Data Collection
This section mainly introduces how to add southbound devices in EMQX Neuron (formerly NeuronEX), bidirectional communication with the devices, and connect them to external applications such as cloud platforms or data processing module.
Capabilities of data collection
Multi-device connection
EMQX Neuron provides a variety of plugin modules, such as Modbus, OPC UA, EtherNet/IP, IEC104, BACnet, Siemens, Mitsubishi, etc. Some of these plugins are widely used in discrete manufacturing, building automation, CNC machine tools, robots, electricity, and various PLC communications.
Low latency collection and control
EMQX Neuron is a real-time asynchronous processing server that makes full use of low-latency network methods at the edge to achieve 100 millisecond high-speed data collection.
Large-scale concurrency
EMQX Neuron can connect to different industrial devices simultaneously. Thanks to the decoupled modular architecture design, each connection can be run independently. The number of concurrent connections depends on hardware resources.
Flexible deployment
EMQX Neuron has a very low memory footprint, less than 100M of memory at startup, and is suitable for running on low-configuration architecture devices, such as X86, ARM and RISC-V. EMQX Neuron also supports Docker containerized deployment, as well as running in a Kubernetes environment.
Better integration
EMQX Neuron supports seamless integration with IIoT platforms, public cloud platforms, and third-party applications. EMQX Neuron can connect to private cloud, EMQX Cloud, AWS, Microsoft Azure or local servers through various methods such as MQTT, SparkPlugB, API, etc., and seamlessly flow real-time industrial data directly to industrial applications, such as MES, ERP, big data, analysis software, to realize various complex data processing and storage scenarios.
Unified data operations
EMQX Neuron helps traditional industrial devices deliver data messages asynchronously as edge nodes specified in the SparkplugB standard. SparkPlugB is an open, unified, interoperable industrial data exchange standard for data exchange between industrial information systems such as ERP, MES, SCADA and history via the MQTT broker.
Key concepts
Plugin
Plugins can be divided into northbound applications and southbound drivers. Northbound plugins are typically used to connect to cloud platforms. Southbound plugins are communication drivers that implement specific protocols to access external devices. In order to implement protocol format conversion, at least one northbound plugin and one southbound plugin are required for data transmission and data collection respectively.
All plugin modules are written based on C language, and SDK files are provided for users who want secondary development. For specific plugin development tutorials, please refer to SDK Tutorial.
Node
In EMQX Neuron, nodes are instantiations of plugins. In a single EMQX Neuron instance, multiple nodes containing various plugins can be created for mutual communication. EMQX Neuron's core framework is responsible for managing message routing between these nodes. EMQX Neuron has powerful performance and supports the simultaneous operation of hundreds of nodes.
Data Tag (Data Point)
Data Tags(or Data Points) are descriptors that describe the storage location, operational attributes, and metadata of data within a device, helping users access and manipulate data.
