Ingest MQTT Data into Apache Doris
Note
The Apache Doris data integration is available for EMQX version 5.91 and later in the Dedicated Flex edition.
Apache Doris is a modern Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) analytical database system known for high concurrency, high performance, and ease of use. It is particularly well-suited for scenarios involving real-time analytics and data warehousing. With EMQX 5.10.0, you can integrate MQTT data with Apache Doris, enabling efficient storage, real-time analysis, and powerful data visualization.
This guide provides practical instructions on how to configure and validate the data integration between EMQX Cloud and Apache Doris.
Note
Apache Doris data integration in EMQX supports Apache Doris version 2.1.7 and later.
How It Works
Apache Doris data integration is an out-of-the-box feature in EMQX Cloud, which enables complex business development through simple configuration. In a typical IoT application, the EMQX Cloud is responsible for device connection and transmitting messages. Apache Doris, as the data storage platform, is responsible for storing device status and metadata, as well as message data storage and data analysis.
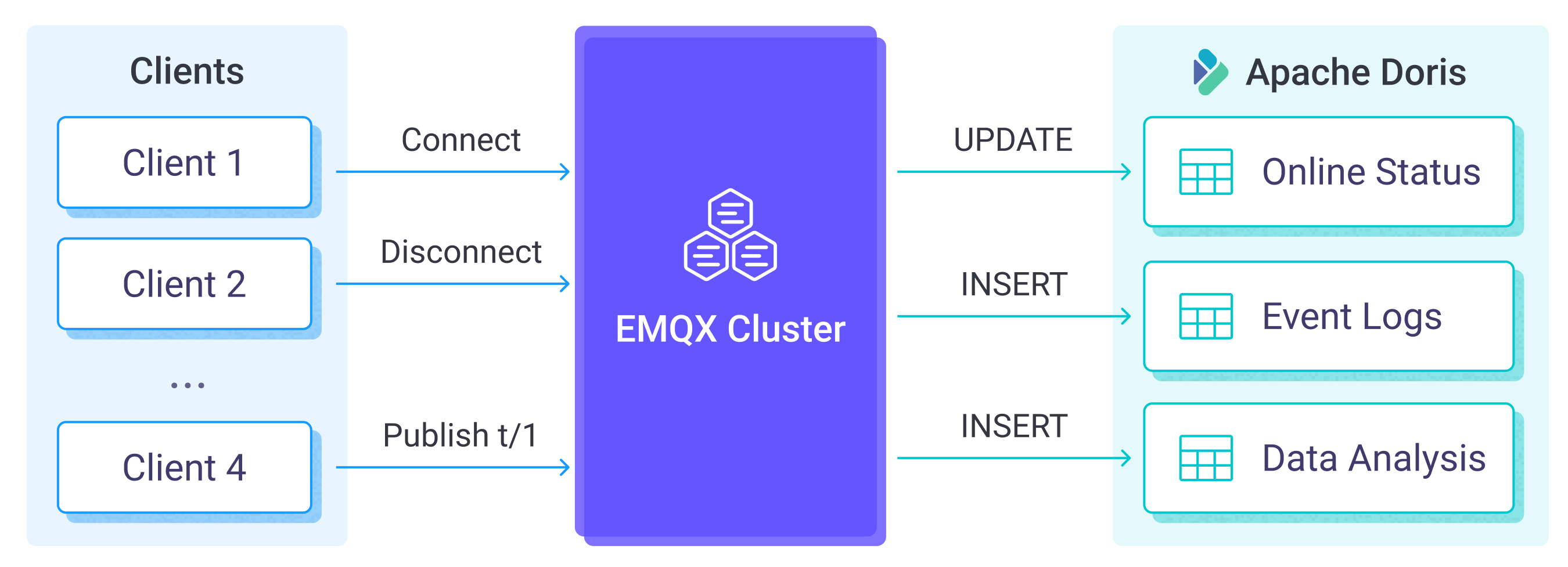
EMQX Cloud forwards device events and data to Apache Doris through the rule engine and action. Applications can read the data in Apache Doris to sense the device status, obtain device online and offline records, and analyze device data. The specific workflow is as follows:
- IoT devices connect to EMQX Cloud: After IoT devices are successfully connected through the MQTT protocol, online events will be triggered. The events include information such as device ID, source IP address, and other attributes.
