Connect with MicroPython + Raspberry Pi
This article mainly introduces the use of MicroPython on the Raspberry Pi (Raspberry Pi 4) to realize the functions of connecting, subscribing, and publishing messages between the client and the MQTT server.
MicroPython is a complete software implementation of the Python 3 programming language, written in C and optimized for a full Python compiler and runtime system running on top of MCU (microcontroller unit) hardware, providing the user with an interactive prompt (REPL) to immediately execute the supported commands. In addition to selected core Python libraries, MicroPython includes modules that give programmers access to low-level hardware, and is a streamlined implementation of the Python 3 language that includes a small portion of the Python standard library optimized to run on microcontrollers and in constrained environments.
Raspberry Pi developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in the UK, is an ARM-based microcomputer motherboard. It provides a USB interface and Ethernet interface to connect the keyboard, mouse and network cable. The motherboard has the basic functions of a PC, while Raspberry Pi has integrated Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and many GPIOs, and is widely used in teaching, home entertainment, IoT, etc.
This article demonstrates how to connect a MicroPython client on a Raspberry Pi 4 to a MQTT broker via the TCP port and the TLS/SSL port, respectively. For serverless deployments, see the demonstration on TLS/SSL port connections. Settings for connections over TCP ports are different from those for connections over TLS or SSL ports, but the code used in the publishing and subscribing functions is the same.
Prerequisites
Before the connection, you need to get the broker and client ready. Ensure you have completed the following prerequisites:
- Deploy MQTT Broker
- Install MicroPython
- Install the MQTT Client Library
Deploy MQTT Broker
To connect your application to the EMQX Cloud, you need to create and configure a deployment.
Serverless Deployment
Create a Serverless deployment in the EMQX Cloud Console.
Once the deployment is created and running, go to the deployment Overview page to find the MQTT connection information, including:
Broker address
Port number (only TLS ports are supported in Serverless)
Serverless deployments require TLS connections. Make sure to download the CA certificate from the Overview page and use port
8883for TLS.Configure the default authentication (username/password) under Access Control -> Client Authentication in the deployment.
For more details, refer to the Serverless Port Guide.
Dedicated Flex or BYOC Deployment
- You can create a Dedicated Flex or BYOC deployment in the EMQX Cloud Console.
- After creation, go to the deployment Overview page to retrieve MQTT connection information, including:
- Broker address
- TCP and TLS port numbers for MQTT and WebSocket (Both TCP and TLS connections are supported).
- Configure the default authentication (username/password) under Access Control -> Client Authentication in the deployment.
For detailed port configurations, see the Dedicated & BYOC Port Guide.
Install MicroPython
To install and write code using MicroPython, we need to complete the following installation on the Raspberry Pi 4. The Raspberry Pi operating system used in this article is Raspberry Pi OS with desktop (Debian version: 10, 64-bit).
When the OS used by the Raspberry Pi is based on Debian version: 10 (buster), you can install MicroPython directly with the following command.
bashsudo apt-get update sudo apt-get -y install micropythonTIP
If you get an E: Unable to locate package micropython error during installation, you can use the snap or build from source code to install.
If your Raspberry Pi OS is based on Debian version: 11 (bullseye), you can install MicroPython using snap.
bashsudo apt update sudo apt install snapd sudo reboot sudo snap install core sudo snap install micropython
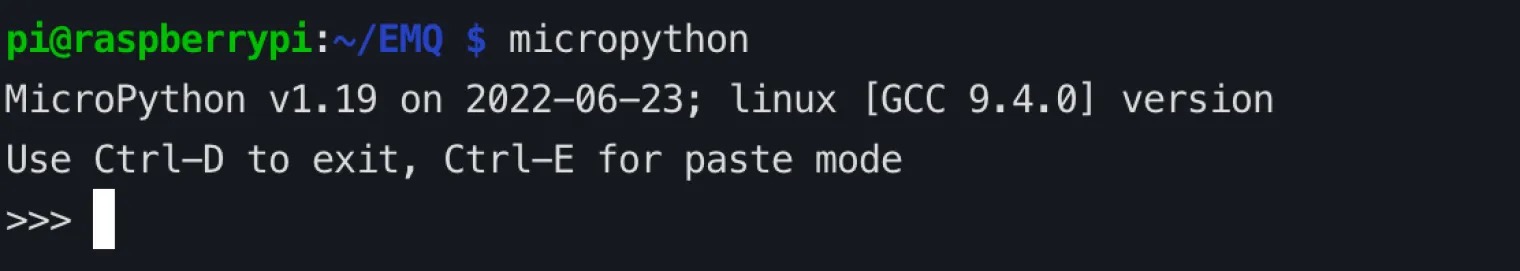
After the installation is complete, execute micropython in the terminal, and if MicroPython x.x (x means number) is returned, the installation is successful.
