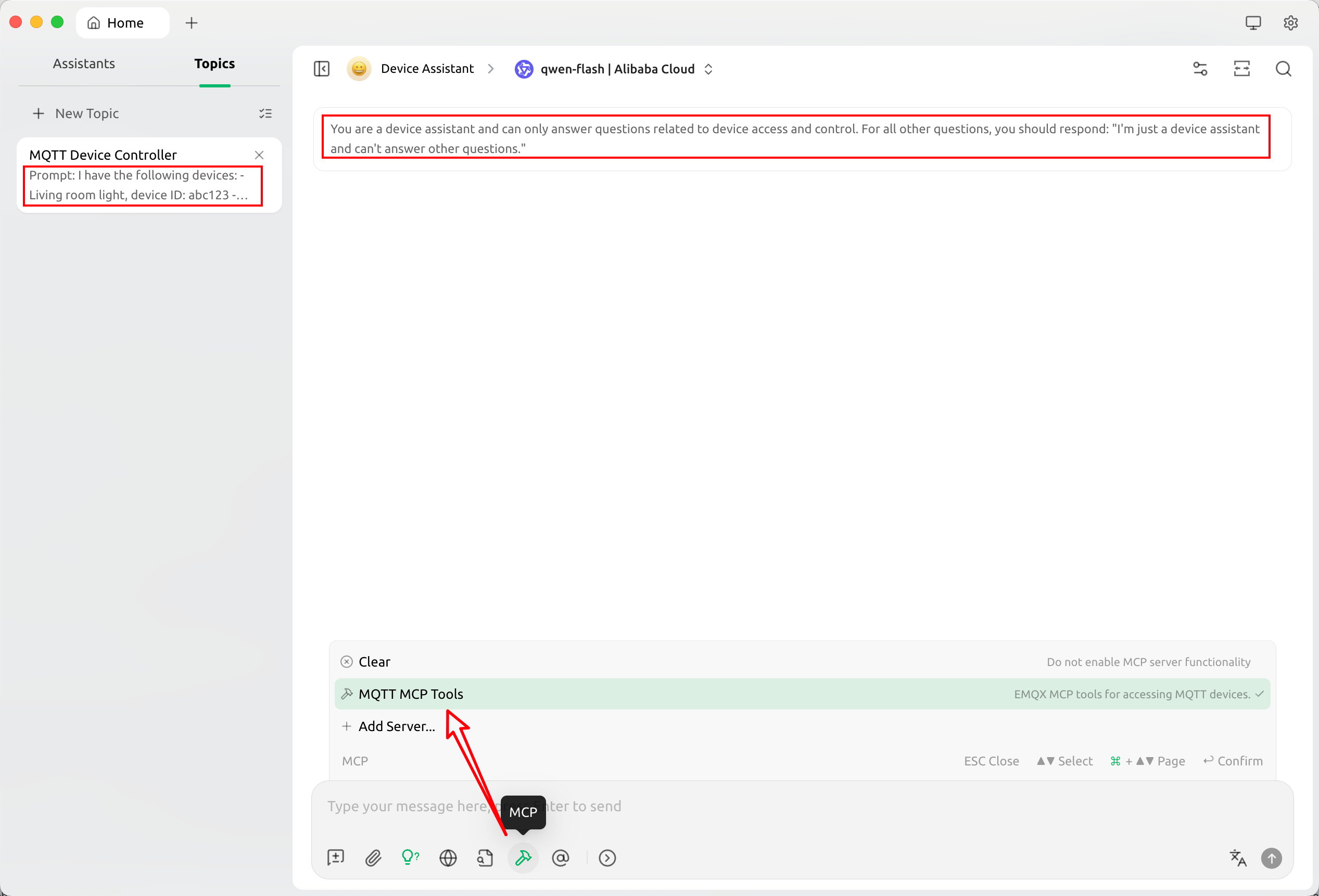
Finally, select a model that supports tool calling (for example,
qwen-flash). You can now enter commands in the chat box to test natural-language device control:Turn on the living room light. Set the bedroom light brightness to 75%.You will see that the device assistant identifies the correct device ID based on the system prompt and invokes the MCP tools to control the corresponding device: