Stream MQTT Data into Amazon Kinesis
AWS Kinesis is a fully managed real-time streaming data processing service on AWS that facilitates easy collection, processing, and analysis of streaming data. It can economically and efficiently handle streaming data of any scale in real-time and offers high flexibility, capable of low-latency processing of any amount of streaming data from hundreds of thousands of sources.
EMQX Cloud supports seamless integration with Amazon Kinesis Data Streams, enabling the connection of massive IoT devices for real-time message collection and transmission. Through the data integration, it connects to Amazon Kinesis Data Streams for real-time data analysis and complex stream processing.
This page provides a detailed introduction to the functional features of Kafka Data Integration and offers practical guidance for creating it. The content includes creating Amazon Kinesis connectors, creating rules, and testing rules. It demonstrates how to report simulated temperature and humidity data to EMQX Cloud via the MQTT protocol and store the data in Amazon Kinesis through configured data integration.
How It Works
Amazon Kinesis data integration is an out-of-the-box feature of EMQX designed to help users seamlessly integrate MQTT data streams with Amazon Kinesis and leverage its rich services and capabilities for IoT application development.
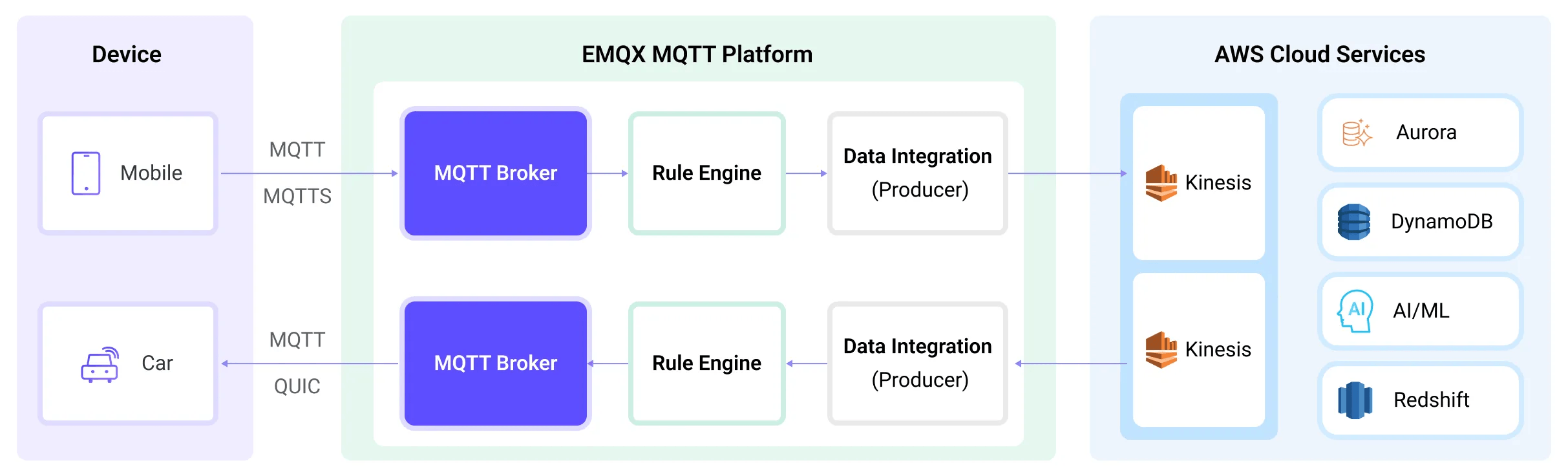
EMQX forwards MQTT data to Amazon Kinesis through the rule engine and Sink. The complete process is as follows:
- IoT Devices Publish Messages: Devices publish telemetry and status data through specific topics, triggering the rule engine.
- Rule Engine Processes Messages: Using the built-in rule engine, MQTT messages from specific sources are processed based on topic matching. The rule engine matches corresponding rules and processes messages, such as converting data formats, filtering specific information, or enriching messages with contextual information.
- Bridging to Amazon Kinesis: The action triggered by rules to forward messages to Amazon Kinesis allows for custom configuration of partition keys, the data stream to write to, and message format, enabling flexible data integration.
After MQTT message data is written to Amazon Kinesis, you can perform flexible application development, such as:
- Real-time Data Processing and Analysis: Utilize powerful Amazon Kinesis data processing and analysis tools and its own streaming capabilities to perform real-time processing and analysis of message data, obtaining valuable insights and decision support.
- Event-Driven Functionality: Trigger Amazon event handling to achieve dynamic and flexible function triggering and processing.
- Data Storage and Sharing: Transmit message data to Amazon Kinesis storage services for secure storage and management of large volumes of data. This allows you to share and analyze this data with other Amazon services to meet various business needs.
Features and Advantages
The data integration between EMQX Cloud and AWS Kinesis Data Streams can bring the following functionalities and advantages to your business:
- Reliable Data Transmission and Sequence Guarantee: Both EMQX and AWS Kinesis Data Streams provide reliable data transmission mechanisms. EMQX ensures the reliable transmission of messages through the MQTT protocol, while AWS Kinesis Data Streams uses partitions and sequence numbers to guarantee message ordering. Together, they ensure that messages sent from devices accurately reach their destination and are processed in the correct order.
- Real-time Data Processing: High-frequency data from devices can undergo preliminary real-time processing through EMQX's rule SQL, effortlessly filtering, extracting, enriching, and transforming MQTT messages. After sending data to AWS Kinesis Data Streams, further real-time analysis can be implemented by combining AWS Lambda and AWS-managed Apache Flink.
- Elastic Scalability Support: EMQX can easily connect millions of IoT devices and offers elastic scalability. AWS Kinesis Data Streams, on the other hand, employs on-demand automatic resource allocation and expansion. Applications built with both can scale with connection and data sizes, continuously meeting the growing needs of the business.