Install the MQTT Client Library
In order to easily connect to the MQTT server, we need to install the umqtt.simple library.
micropython -m upip install umqtt.simpleConnect over TCP Port
This section introduces how to connect MicroPython and MQTT servers through the TCP port on the Raspberry Pi. The complete code example is as follows:
Subscribe
Open any editor, type the following code and save it as a sub.py file:
# sub.py
import time
from umqtt.simple import MQTTClient
SERVER="broker.emqx.io"
ClientID = f'raspberry-sub-{time.time_ns()}'
user = "emqx"
password = "public"
topic = "raspberry/mqtt"
msg = b'{"msg":"hello"}'
def sub(topic, msg):
print('received message %s on topic %s' % (msg, topic))
def main(server=SERVER):
client = MQTTClient(ClientID, server, 1883, user, password)
client.set_callback(sub)
client.connect()
print('Connected to MQTT Broker "%s"' % (server))
client.subscribe(topic)
while True:
if True:
client.wait_msg()
else:
client.check_msg()
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Publish
Open any editor, type the following code, and save it as a pub.py file:
# pub.py
import time
from umqtt.simple import MQTTClient
server="broker.emqx.io"
ClientID = f'raspberry-pub-{time.time_ns()}'
user = "emqx"
password = "public"
topic = "raspberry/mqtt"
msg = b'{"msg":"hello"}'
def connect():
print('Connected to MQTT Broker "%s"' % (server))
client = MQTTClient(ClientID, server, 1883, user, password)
client.connect()
return client
def reconnect():
print('Failed to connect to MQTT broker, Reconnecting...' % (server))
time.sleep(5)
client.reconnect()
try:
client = connect()
except OSError as e:
reconnect()
while True:
print('send message %s on topic %s' % (msg, topic))
client.publish(topic, msg, qos=0)
time.sleep(1)Connect over TLS/SSL Port
This section introduces how to connect MicroPython and MQTT servers through the TLS/SSL port on the Raspberry Pi. The TCP port and TLS/SSL port connections are slightly different in the connection setup part, and the publish and subscribe part codes are the same. The complete code example is as follows:
Subscribe
Open any editor, type the following code, and save it as a sub-tls.py file:
# sub-tls.py
import time
import ussl
from umqtt.simple import MQTTClient
SERVER="broker.emqx.io"
ClientID = f'raspberry-sub-{time.time_ns()}'
user = "emqx"
password = "public"
topic = b'raspberry/mqtt'
msg = b"hello"
def sub(topic, msg):
print('received message %s on topic %s' % (msg, topic))
def main(server=SERVER):
client = MQTTClient(ClientID, server, 8883, user, password, ssl=True, ssl_params={'server_hostname': server})
client.set_callback(sub)
client.connect()
print('Connected to MQTT Broker "%s"' % (server))
client.subscribe(topic)
while True:
if True:
client.wait_msg()
else:
client.check_msg()
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Publish
Open any editor, type the following code, and save it as a pub-tls.py file:
# pub-tls.py
import time
import ussl
from umqtt.simple import MQTTClient
server = "broker.emqx.io"
ClientID = f'raspberry-pub-{time.time_ns()}'
user = "emqx"
password = "public"
topic = b'raspberry/mqtt'
msg = b'{"msg":"hello"}'
def connect():
print('Connected to MQTT Broker "%s"' % server)
client = MQTTClient(ClientID, server, 8883, user, password, ssl=True, ssl_params={'server_hostname': server})
try:
client.connect()
return client
except Exception as e:
print('Failed to connect to MQTT broker:', e)
raise
def reconnect():
print('Failed to connect to MQTT broker. Reconnecting...')
time.sleep(5)
client = connect()
return client
try:
client = connect()
except Exception:
client = reconnect()
while True:
try:
print('Sending message %s on topic %s' % (msg, topic))
client.publish(topic, msg, qos=0)
time.sleep(1)
except Exception as e:
print('Failed to publish message:', e)
client = reconnect()Testing
We use the MQTT 5.0 client tool MQTTX for the following tests:
Test subscribe
After successfully connecting to the MQTT server, you can use the Raspberry Pi and MQTTX to test the connection.
