Upstream/Downstream Data Format
The following contents describe how MQTT plugin publishes collected data, and how to read or write data through MQTT plugin.
Data Upload
The MQTT plugin publishes collected data in JSON format to some user-defined topics. The exact format of the data reported is controlled by the Upload Format parameter. There are four formats, Values-format, Tags-format, ECP-format, and Custom.
Upload Topic
The upload topic is specified by the upload-topic parameter, and the default one set through the dashboard is /neuron/{MQTT driver name}.
Values Format
In Values-format, the upload data has the following fields:
timestamp: the Unix timestamp when the data was collectednode: name of the south node from which data was collectedgroup: name of the south node group that the tags belong tovalues: dictionary storing tags with successfully collected valueserrors: dictionary storing tags with encountered error codesmetas: driver related metadata information
The following example is in Values-format, where tag values collected successfully are stored in a dictionary, while error codes in another.
{
"timestamp": 1650006388943,
"node": "modbus",
"group": "grp",
"values":
{
"tag0": 123
},
"errors":
{
"tag1": 2014
},
"metas":{}
}TIP
When a tag is collected successfully, the collected data is returned. When a tag collection fails, the error code is returned instead of the value.
When the Upload Tag Error Code parameter is set to False, the error code is not reported.
Tags Format
In Tags-format, the upload data has the following fields:
timestamp: the Unix timestamp when the data was collectednode: name of the south node from which data was collectedgroup: name of the south node group that the tags belong totags: tags data array where each element corresponds to one tag in the groupname: the name of the tagvalue: the value of the tagerror: the error code of the tag
The following example is in Tags-format, where tag data are stored in an array. Each element has the name of the tag, and the tag value or error code if something went wrong.
{
"timestamp": 1647497389075,
"node": "modbus",
"group": "grp",
"tags": [
{
"name": "tag0",
"value": 123,
},
{
"name": "tag1",
"error": 2014
}
]
}TIP
Tag value is returned only when the tag is read successfully. If something goes wrong when reading a tag, the error code is returned.
When the Upload Tag Error Code parameter is set to False, the error code is not reported.
ECP Format
In ECP-format, the upload data has the following fields:
timestamp: the Unix timestamp when the data was collectednode: name of the south node from which data was collectedgroup: name of the south node group that the tags belong totags: tags data array where each element corresponds to one tag in the groupname: the name of the tagvalue: the value of the tagtype: the type of the tag, which can be Boolean, Integer, Float, or String
The following example data is in ECP-format, where tag data are stored in an array. Each element has the name of the tag, the tag type and the tag value, excluding tags where collection failed.
Data classes are divided into four types: Boolean, Integer, Float, and String.
- type = 1 Boolean
- type = 2 Integer
- type = 3 Float
- type = 4 String
{
"timestamp": 1647497389075,
"node": "modbus",
"group": "grp",
"tags": [
{
"name": "tag_boolean",
"value": true,
"type": 1,
},
{
"name": "tag_int32_",
"value": 123,
"type": 2,
},
{
"name": "tag_float",
"value": 1.23,
"type": 3,
},
{
"name": "tag_string",
"value": "abcd",
"type": 4,
}
]
}TIP
ECP-format does not support reporting tag error codes.
Regardless of whether the Upload Tag Error Code parameter is set to False or True, tag error codes are not reported.
Custom Format
In the custom format, use built-in variables to define the data upload format.