- Persistent Data Storage: AWS Kinesis Data Streams provides persistent data storage capabilities, reliably saving millions of incoming device data streams per second. It allows for the retrieval of historical data when needed and facilitates offline analysis and processing.
Utilizing AWS Kinesis Data Streams to build a streaming data pipeline significantly reduces the difficulty of integrating EMQX with the AWS platform, providing users with richer and more flexible data processing solutions. This can help EMQX users to build functionally complete and high-performance data-driven applications on AWS.
Before You Start
This section outlines the required setup steps before creating an AWS Kinesis Data Integration on the EMQX Cloud. You'll configure the network, create necessary AWS resources, and optionally set up a local testing environment.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure that you are familiar with the concepts used in EMQX Data Integration:
- Rules in EMQX
- Data Integration capabilities
Set up Network
To enable EMQX to communicate with AWS Kinesis, you need to configure network access. This section explains the following two supported approaches:
- NAT Gateway: Configure a NAT Gateway in your deployment to access AWS services using a public IP. For configuration guidance, see NAT Gateway.
- AWS PrivateLink: Establish a PrivateLink connection between EMQX and AWS Kinesis. Follow the instructions in the sections below to create a VPC endpoint and set up the PrivateLink connection.
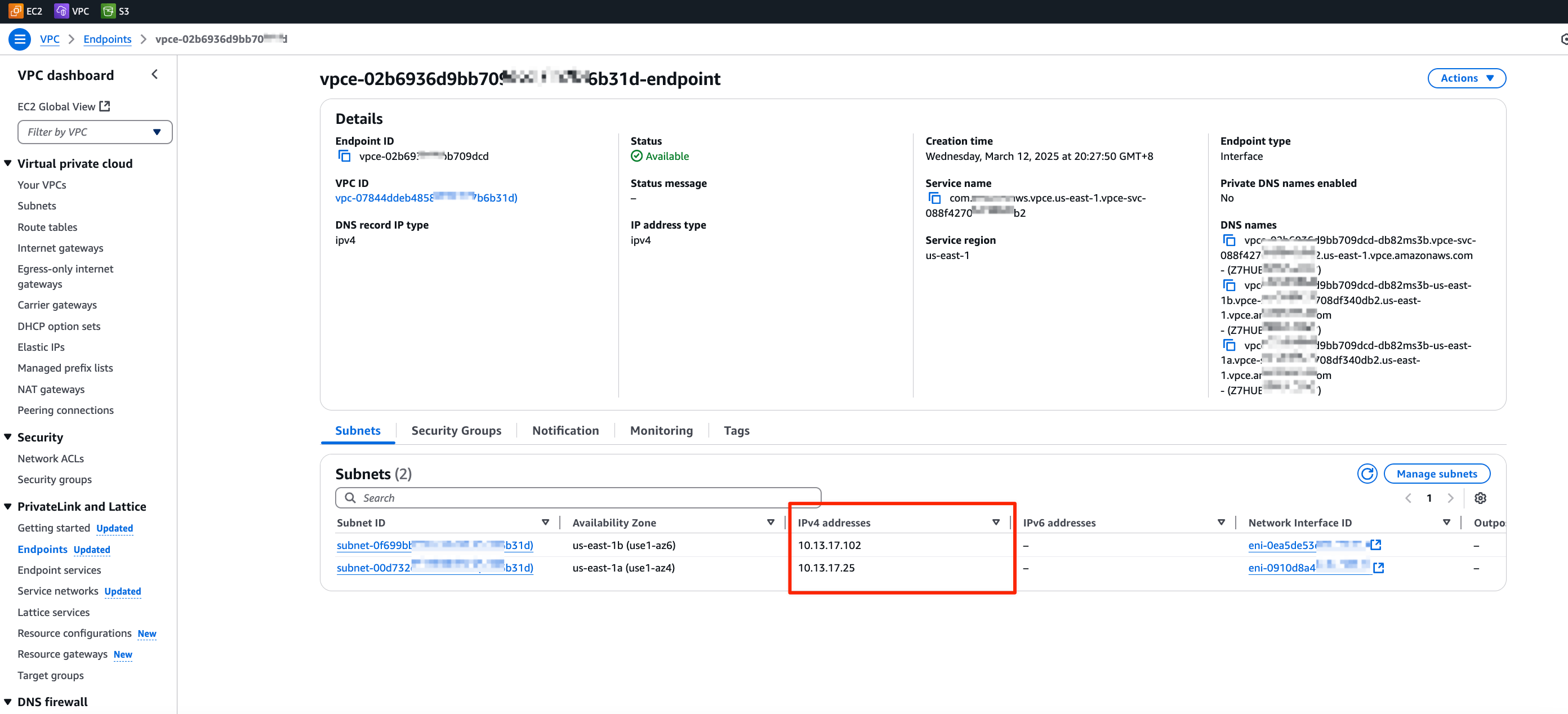
Create an Interface VPC Endpoint to Access Kinesis
This subsection guides you through creating an Interface VPC Endpoint in AWS. This endpoint enables private and secure connectivity between your VPC and AWS Kinesis without traversing the public internet.
