Stream management
Streaming is the main mode of operation for data source access in NeuronEX. Users can define how to connect to external resources by selecting the data source type and configuration parameters. Whenever data flows into the data stream, calculations in the rules will be triggered.
Stream type
Currently, the following stream types are supported built-in:
| stream type | description |
|---|---|
| Neuron | Read data from NeuronEX's data collection module |
| MQTT | Read data from MQTT topic |
| HTTP pull | Pull data from HTTP server |
| HTTP push | Push data to NeuronEX via HTTP |
| Memory | Read data from the NeuronEX memory to form a rule pipeline |
| SQL | Query data from the database |
| File | Read data from a file |
| Video | Query data from video stream |
| Simulator | Read data from simulator |
| CAN | Read data from CAN bus |
| Kafka | Read data from Kafka |
| WebSocket | Read data from WebSocket |
Create stream
On the NeuronEX page, click Data Processing -> Sources. On the stream management page, click the Create Stream button to create a stream.
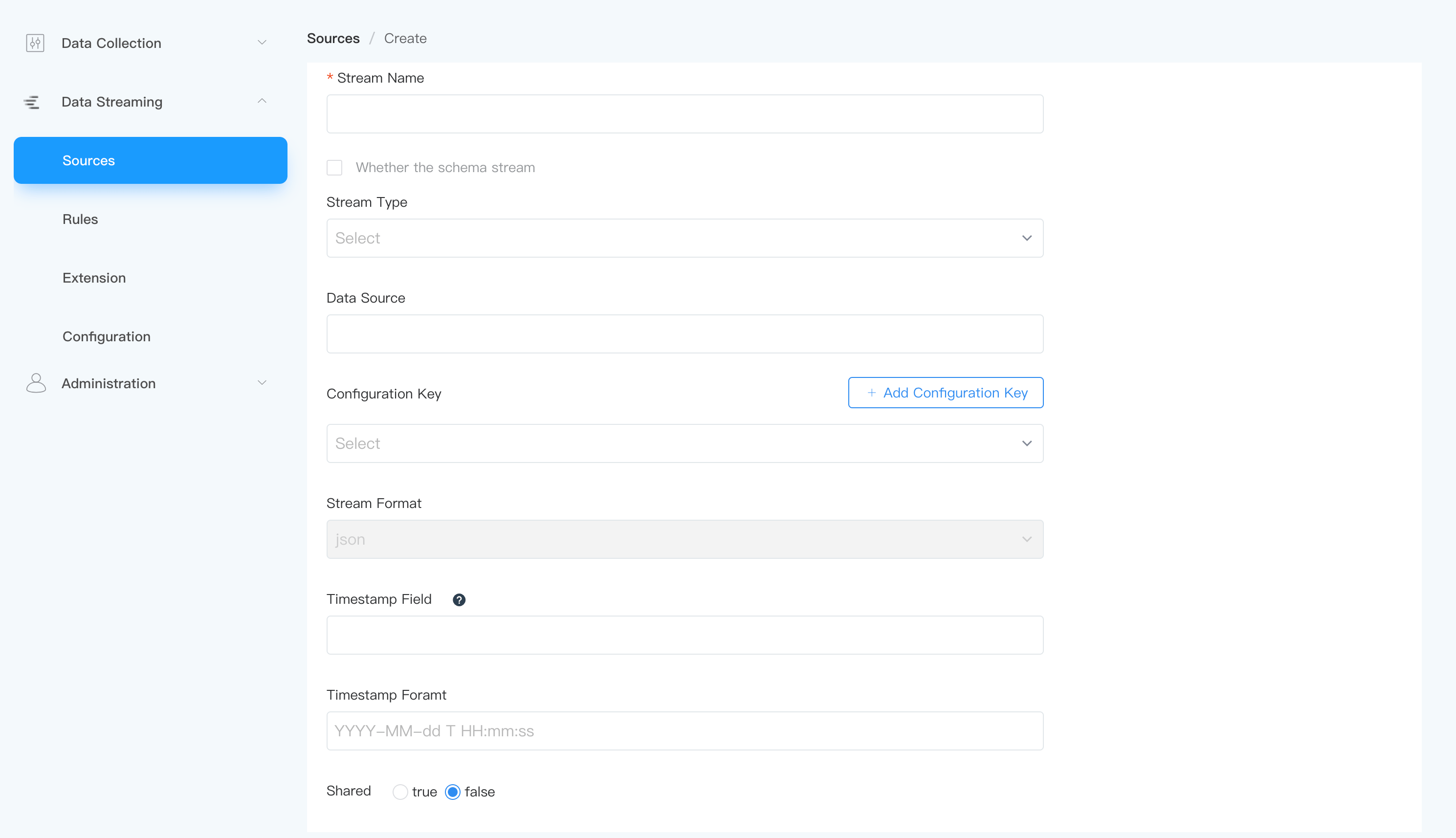
Stream parameter configuration
Whether the schema stream
NeuronEX supports structured/unstructured streams, with the default being unstructured. That is, when Sources -> Create Stream, the
Whether the schema streamoption is not checked. Please refer to data structure for detailed description.- unstructured streams
Schemaless, users do not need to define any form of schema, mainly used for weakly structured data flow, or when the data structure changes frequently.