Open the terminal, run the MicroPython code, and listen for messages.
bashmicropython sub.py
Use the MQTTX client to establish a connection with the MQTT server and send messages to the topic
raspberry/mqtt.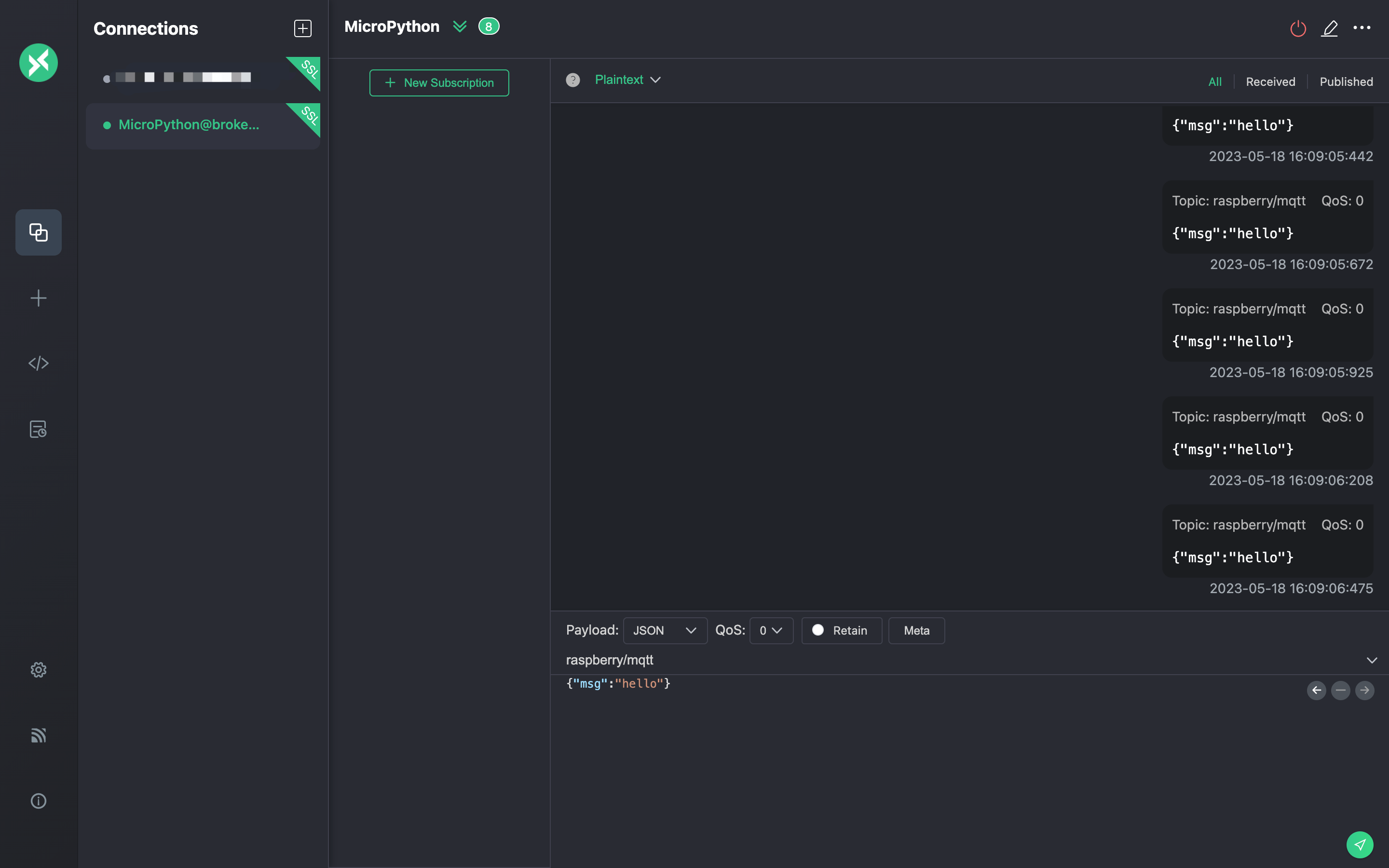
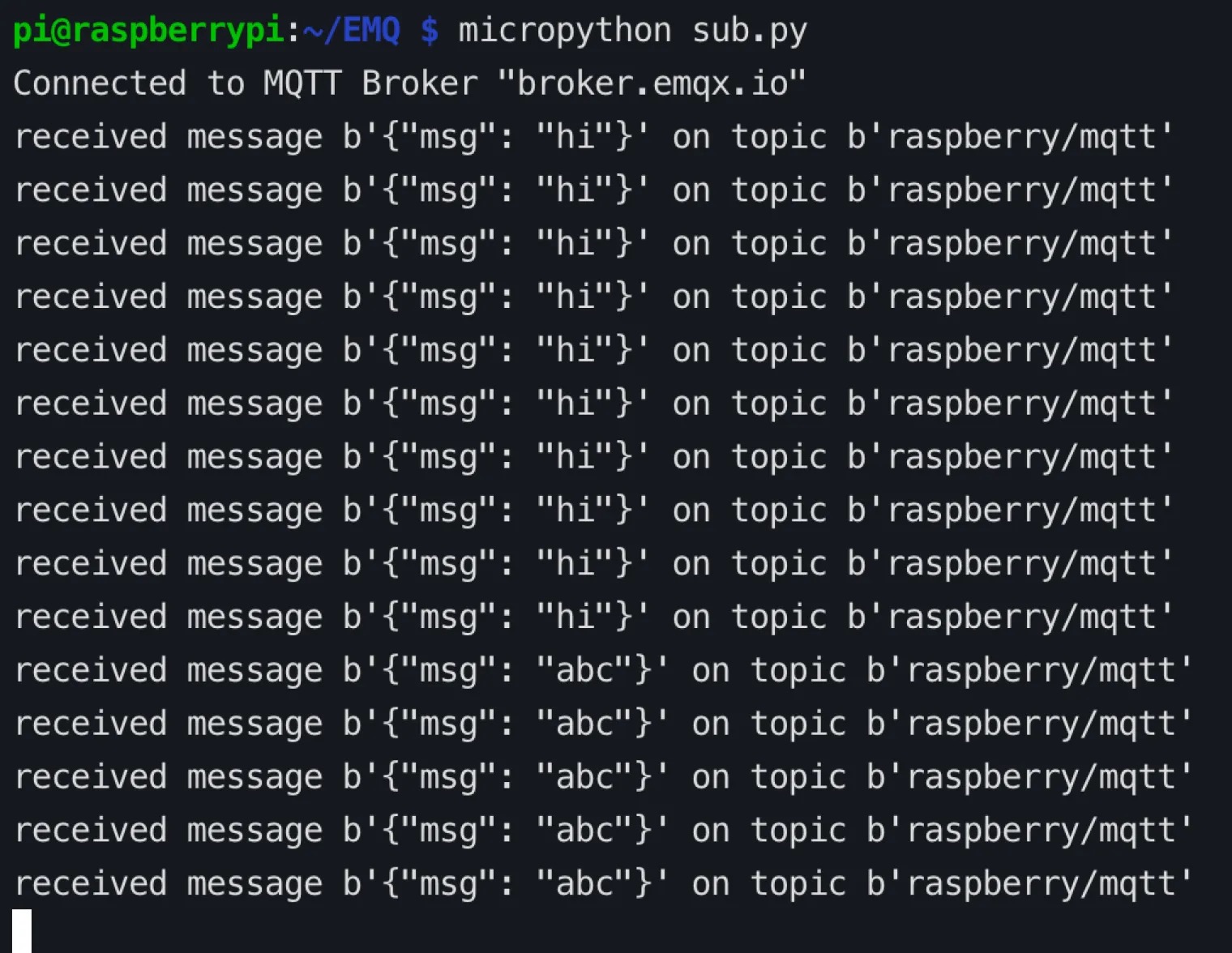
View messages received by MicroPython on the Raspberry Pi.