- Open the Amazon VPC console.
- In the navigation pane, select Endpoints.
- Click Create endpoint.
- For Type, select AWS services.
- For Service name, select the Kinesis service.
- Configure the VPC, Subnet(s), and configure the Security Group to allow access from your EMQX deployment.
- Ensure the selected subnets are in the same Availability Zone as your EMQX deployment. See Obtain AZ ID from EMQX Cloud Console for guidance.
- Click Create Endpoint and record the IP address for use when configuring the target group.
For more details, refer to the AWS official documentation.
Create a PrivateLink Connection between EMQX and Kinesis
To enable secure and private communication between EMQX and AWS Kinesis, especially in environments without public internet access, you need to establish a PrivateLink connection. The steps below guide you through configuring the required AWS resources and enabling PrivateLink support in the EMQX Cloud.
Complete steps 1 to 3 in Complete Preparatory Steps on the AWS Platform.
In Step 3 "Create a target group for load balancing", configure the following:
Basic configuration:
- Choose a target type: Select
IP addresses - Protocol: Port:
TPC : 443 - VPC: Select the same VPC as the Kinesis Endpoint.
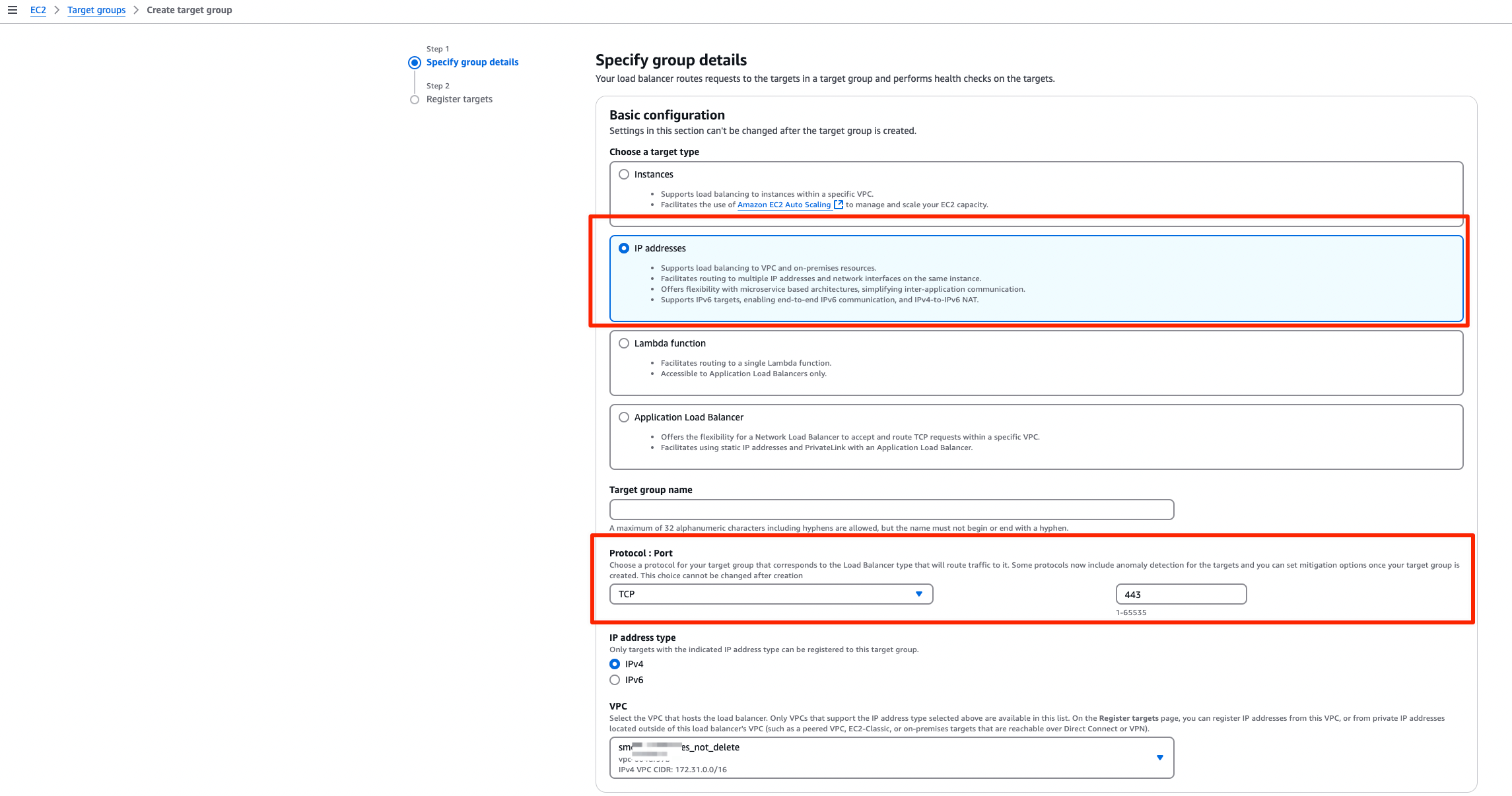
- Choose a target type: Select
Register targets: Enter the subnet IP address recorded in Create an Interface VPC Endpoint to Access Kinesis and set the Port to
443.
Continue with Step 4 in Complete Preparatory Steps on the AWS Platform to create and configure the Network Load Balancer (NLB).
Make sure that the Availability Zones match your EMQX deployment.
Set the Protocol:Port in Lisenters to
TCP:443.