- Message publication and reception: The devices publish telemetry and status data to specific topics. When EMQX Cloud receives these messages, it initiates the matching process within its rules engine.
- Rule Engine Processing Messages: With the built-in rules engine, messages and events from specific sources can be processed based on topic matching. The rules engine matches the corresponding rules and processes messages and events, such as converting data formats, filtering out specific information, or enriching messages with contextual information.
- Write to Apache Doris: The rule triggers the writing of messages to Apache Doris. With the help of SQL templates, users can extract data from the rule processing results to construct SQL and send it to Apache Doris for execution, so that specific fields of the message can be written or updated into the corresponding tables and columns of the database.
After the event and message data are written to Apache Doris, you can connect to Apache Doris to read the data for flexible application development, such as:
- Connect to visualization tools, such as Grafana, to generate charts based on data and show data changes.
- Connect to the device management system, view the device list and status, detect abnormal device behavior, and eliminate potential problems in a timely manner.
Features and Benefits
The data integration with Apache Doris can bring the following features and advantages to your business:
- Flexible Event Handling: Through the EMQX rules engine, Apache Doris can handle device lifecycle events, greatly facilitating the development of various management and monitoring tasks required for implementing IoT applications. By analyzing event data, you can promptly detect device failures, abnormal behavior, or trend changes to take appropriate measures.
- Message Transformation: Messages can undergo extensive processing and transformation through EMQX rules before being written to Apache Doris, making storage and usage more convenient.
- Real-Time Data Ingestion: Apache Doris supports real-time data ingestion via HTTP and JDBC interfaces. When integrated with EMQX, MQTT data can be written directly into Doris tables with low latency, making it ideal for scenarios that require immediate query and analytics capabilities.
- Streaming Synchronization: Apache Doris also supports ingesting real-time data streams from sources like Flink, Kafka, and transactional databases. This makes it ideal for building unified pipelines that combine MQTT data from EMQX with other streaming data sources for comprehensive real-time analysis.
- Standard SQL and Ecosystem Compatibility: Doris is fully compatible with MySQL syntax and supports standard SQL, allowing users to perform powerful analytical queries without learning new languages. It integrates easily with business intelligence (BI) tools and client applications for dashboards, reports, and automation workflows.
- Runtime Metrics: Support for viewing runtime metrics of each action, such as total message count, success/failure counts, current rates, and more.
Through flexible event handling, extensive message transformation, flexible data operations, and real-time monitoring and analysis capabilities, you can build efficient, reliable, and scalable IoT applications, benefiting your business decisions and optimizations.
Before You Start
This section describes the preparations you need to complete before you start to create the Apache Doris data integration in the EMQX Cloud Console, including installing the Apache Doris server and creating data tables.
Prerequisites
- Understand rules.
- Understand data integration.
Set up Network
Before configuring data integration, you must create an EMQX Cloud deployment and ensure network connectivity between EMQX Cloud and the target service.
For Dedicated Flex deployments:
Create a VPC Peering Connection between the EMQX Cloud VPC and the target service VPC. After the peering connection is established, EMQX Cloud can access the target service through its private IP address.
If access through a public IP is required, configure a NAT Gateway to enable outbound connectivity.
For BYOC (Bring Your Own Cloud) deployments:
Create a VPC peering connection between the VPC where the BYOC deployment is running and the VPC hosting the target service. Once peering is in place, the target service can be accessed via its private IP address.
If the target service must be accessed through a public IP, configure a NAT Gateway in the BYOC VPC using your cloud provider’s console.
Install Apache Doris Server
Follow the official guide to run Doris locally using Docker Compose.
Create Data Tables
You can use a MySQL client to connect to a Doris Frontend and issue commands. See the official documentation.
For example:
mysql -uroot -P9030 -h127.0.0.1You need to create a database and two tables in Apache Doris:
- The data table
emqx_messagesis for storing the client ID, topic, payload, and creation time of every message. - The data table
emqx_client_eventsis for storing the client ID, event type, and creation time of every event.
create database mqtt;
use mqtt;
create table if not exists
emqx_messages(
clientid varchar,
topic string,
payload string,
created_at datetime
)
properties (replication_num = 1);
create table if not exists
emqx_client_events(
clientid varchar,
event varchar,
created_at datetime)
properties (replication_num = 1);Create a Connector
This section demonstrates how to create a Connector to allow EMQX Cloud to send data to the Apache Doris server.
