Connect to Deployment using Node.js via MQTT.js SDK
This article mainly introduces how to use MQTT in the Node.js project to realize the functions of connecting, subscribing, unsubscribing, sending and receiving messages between the client and the MQTT broker.
Prerequisites
Before connecting your application to the EMQX Cloud using the Node.js client, ensure you have completed the following prerequisites:
- Deploy MQTT Broker
- Check Node.js version
Deploy MQTT Broker
To connect your application to the EMQX Cloud, you need to create and configure a deployment.
Serverless Deployment
Create a Serverless deployment in the EMQX Cloud Console.
Once the deployment is created and running, go to the deployment Overview page to find the MQTT connection information, including:
Broker address
Port number (only TLS ports are supported in Serverless)
Serverless deployments require TLS connections. Make sure to download the CA certificate from the Overview page and use port
8883for TLS.Configure the default authentication (username/password) under Access Control -> Client Authentication in the deployment.
For more details, refer to the Serverless Port Guide.
Dedicated Flex or BYOC Deployment
- You can create a Dedicated Flex or BYOC deployment in the EMQX Cloud Console.
- After creation, go to the deployment Overview page to retrieve MQTT connection information, including:
- Broker address
- TCP and TLS port numbers for MQTT and WebSocket (Both TCP and TLS connections are supported).
- Configure the default authentication (username/password) under Access Control -> Client Authentication in the deployment.
For detailed port configurations, see the Dedicated & BYOC Port Guide.
Check Node.js Version
This project uses Node.js v16.19.1 for development and testing. You can confirm the version of Node.js with the following command.
node --version
v16.19.1Install Dependencies
MQTT.js is a fully open-source client-side library for the MQTT protocol, written in JavaScript and available for Node.js and browsers. For more information and usage of MQTT.js, please refer to the MQTT.js GitHub.
MQTT.js can be installed via NPM or Yarn, or can be imported through CDN or relative path. This example will install MQTT.js through Yarn command.
Using NPM or Yarn:
Install MQTT.js
shell# NPM npm install mqtt # or Yarn yarn add mqtt
Connect over TCP port
You can set a client ID, username, and password with the following code. The client ID should be unique.
const clientId = 'emqx_nodejs_' + Math.random().toString(16).substring(2, 8)
const username = 'emqx_test'
const password = 'emqx_test'Establish a connection between the client and MQTT Broker using the following code.
const client = mqtt.connect('mqtt://broker.emqx.io:1883', {
clientId,
username,
password,
// ...other options
})Connect over TCP Secure port
If TLS/SSL encryption is enabled, the connection parameter options are consistent with establishing a connection through the TCP port. You only need to pay attention to changing the protocol to mqtts and matching the correct port number.
Establish a connection between the client and MQTT Broker using the following code.
const client = mqtt.connect('mqtts://broker.emqx.io:8883', {
clientId,
username,
password,
// ...other options
})Connect over WebSocket Port
MQTT WebSocket uniformly uses /path as the connection path, which needs to be specified when connecting, while EMQX Broker uses /mqtt as the path.
Therefore, when using WebSocket connection, in addition to modifying the port number and switching the protocol to ws, you also need to add the /mqtt path.
Establish a connection between the client and MQTT Broker using the following code.
const client = mqtt.connect('ws://broker.emqx.io:8083/mqtt', {
clientId,
username,
password,
// ...other options
})Connect over WebSocket Secure Port
If TLS/SSL encryption is enabled, the connection parameter option is consistent with establishing a connection through the WebSocket port. You only need to pay attention to changing the protocol to 'wss' and matching the correct port number
Establish a connection between the client and MQTT Broker using the following code.
const client = mqtt.connect('wss://broker.emqx.io:8084/mqtt', {
clientId,
username,
password,
// ...other options
})Subscribe and Publish
Subscribe to Topics
Specify a topic and the corresponding QoS level to be subscribed.
const topic = '/nodejs/mqtt'
const qos = 0
client.subscribe(topic, { qos }, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log('subscribe error:', error)
return
}
console.log(`Subscribe to topic '${topic}'`)
})Unsubscribe to Topics
You can unsubscribe using the following code, specifying the topic and corresponding QoS level to be unsubscribed.
