Ingest MQTT Data into Cassandra
Apache Cassandra is a popular open-source, distributed NoSQL database management system designed to handle large datasets and build high-throughput applications. EMQX Cloud's integration with Apache Cassandra provides the ability to store messages and events in the Cassandra database, enabling functionalities such as time-series data storage, device registration and management, as well as real-time data analysis.
This page provides a comprehensive introduction to the data integration between EMQX Cloud and Cassandra with practical instructions on creating and validating the data integration.
TIP
The current implementation only supports Cassandra v3.x, not yet compatible with v4.x.
How It Works
Cassandra data integration is an out-of-the-box feature in EMQX Cloud that combines EMQX Cloud's device connectivity and message transmission capabilities with Cassendra's powerful data storage capabilities. With a built-in rule engine component, the integration simplifies the process of ingesting data from EMQX Cloud to Cassandra for storage and management, eliminating the need for complex coding.
The diagram below illustrates a typical architecture of data integration between EMQX and Cassandra:
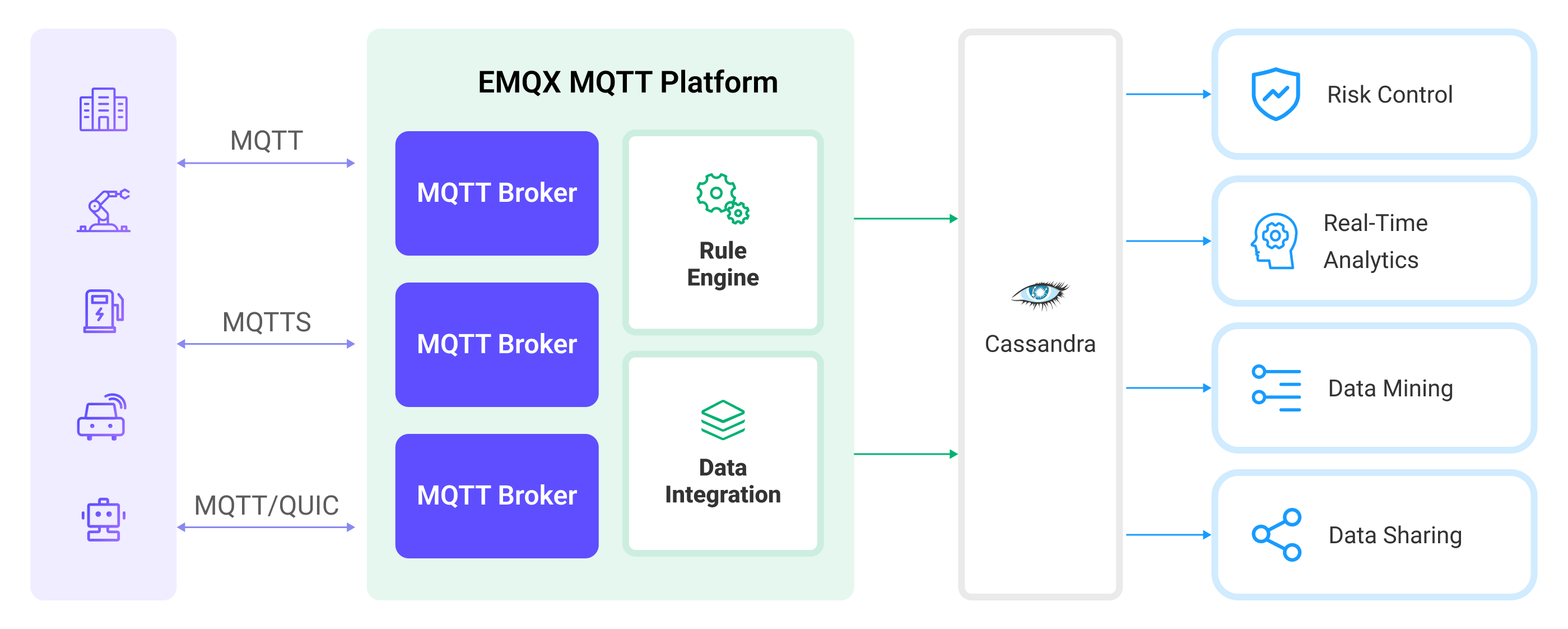
Ingesting MQTT data into Cassandra works as follows:
- Message publication and reception: IoT devices, whether they are part of connected vehicles, IIoT systems, or energy management platforms, establish successful connections to EMQX Cloud through the MQTT protocol and publish MQTT messages to specific topics. When EMQX Cloud receives these messages, it initiates the matching process within its rules engine.
- Message data processing: When a message arrives, it passes through the rule engine and is then processed by the rule defined in EMQX Cloud. The rules, based on predefined criteria, determine which messages need to be routed to Cassandra. If any rules specify payload transformations, those transformations are applied, such as converting data formats, filtering out specific information, or enriching the payload with additional context.
- Data ingestion into Cassandra: Once the rule engine identifies a message for Cassandra storage, it triggers an action of forwarding the messages to Cassandra. Processed data will be seamlessly written into the collection of the Cassandra database.
- Data storage and utilization: With the data now stored in Cassandra, businesses can harness its querying power for various use cases. For instance, in the realm of connected vehicles, this stored data can inform fleet management systems about vehicle health, optimize route planning based on real-time metrics, or track assets. Similarly, in IIoT settings, the data might be used to monitor machinery health, forecast maintenance, or optimize production schedules.