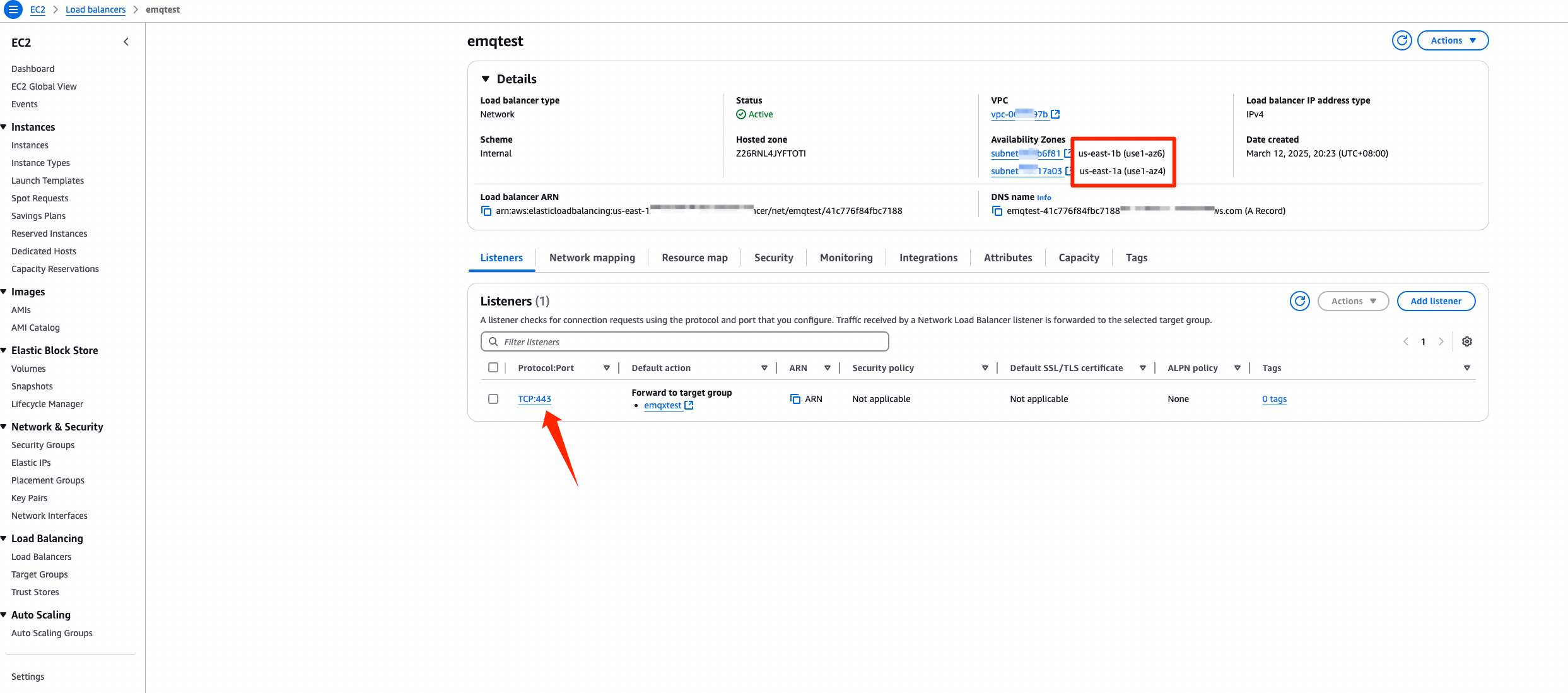
Follow Create An Endpoint Service.
- In Available load balancers, select the NLB created in the previous step.
Follow Enable PrivateLink on EMQX Cloud.
Save the generated PrivateLink address. It will be required when configuring the Kinesis connector.
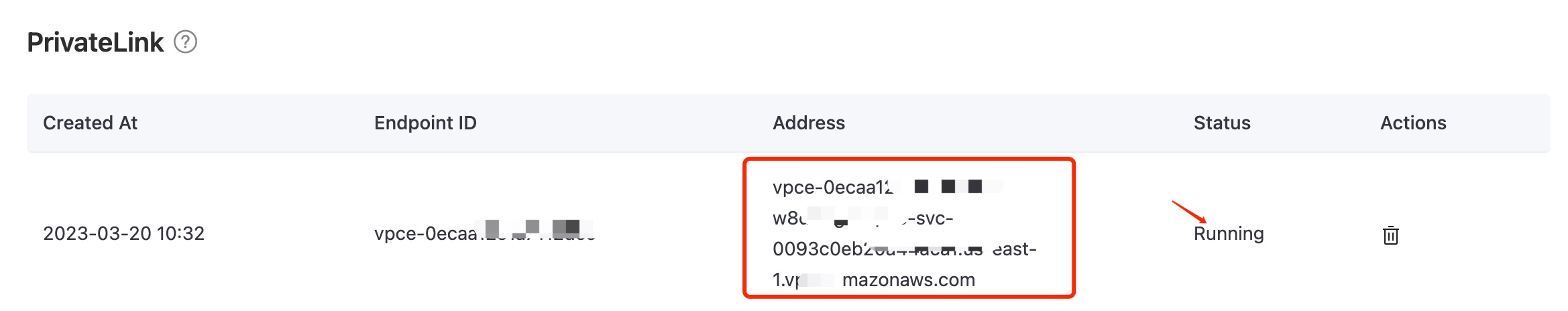
Create Stream in Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
In this step, you will create a Kinesis Data Stream via the AWS Management Console (see this tutorial for more details). The data stream will serve as the destination for messages sent from EMQX Cloud.
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Kinesis console.
In the navigation bar, expand the Region selector and choose a Region.
Choose Create data stream.
On the Create Kinesis stream page, enter a name for your data stream and then choose the On-demand or Provisioned capacity mode.
Emulate Amazon Kinesis Data Streams locally (Optional)
For development and testing purposes, you can emulate the Kinesis service locally using LocalStack. This allows you to run AWS-compatible services on your local machine without connecting to the cloud.
Install and run it using a Docker Image:
bash# To start the LocalStack docker image locally docker run --name localstack -p '4566:4566' -e 'KINESIS_LATENCY=0' -d localstack/localstack:2.1 # Access the container docker exec -it localstack bashCreate a stream named my_stream with only one shard:
bashawslocal kinesis create-stream --stream-name "my_stream" --shard-count 1
Create a Amazon Kinesis Connector
Before creating data integration rules, you must first create a Amazon Kinesis connector to allow EMQX Cloud to send data to the Kinesis service.