- Structured streams
Users define data schema at the data source (Source) layer. Data applicable to users has a fixed or approximately fixed format.
Tips
Some data formats have data structures themselves, such as the
protobufformat. When creating a source, users can define a stream format to point to the data structure definition in the Schema Registry. At this time, the data structure of the data source will be overwritten by the definition in the schema registry. For a detailed introduction to modes, see the Mode chapter.Stream Type
NeuronEX supports multiple stream types. For details, please refer to Streaming Data Source.
data source
Depends on different data source types; if it is an MQTT source, it is the MQTT data source topic name; for other sources, please refer to the relevant documentation.
Configuration Key
Define related configuration items for each type of data source. For details, please refer to the relevant documents. Each data source provides a
defaultconfiguration key for reference.Streaming Format
Used to define the incoming data type, supporting
json,protobuf,binary,delimitedandcustom, the default isjson. The following is an introduction to other streaming formats:delimited
For CSV file data source, you need to select the
delimitedformat, and also specify a delimiter to distinguish the data fields, such as ","protobuf
Protobuf is a way to serialize structured data. When the stream format is set to
protobuf, the mode used when decoding should also be configured. Modes can be defined in Data Processing -> Configuration -> Schema. For a detailed introduction to modes, see the Mode chapter.Binary
For binary data streams, such as images or video streams, the data format needs to be specified as
binary.custom
customis a data format customized by the user.
SHARED
By default, the
SHAREDattribute is set tofalse. If the user wants multiple rules to share the same data source instance, theSHAREDattribute can be set totrue.- When shared data source is
false, each rule will start an independent data source runtime, and data sources with the same name in different rules are completely isolated. - When shared data source is
true, the same data source instance is shared in multiple rules.
- When shared data source is
Tips
If you need to use the exact same input data or improve performance, the shared field of the data source can be defined with true.
tip
In some scenarios, users need different rules to handle the exact same data flow. For example, when processing sensor temperature data, the user may need a rule to trigger a warning when the average temperature over a period of time is greater than 30 degrees; and another rule to trigger a warning when the average temperature over a period of time is less than 0 degrees. When using the default configuration, both rules instantiate the source instance independently. Due to reasons such as network delays, rules may get data streams in different orders or even have missing data, thus calculating averages in different data dimensions. By configuring a shared source instance, users can ensure that both rules process the exact same data.
data structure
When you create a data source, you can define the data structure of the data source. When NeuronEX runs, it performs data validation and type conversion based on the defined structure. Data structure validation is not enabled by default. If you want to enable it, you can check the "Whether the schema stream" field when creating a data source and fill in the field information.
Currently NeuronEX supports the following field types:
| # | data type | description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | bigint | bigint type |
| 2 | float | float type |
| 3 | string | Text value consisting of Unicode characters. |
| 4 | datetime | Datetime type |
| 5 | boolean | boolean type |
| 6 | bytea | A byte array used to store binary data. If you use this type in a stream formatted "JSON", the incoming data needs to be a base64-encoded string. |
| 7 | array | arraytype |
| 8 | struct | Complex type |
Tips
If the data accessed by the data source is inconsistent with the defined data schema, the message will be discarded and no rule processing will be performed.
Example
Example 1
my_stream
(id bigint, name string, score float)
WITH (datasource = "topic/temperature", FORMAT = "json", KEY = "id");The stream will subscribe to the MQTT topic topic/temperature and the server connection uses the server key in the default section of the configuration file $ekuiper/etc/mqtt_source.yaml.
Example 2
demo (
USERID BIGINT,
FIRST_NAME STRING,
LAST_NAME STRING,
NICKNAMES ARRAY(STRING),
Gender BOOLEAN,
ADDRESS STRUCT(STREET_NAME STRING, NUMBER BIGINT),
) WITH (DATASOURCE="test/", FORMAT="JSON", KEY="USERID", CONF_KEY="demo");The stream will subscribe to the MQTT topic test/ and the server connection uses the settings in the demo section of the configuration file $ekuiper/etc/mqtt_source.yaml.
Example 3
demo () WITH (DATASOURCE="test/", FORMAT="protobuf", SCHEMAID="proto1.Book");The stream will subscribe to the MQTT topic test/, using the PROTOBUF format, decoding the incoming data according to the Book definition in the $ekuiper/data/schemas/protobuf/schema1.proto file. For details on mode management, see Mode.