The data tag defines the data storage location and data operation properties in the device. It also contains some metadata information about the data, such as scaling, accuracy, and read/write properties. Tag information helps describe an item and allows it to be found in a device or processed for automatic reading/writing. The user will identify those tags of interest in the device to read data from or write data to the device.
Group
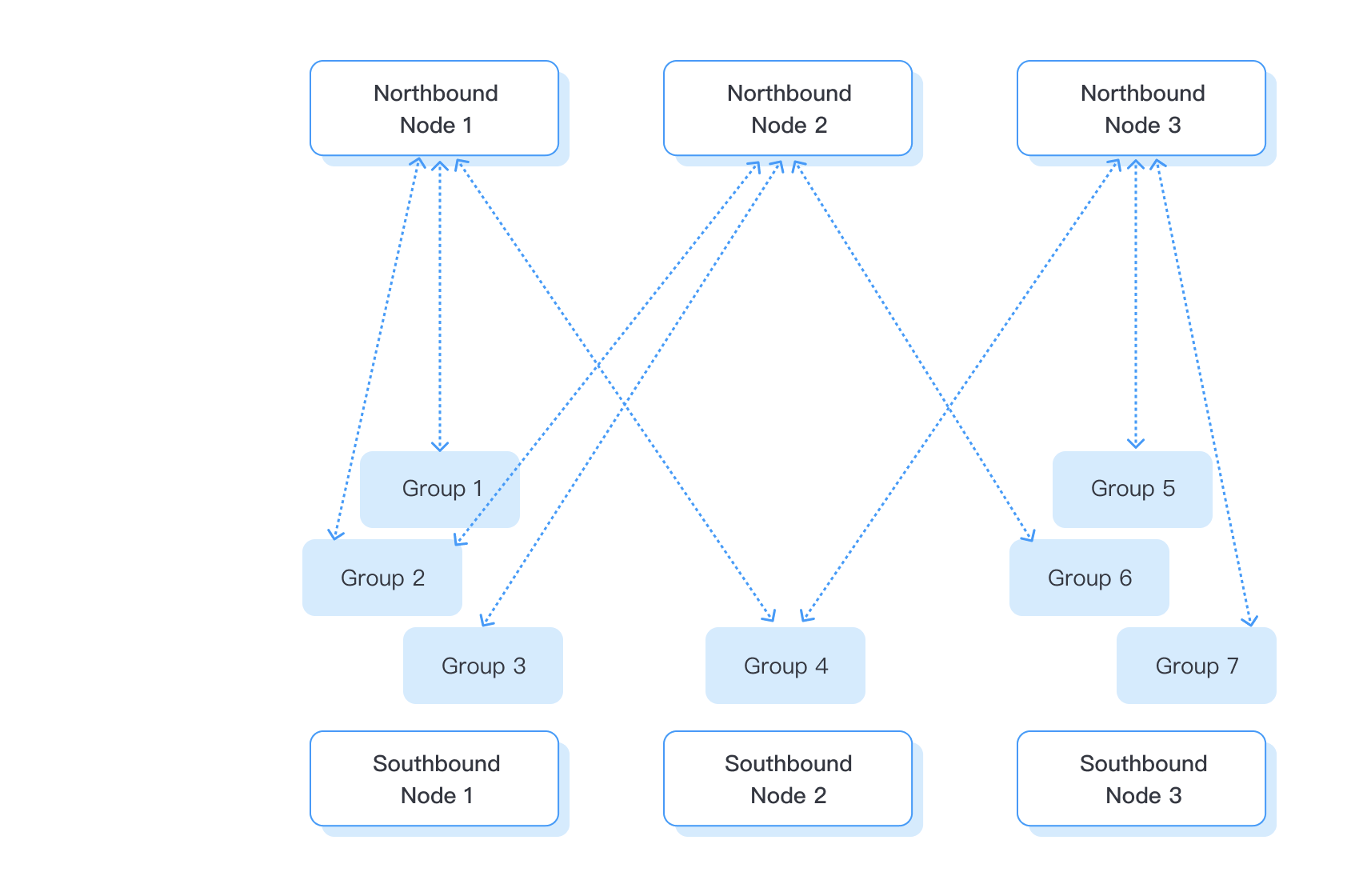
Data tags will be assigned to groups. Each group has an independent polling frequency to read data from the device. The collection of tags in the device that the user is interested in is divided into several groups for better management. The routing mechanism is based on these groups being exchanged between nodes as units of information. A northbound node can subscribe to any group in any southbound node. These subscriptions will be used to route data messages between nodes. Additionally, there is a Group Polling Frequency that controls the time interval at which devices are polled.
Configuration process
The following is the workflow of how to set up EMQX Neuron to convert various industrial protocols and then complete data transmission and collection.
View all available plugins: The data collection and transmission functions of EMQX Neuron can be realized using various protocol plugins.
Create southbound driver: According to the protocol type of the device, select the southbound plugin driver on EMQX Neuron and create a node. Configure the parameters of the driver to establish a communication connection between EMQX Neuron and the device.
Establish communication between device and EMQX Neuron: First add groups and tags for the southbound driver. Once the group and tags are created, the real-time value of the tags can be obtained from data monitoring. To facilitate user operations, EMQX Neuron supports related configuration information through offline Excel files [batch import] (./import-export/import-export.md).
TIP
Repeat steps 2 and 3 until all necessary drives, groups, and tags have been created.
Create a northbound application and subscribe to a southbound device: Select the required northbound plugin to realize data transmission. Each northbound plugin can only connect to one destination, such as stream processing module, EMQX message middleware, industrial Internet platform, etc. After creating the northbound device, you need to subscribe to the group. In this step, there is no need to set up groups and tags. Northbound nodes can subscribe to any group created in southbound nodes. After the subscription is established, the data of the corresponding group will be continuously published to the northbound node according to the frequency of the group.
The overall process is shown in the figure below:
Configuration Specification
| Object | Specification Limit |
|---|---|
| Node Name Length | Maximum 128 characters |
| Tag Name Length | Maximum 128 characters |
| Tag Address Length | Maximum 128 characters |
| Group Name Length | Maximum 128 characters |
| Maximum groups per southbound driver | Maximum 512 |
| Maximum subscribed groups per northbound application | unlimited |
| Plugin Module Name Length | Maximum 32 characters |
| Plugin File Name Length | Maximum 64 characters |
| Plugin Description Length | Maximum 512 characters |
| Southbound Driver collection interval | Minimum 100 milliseconds |