Go to your deployment. Click Data Integration from the left-navigation menu.
If this is your first time creating a connector, select Amazon Kinesis under the Data Forward category. If you have existing connectors, click New Connector, then select Amazon Kinesis under Data Forward.
On the New Connector page, configure the following options:
- Amazon Kinesis Endpoint:
- If using a NAT Gateway, enter the endpoint in the format
https://kinesis.<region>.amazonaws.com. Replace<region>with the region where your AWS Kinesis services is hosted. - If using AWS PrivateLink, enter the PrivateLink address of the Kinesis service. Make sure it starts with
https://. - If using LocalStack, use
http://localhost:4566.
- If using a NAT Gateway, enter the endpoint in the format
- AWS Access Key ID: Enter the Access key ID. If using LocalStack, enter any value.
- AWS Secret Access Key: Enter the secret access key. If using LocalStack, enter any value.
- Use default values for other settings, or configure them according to your business needs.
- Amazon Kinesis Endpoint:
Click the Test button to verify connectivity to the Kinesis service. If the connection is successful, a confirmation message will appear.
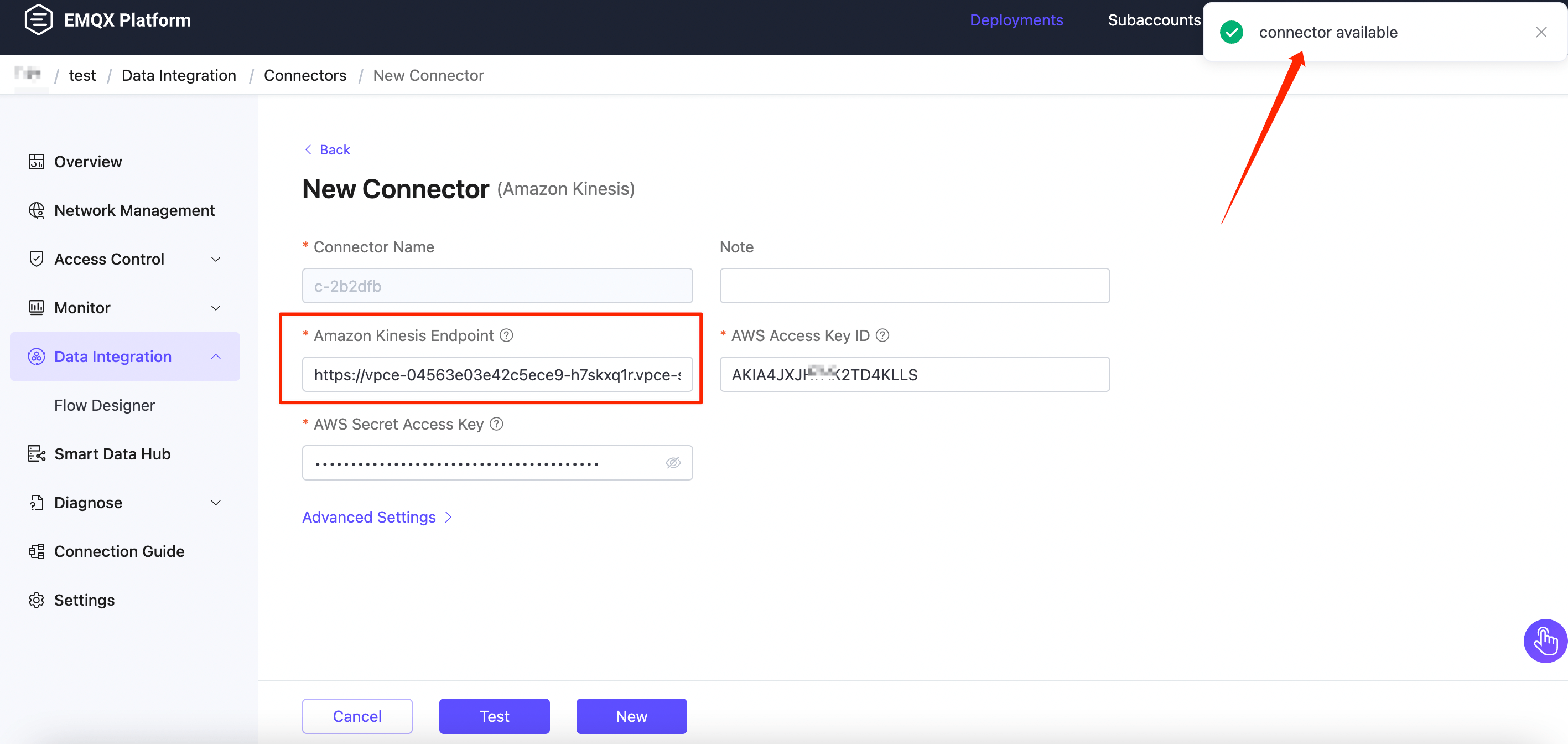
Click New to complete the connector setup.