const topic = '/nodejs/mqtt'
const qos = 0
client.unsubscribe(topic, { qos }, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log('unsubscribe error:', error)
return
}
console.log(`unsubscribed topic: ${topic}`)
})Publish Messages
When publishing a message, the MQTT broker must be provided with information about the target topic and message content.
const topic = '/nodejs/mqtt'
const payload = 'nodejs mqtt test'
const qos = 0
client.publish(topic, payload, { qos }, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.error(error)
}
})Receive Messages
The following code listens for message events and prints the received message and topic to the console when a message is received.
client.on('message', (topic, payload) => {
console.log('Received Message:', topic, payload.toString())
})Disconnect from MQTT Broker
To disconnect the client from the broker, use the following code:
if (client.connected) {
try {
client.end(false, () => {
console.log('disconnected successfully')
})
} catch (error) {
console.log('disconnect error:', error)
}
}The above section only shows some key code snippets, for the full project code, please refer to MQTT-Client-Node.js. You can download and try it out yourself.
Test the Connection
We add a line of startup script to the script field in the package.json file.
"scripts": {
"start": "node index.js"
}Then we can simply use npm start to run the project.
npm startAfter running, we can see the output information of the console as follows:
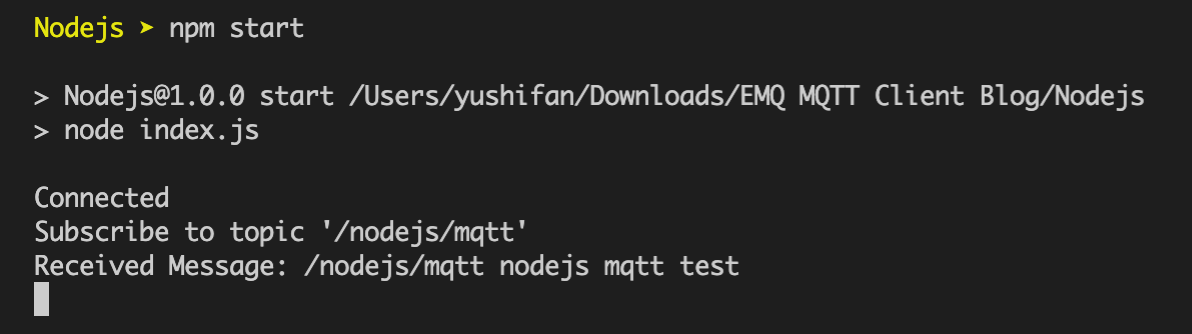
We see that the client has successfully connected to the MQTT broker and subscribed to the topic, received and published messages successfully. At this point, we will use MQTT 5.0 Client Tool - MQTTX as another client for the message publishing and receiving test.
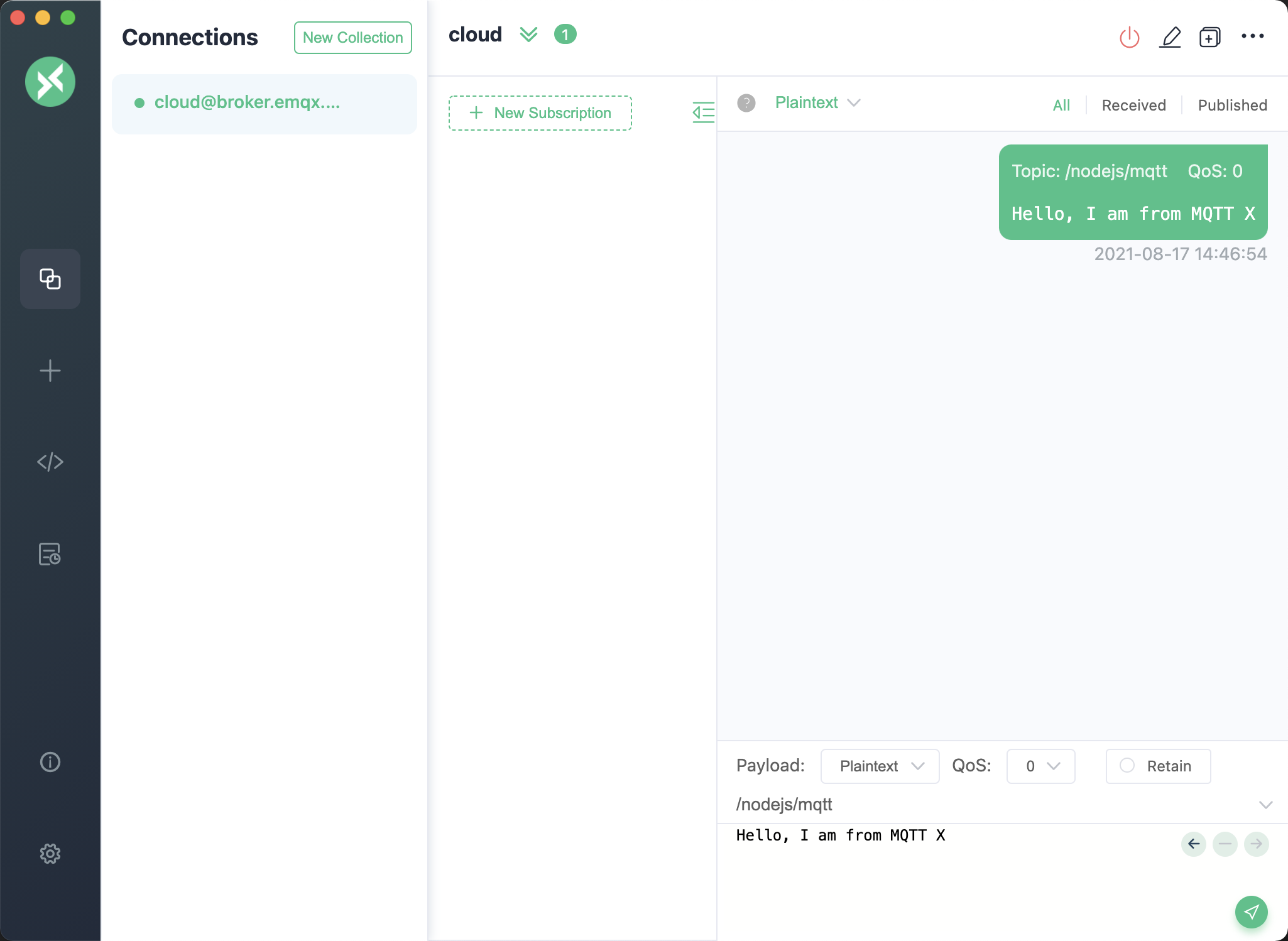
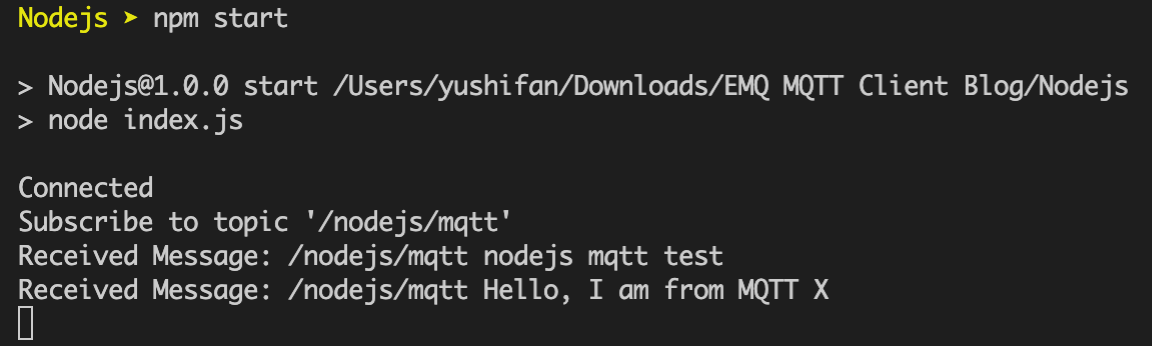
We can see that the message sent by MQTTX is printed in the console.
More
In conclusion, we have implemented creating MQTT connections in a Node.js project and simulated scenarios of subscribing, publishing messages, unsubscribing, and disconnecting between clients and MQTT servers. You can download the complete example source code on the MQTT-Client-Node.js page, and we also welcome you to explore more demo examples in other languages on the MQTT Client example page.