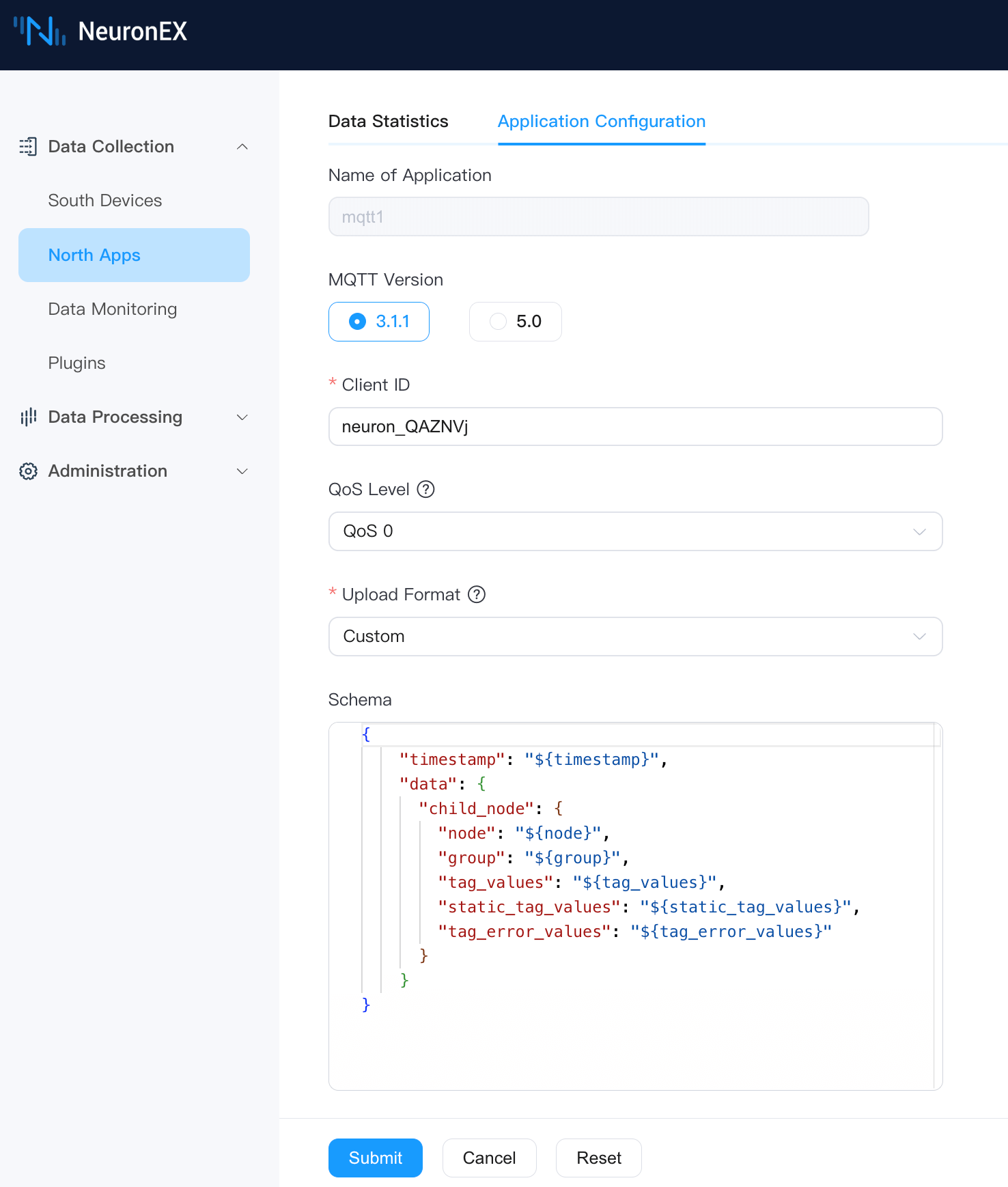
Variables
| variable | description |
|---|---|
${timestamp} | The UNIX timestamp when the data was read. |
${node} | The name of the southbound node. Example: modbus |
${group} | The name of the group. Example: group |
${tags} | The array of valid tag values. Example: [{"name": "tag1", "value": 123}, {"name": "tag2", "value": 456}] |
${tag_values} | The array of valid tag values, Value Format Example: {"tag1": 123, "tag2": 456} |
${tag_errors} | The array of error codes. Example: [{"name": "tag3", "error": 2014}, {"name": "tag4", "error": 2015}] |
${tag_error_values} | The array of error codes, Value Format Example: {"tag3": 2014, "tag4": 2015} |
${static_tags} | The array of static tags. Example: [{"name": "static_tag1", "value": "abc"}, {"name": "static_tag2", "value": "def"}] See Static Tags |
${static_tag_values} | The array of static tags, Value Format Example: {"static_tag1": "abc", "static_tag2": "def"} See Static Tags |
TIP
${tags} and ${tag_values} are two different formats for tag values. ${tags} is an Array format, and ${tag_values} is a JSON format. In most cases, use one of them.
${static_tags} and ${static_tag_values}, ${tag_errors} and ${tag_error_values} are similar. Use one of them.
When the Upload Tag Error Code parameter is set to False, even if ${tag_errors} and ${tag_error_values} are configured, tag error codes are not reported.
The example above is based on the original southbound driver modbus1 and group group1, which contains 4 tags. tag1 and tag2 are collected successfully, while tag3 and tag4 are collected with errors. When subscribing to the northbound node, the static tags are configured as static_tag1 and static_tag2, with values of abc and def respectively.
The above configuration, when reported in Values-format data format, is as follows:
{
"timestamp": 1650006388943,
"node": "modbus1",
"group": "group1",
"values": {"tag1": 123, "tag2": 456, "static_tag1": "abc", "static_tag2": "def"},
"errors": {"tag3": 2014, "tag4": 2015},
"metas":{}
}The following example shows how to output the above JSON message in different data reporting formats by setting different Custom configurations.
Example One
Convert tag data to array format and customize the Json key name.