Create a Rule
Next, you need to create a rule to specify the data to be written and add corresponding actions in the rule to forward the processed data to Amazon Kinesis.
Click New Rule in Rules area or click the New Rule icon in the Actions column of the connector you just created.
Enter the rule matching SQL statement in the SQL editor. The following SQL example reads the message reporting time
up_timestamp, client ID, and message body (Payload) from messages sent to thetemp_hum/emqxtopic, extracting temperature and humidity.sqlSELECT timestamp, clientid, payload.temp as temp, payload.hum as hum FROM "temp_hum/emqx"You can use Try It Out to simulate data input and test the results.
Click Next to add an action.
Select the connector you just created from the Connector dropdown box.
Configure the following information:
Action Name: The system will automatically generate an action name.
Amazon Kinesis Stream: Enter the stream name you created in Create Stream in Amazon Kinesis Data Streams.
Partition Key: Enter the Partition Key that shall be associated with records that are sent to this stream. Placeholders of the form ${variable_name} are allowed (see next step for example on placeholders).
In the Payload Template field, leave it blank or define a template.
If left blank, it will encode all visible inputs from the MQTT message using JSON format, such as clientid, topic, payload, etc.
If using the defined template, placeholders in the format of ${variable_name} will be substituted with the corresponding values from the MQTT context.
For instance, if the MQTT message topic is my/topic, ${topic} will be replaced with it. And you have the flexibility to adjust the template according to your requirements. Simply input the temperature and humidity values that need to be forwarded.
bash{"timestamp": ${timestamp}, "client_id": ${client_id}, "temp": ${temp}, "hum": ${hum}}
Advanced settings (optional): Choose whether to use buffer queue and batch mode as needed.
Click the Confirm button to complete the rule creation.
In the Successful new rule pop-up, click Back to Rules, thus completing the entire data integration configuration chain.