Features and Benefits
The data integration with Cassandra offers a range of features and benefits tailored to ensure efficient data transmission, storage, and utilization:
- Large-Scale Time-Series Data Storage: EMQX Cloud can handle massive device connections and message transmissions. Leveraging Cassandra's high scalability and distributed storage features, it can achieve storage and management of large-scale datasets, including time-series data, and supports time-range based queries and aggregation operations.
- Real-time Data Streaming: EMQX Cloud is built for handling real-time data streams, ensuring efficient and reliable data transmission from source systems to Cassandra. It enables organizations to capture and analyze data in real-time, making it ideal for use cases requiring immediate insights and actions.
- High Availability Assurance: Both EMQX and Cassandra provide clustering capabilities. When used in combination, device connections and data can be distributed across multiple servers. In case of a node failure, the system can automatically switch to other available nodes, thus ensuring high scalability and fault tolerance.
- Flexibility in Data Transformation: EMQX Cloud provides a powerful SQL-based Rule Engine, allowing organizations to pre-process data before storing it in Cassandra. It supports various data transformation mechanisms, such as filtering, routing, aggregation, and enrichment, enabling organizations to shape the data according to their needs.
- Flexible Data Model: Cassandra uses a column-based data model, supporting flexible data schemas and dynamic addition of columns. This is suitable for storing and managing structured device events and message data, and can easily store various MQTT message data.
Before You Start
This section describes the preparations you need to complete before you start to create a TimescaleDB data bridge, including how to install a Cassandra server and create keyspace and table.
Prerequisites
- Understand rules.
- Understand data integration.
Set up Network
Before configuring data integration, you must create an EMQX Cloud deployment and ensure network connectivity between EMQX Cloud and the target service.
For Dedicated Flex deployments:
Create a VPC Peering Connection between the EMQX Cloud VPC and the target service VPC. After the peering connection is established, EMQX Cloud can access the target service through its private IP address.
If access through a public IP is required, configure a NAT Gateway to enable outbound connectivity.
For BYOC (Bring Your Own Cloud) deployments:
Create a VPC peering connection between the VPC where the BYOC deployment is running and the VPC hosting the target service. Once peering is in place, the target service can be accessed via its private IP address.
If the target service must be accessed through a public IP, configure a NAT Gateway in the BYOC VPC using your cloud provider’s console.
Install Cassandra Server
Start the simple Cassandra service via docker:
docker run --name cassa --rm -p 9042:9042 cassandra:3.11.14Create Keyspace and Table
You need to create keyspace and tables before you create the data bridge for Cassandra.
- Create a Keyspace named
mqtt:
docker exec -it cassa cqlsh "-e CREATE KEYSPACE mqtt WITH REPLICATION = {'class': 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor': 1}"- Create a table in Cassandra:
temp_hum:
docker exec -it cassa cqlsh "-e \
CREATE TABLE mqtt.temp_hum( \
msgid text, \
temp text, \
hum text, \
arrived timestamp, \
PRIMARY KEY(msgid));"Create a Cassandra Connector
Before creating data integration rules, you need to first create a Cassandra connector to access the Cassandra server.
Go to your deployment. Click Data Integration from the left-navigation menu.
If it is the first time for you to create a connector, select Cassandra under the Data Persistence category. If you have already created connectors, select New Connector and then select Cassandra under the Data Persistence category.
Enter the connection information:
- Servers: IP address and port of the server.
- Keyspace:
mqttas the Keyspace. - leave others as default.
- If you want to establish an encrypted connection, click the Enable TLS toggle switch.
Advanced Settings (Optional).
Click the Test button. If the Cassandra service is accessible, a success prompt will be returned.
Click the New button to complete the creation.
Create a Rule
Next, you need to create a rule to specify the data to be written and add corresponding actions in the rule to forward the processed data to Cassandra.
Click New Rule in Rules area or click the New Rule icon in the Actions column of the connector you just created.
Enter the rule matching SQL statement in the SQL Editor. In the following rule, we read the time when the message was reported
arrived, client ID, payload viatemp_hum/emqxtopic. Also, we can read temperature and humidity from this topic.sqlSELECT id as msgid, payload.temp as temp, payload.hum as hum, timestamp as arrived FROM "temp_hum/emqx"TIP
If you are a beginner user, click SQL Examples and Try It Out to learn and test the SQL rule.
Click Next to add an action.
Select the connector you just created from the Connector dropdown box.
Configure the CQL template to save
msgid,temp,humandarrivedto Cassandra. This template will be executed via Cassandra Query Language, and the sample code is as follows:sqlINSERT INTO temp_hum(msgid, temp, hum, arrived) VALUES ( ${msgid}, ${temp}, ${hum}, ${arrived} )Advanced settings (optional).
Click the Confirm button to complete the rule creation.
In the Successful new rule pop-up, click Back to Rules, thus completing the entire data integration configuration chain.
Test the Rule
You are recommended to use MQTTX to simulate temperature and humidity data reporting, but you can also use any other client.
Use MQTTX to connect to the deployment and send messages to the following Topic.
topic:
temp_hum/emqxpayload:
json{ "temp": "27.5", "hum": "41.8" }
Check whether messages are stored into Cassandra with the following command:
bash$ docker exec -it cassa cqlsh "-e SELECT * FROM mqtt.temp_hum;" msgid | arrived | hum | temp ----------------------------------+---------------------------------+------+------ 00061488D7FBFE8F2C770000467D0011 | 2024-03-26 04:37:11.987000+0000 | 41.8 | 27.5 (1 rows)View operational data in the console. Click the rule ID in the rule list, and you can see the statistics of the rule and the statistics of all actions under this rule.