{
"timestamp": "${timestamp}",
"node": "${node}",
"group": "${group}",
"custom_tag_name": "${tags}",
"custom_tag_errors": "${tag_errors}",
}The actual output result is as follows:
{
"timestamp": 1650006388943,
"node": "modbus1",
"group": "group1",
"custom_tag_name": [{"name": "tag1", "value": 123}, {"name": "tag2", "value": 456}],
"custom_tag_errors": [{"name": "tag3", "error": 2014}, {"name": "tag4", "error": 2015}]
}Example Two
Add global static tags through custom data format. These static tags will be carried in all driver group data reporting. For example, if NeuronEX is deployed on a gateway hardware, you can add the gateway's SN number, IP address, and location information to all driver groups.
{
"timestamp": "${timestamp}",
"node": "${node}",
"group": "${group}",
"values": "${tag_values}",
"gateway_info": {
"ip": "192.168.1.100",
"sn": "SN123456789",
"location": "shanghai"
}
}The actual output result is as follows:
{
"timestamp": 1650006388943,
"node": "modbus1",
"group": "group1",
"values": {"tag1": 123, "tag2": 456},
"gateway_info": {
"ip": "192.168.1.100",
"sn": "SN123456789",
"location": "shanghai"
}
}Example Three
Put tag data, static tags, driver, and group information into a Json sub-node, and customize the Json node name. Currently, the custom data structure supports up to three sub-levels.
{
"timestamp": "${timestamp}",
"data": {
"child_node": {
"node": "${node}",
"group": "${group}",
"tag_values": "${tag_values}",
"static_tag_values": "${static_tag_values}",
"tag_error_values": "${tag_error_values}"
}
}
}The data reporting format is as follows:
{
"timestamp": 1650006388943,
"data": {
"child_node": {
"node": "modbus",
"group": "group",
"tag_values": {"tag1": 123, "tag2": 456},
"static_tag_values": {"static_tag1": "abc", "static_tag2": "def"},
"tag_error_values": {"tag3": 2014, "tag4": 2015}
}
}
}Static Tags
The static tag feature supports configuring static tags manually in the North Application Group List page, and reporting static tag data together with the collected data.
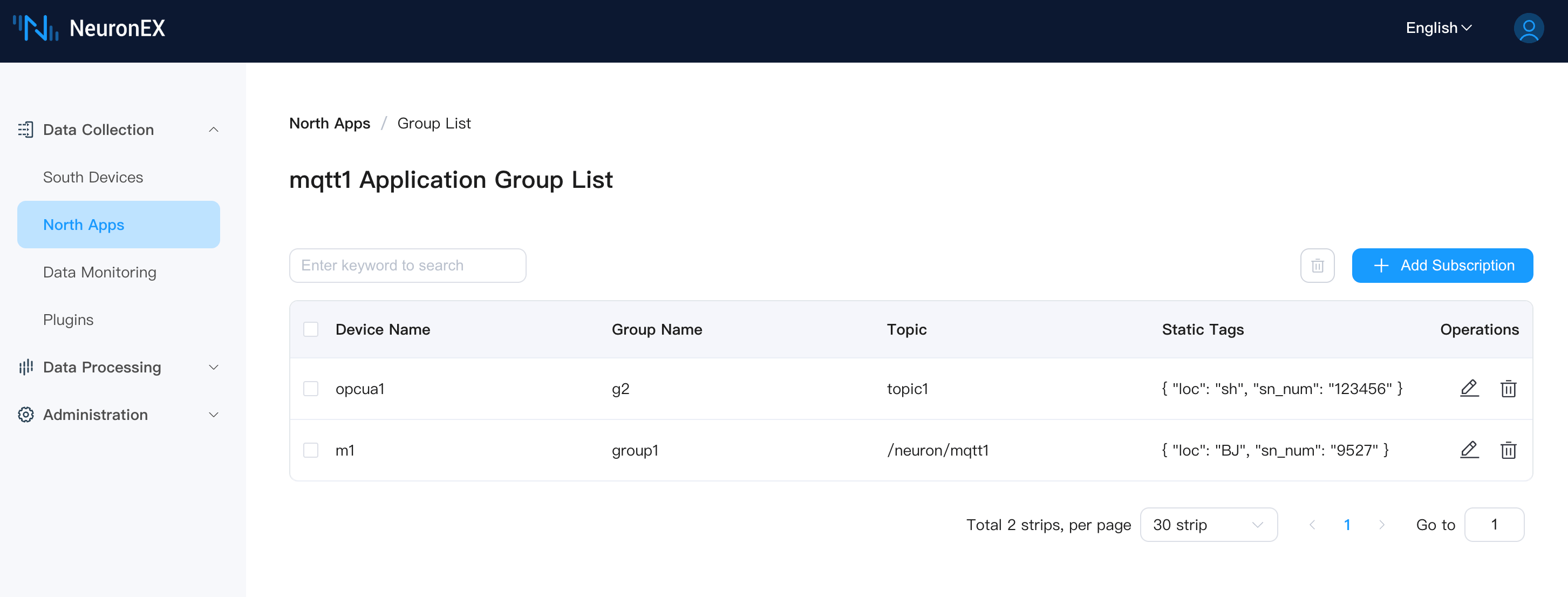
Static tag configuration requires inputting standard JSON format content, where each static tag is a key-value pair in the JSON object. Static tags will be reported together with the collected data according to the configured data reporting format (Values-format, Tags-format, ECP-format).