Test the Rule
You are recommended to use MQTTX to simulate temperature and humidity data reporting, but you can also use any other client.
Use MQTTX to connect to the deployment and send messages to the following Topic.
topic:
temp_hum/emqxpayload:
json{"temp":"23.5","hum":"32.6"}
View operational data in the console. Click the rule ID in the rule list, and you can see the statistics of the rule and the statistics of all actions under this rule.
Go to Amazon Kinesis Data Viewer. You should see the message when getting records.
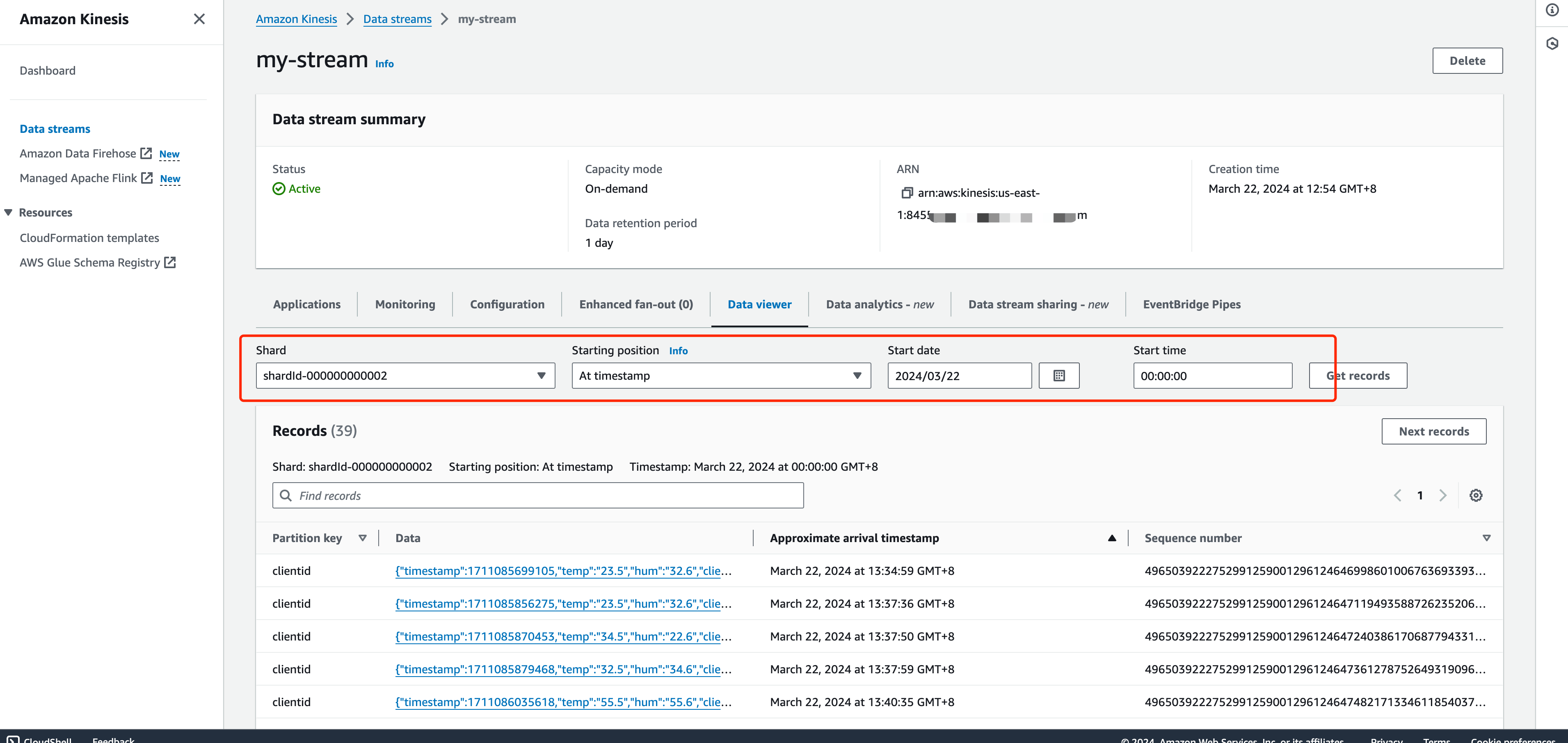
Use LocalStack to Check.
If you use LocalStack, follow the steps below to check the received data.
- Use the following command to get the ShardIterator before sending the message to the EMQX.
bashawslocal kinesis get-shard-iterator --stream-name my_stream --shard-id shardId-000000000000 --shard-iterator-type LATEST { "ShardIterator": "AAAAAAAAAAG3YjBK9sp0uSIFGTPIYBI17bJ1RsqX4uJmRllBAZmFRnjq1kPLrgcyn7RVigmH+WsGciWpImxjXYLJhmqI2QO/DrlLfp6d1IyJFixg1s+MhtKoM6IOH0Tb2CPW9NwPYoT809x03n1zL8HbkXg7hpZjWXPmsEvkXjn4UCBf5dBerq7NLKS3RtAmOiXVN6skPpk=" }Use MQTTX to send messages on the topic
temp_hum/emqx.Read the records and decode the received data.
bashawslocal kinesis get-records n--shard-iterator="AAAAAAAAAAG3YjBK9sp0uSIFGTPIYBI17bJ1RsqX4uJmRllBAZmFRnjq1kPLrgcyn7RVigmH+WsGciWpImxjXYLJhmqI2QO/DrlLfp6d1IyJFixg1s+MhtKoM6IOH0Tb2CPW9NwPYoT809x03n1zL8HbkXg7hpZjWXPmsEvkXjn4UCBf5dBerq7NLKS3RtAmOiXVN6skPpk=" { "Records": [ { "SequenceNumber": "49642650476690467334495639799144299020426020544120356866", "ApproximateArrivalTimestamp": 1689389148.261, "Data": "eyAibXNnIjogImhlbGxvIEFtYXpvbiBLaW5lc2lzIiB9", "PartitionKey": "key", "EncryptionType": "NONE" } ], "NextShardIterator": "AAAAAAAAAAFj5M3+6XUECflJAlkoSNHV/LBciTYY9If2z1iP+egC/PtdVI2t1HCf3L0S6efAxb01UtvI+3ZSh6BO02+L0BxP5ssB6ONBPfFgqvUIjbfu0GOmzUaPiHTqS8nNjoBtqk0fkYFDOiATdCCnMSqZDVqvARng5oiObgigmxq8InciH+xry2vce1dF9+RRFkKLBc0=", "MillisBehindLatest": 0 } echo 'eyAibXNnIjogImhlbGxvIEFtYXpvbiBLaW5lc2lzIiB9' | base64 -d {"temp":"23.5","hum":"32.6"}