- Go to your deployment. Click Data Integration from the left-navigation menu.
- If it is the first time for you to create a connector, select Doris under the Data Persistence category. If you have already created connectors, select New Connector and then select Doris under the Data Persistence category.
- On the New Connector page, configure the following information:
- Connector name: The system will automatically generate a connector name.
- Server Host: Enter
127.0.0.1:9030, or the actual hostname if the Apache Doris server is running remotely. - Database Name: Enter
mqtt. - Username: Enter
root. - Password: Enter
public.
- Configure advanced settings (optional) according to your business needs.
- Before clicking New, you can click Test to test if the connector can connect to the Apache Doris server.
- Click the New button at the bottom to complete the creation of the connector.
Create a Rule for Message Storage
This section demonstrates how to create a rule for processing messages from the source MQTT topic t/#, and saving the processed data to the Apache Doris data table emqx_messages via the configured action.
Click New Rule in the Rules area or click the New Rule icon in the Actions column of the connector you just created.
Enter
my_ruleas the rule ID, and set the rules in the SQL Editor with the following statement, which means the MQTT messages under topict/#will be saved to Apache Doris.Note: If you want to specify your own SQL syntax, make sure that you have included all fields required by the action in the
SELECTpart.sqlSELECT * FROM "t/#"TIP
If you are a beginner user, click SQL Examples and Try It Out to learn and test the SQL rule.
Click Next to add an action.
Select the connector you just created from the Connector dropdown box.
Configure the SQL Template based on the feature to use:
Note: This is a preprocessed SQL, so the fields should not be enclosed in quotation marks, and do not write a semicolon at the end of the statements.
sqlINSERT INTO emqx_messages(clientid, topic, payload, created_at) VALUES( ${clientid}, ${topic}, ${payload}, FROM_UNIXTIME(${timestamp}/1000) )If a placeholder variable is undefined in the SQL template, you can toggle the Undefined Vars as Null switch above the SQL template to define the rule engine behavior:
Disabled (default): The rule engine can insert the string
undefinedinto the database.Enabled: Allow the rule engine to insert
NULLinto the database when a variable is undefined.TIP
If possible, this option should always be enabled; disabling the option is only used to ensure backward compatibility.
Fallback Actions (Optional): If you want to improve reliability in case of message delivery failure, you can define one or more fallback actions. These actions will be triggered if the primary action fails to process a message. See Fallback Actions for more details.
Click the Confirm button to complete the action configuration.
In the Successful new rule pop-up, click Back to Rules, thus completing the entire data integration configuration chain.
Create a Rule for Events Recording
This section demonstrates how to create a rule for recording the clients' online/offline status and saving the events data to the Apache Doris table emqx_client_events via a configured action.
The rule creation steps are similar to those in Creating a rule for Message Storage, except for the SQL rule syntax and SQL template.
To create a rule for online/offline status recording, you can enter the following statement in the SQL Editor:
SELECT
*
FROM
"$events/client/connected", "$events/client/disconnected"To insert the client events data to the data table, you can use the following SQL template:
INSERT INTO emqx_client_events(clientid, event, created_at) VALUES (
${clientid},
${event},
FROM_UNIXTIME(${timestamp}/1000)
)Test the Rules
Use MQTTX to send a message to topic t/1 to trigger an online/offline event.
mqttx pub -i emqx_c -t t/1 -m '{ "msg": "hello Apache Doris" }'Check the running status of the two actions, there should be one new incoming and one new outgoing message, and 2 event records.
Check whether the data is written into the emqx_messages data table.
mysql> select * from emqx_messages;
+----------+-------+--------------------------+---------------------+
| clientid | topic | payload | created_at |
+----------+-------+--------------------------+---------------------+
| emqx_c | t/1 | { "msg": "hello Apache Doris" } | 2022-12-09 08:44:07 |
+----------+-------+--------------------------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)Check whether the data is written into the emqx_client_events table.
mysql> select * from emqx_client_events;
+----------+---------------------+---------------------+
| clientid | event | created_at |
+----------+---------------------+---------------------+
| emqx_c | client.connected | 2022-12-09 08:44:07 |
| emqx_c | client.disconnected | 2022-12-09 08:44:07 |
+----------+---------------------+---------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)