{
"location": "sh",
"sn_number": "123456"
}Each southbound collection group can configure different static tags. This represents the physical device represented by the collection group, with which static attribute information.
Static tag feature supports Boolean, Integer, Float, and String data types. Complex data types, such as arrays and structures, will be reported as String.
If the static tags added are shared by all collection groups in the NeuronEX instance, you can select All Collection Groups to add static tags, or add static tags in the Custom custom format, as shown in Custom Format: Example Two.
TIP
Static tag names must not be the same as the tag names collected by the southbound driver.
If the names are the same:
- When using
Values-formatfor data upload, the static tag data will overwrite the tag data collected by the southbound driver. - When using
Tags-format,ECP-format, orCustomfor data upload, both the static tag data and the southbound driver collected tag data will be reported together (resulting in duplicate reporting).
Read Tag
Request
You can read a group of tags by sending requests in JSON to the MQTT topic /neuron/{node_name}/read/req.
Body
The read request body should have the following fields:
uuid: a unique identifier, which will be echoed back in the response to help identify the corresponding requestnode: the name of a southbound nodegroup: the name of a group to read
Below is an example read request:
{
"uuid": "bca54fe7-a2b1-43e2-a4b4-1da715d28eab",
"node": "modbus",
"group": "grp"
}Response
Read response will be published to the MQTT topic /neuron/{node_name}/read/resp.
Body
The read response body has the following fields:
uuid: the same unique identifier which is set by the corresponding requesttags: tags data array, same as that in tags format
Below is an example read response:
{
"uuid": "bca54fe7-a2b1-43e2-a4b4-1da715d28eab",
"tags": [
{
"name": "tag0",
"value": 4,
},
{
"name": "tag1",
"error": 2014
}
]
}TIP
Tag value is returned only when the tag is read successfully. If something goes wrong when reading a tag, the error code is returned.
Write Tag
Request
You could write a tag by sending requests in JSON to the MQTT topic designated by the Write Request Topic parameter.
TIP
Before Neuron version 2.4.5, the write request topic was hard-coded to /neuron/{random_str}/write/req.
Body
Write one tag
The write request body should have the following fields:
uuid: a unique identifier, which will be echoed back in the response to help identify the corresponding requestnode: the name of a southbound nodegroup: the name of a grouptag: the name of a tagvalue: the value to write
Below is an example of write request:
{
"uuid": "cd32be1b-c8b1-3257-94af-77f847b1ed3e",
"node": "modbus",
"group": "grp",
"tag": "tag0",
"value": 1234
}Write multiple tags
Since Neuron version 2.6.0, write requests also support writing multiple tags at a time. To write multiple tags at a time, the request body should have the following fields:
uuid: a unique identifier, which will be echoed back in the response to help identify the corresponding request.node: the name of a southbound node.group: the name of a group.tags: tags data array where each element corresponds to one tag in the group.
Below is an example write request:
{
"uuid": "cd32be1b-c8b1-3257-94af-77f847b1ed3e",
"node": "modbus",
"group": "grp",
"tags": [
{
"tag": "tag0",
"value": 1234
},
{
"tag": "tag1",
"value": 5678
}
]
}Response
Write response will be published to the MQTT topic designated by the Write Response Topic parameter.
TIP
Before Neuron version 2.4.5, the write response topic was hard-coded to /neuron/{random_str}//write/resp.
Body
The write response body has the following fields:
uuid: the same unique identifier which is set by the corresponding request.error: error code if something bad happens,0represents success.
Below is an example of write response:
{
"uuid": "cd32be1b-c8b1-3257-94af-77f847b1ed3e",
"error": 0
}Driver Status Report
Reports status of all the southbound nodes to the specified topic.
Status Report Topic
The status report topic is specified in the northbound node configuration. Its default value is /neuron/{random_str}/state/update.
Status Report Interval
The status report interval is specified in the northbound node configuration, indicating the number of seconds between each message. The default value is 1, with an allowed range of 1-3600.
Reporting Message Format
The reported data consists of the following fields:
timestamp: The UNIX timestamp when the data was collected.states: An array of node status information.
Below is an example of a driver status reporting message.
{
"timestamp": 1658134132237,
"states": [
{
"node": "modbus-tcp",
"link": 1,
"running": 3
},
{
"node": "modbus-rtu",
"link": 1,
"running": 3
}
]
}