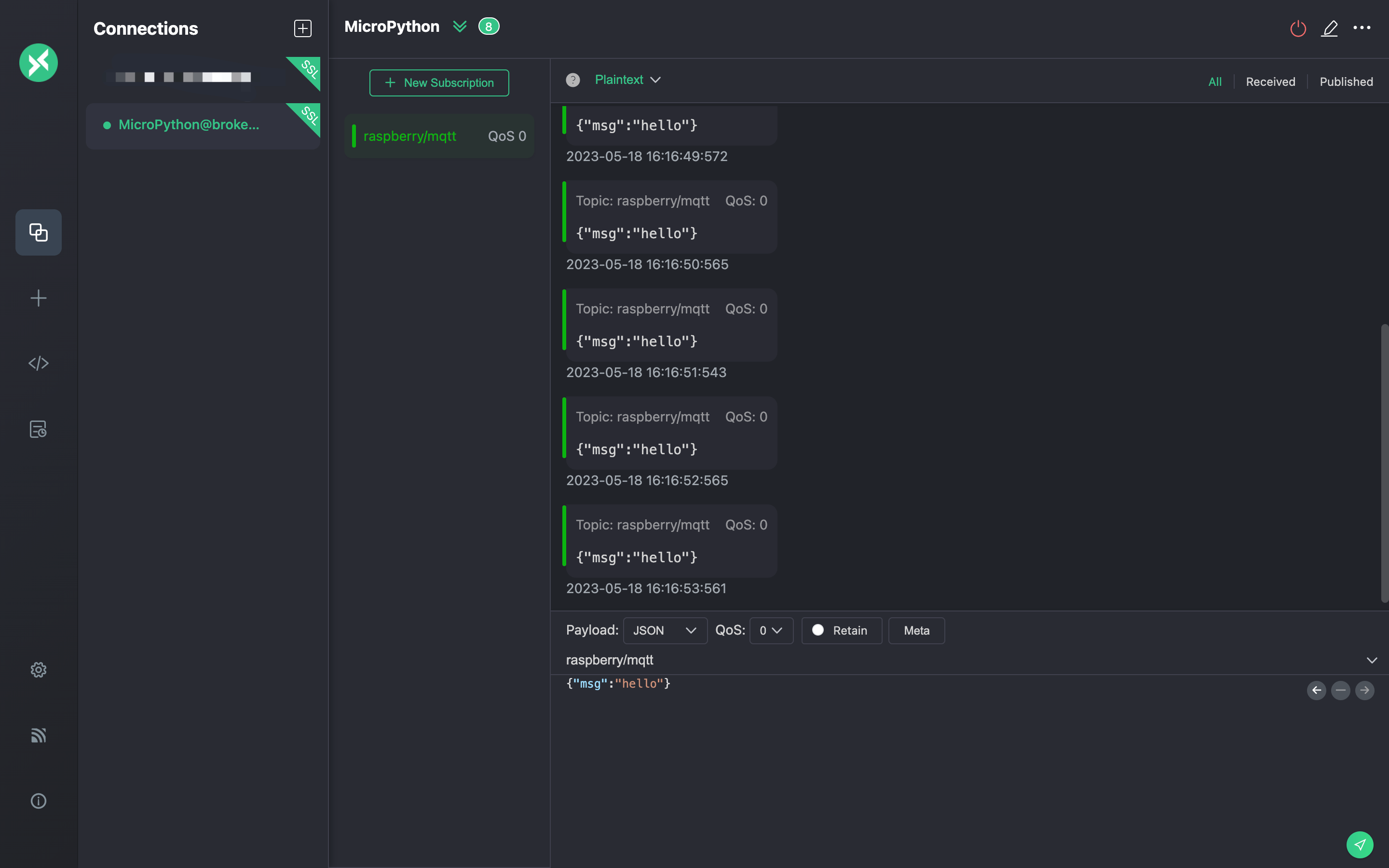
Test publish
Subscribe to the
raspberry/mqtttopic in the MQTTX client.Run the MicroPython code in the terminal, publish the message.
bashmicropython pub.py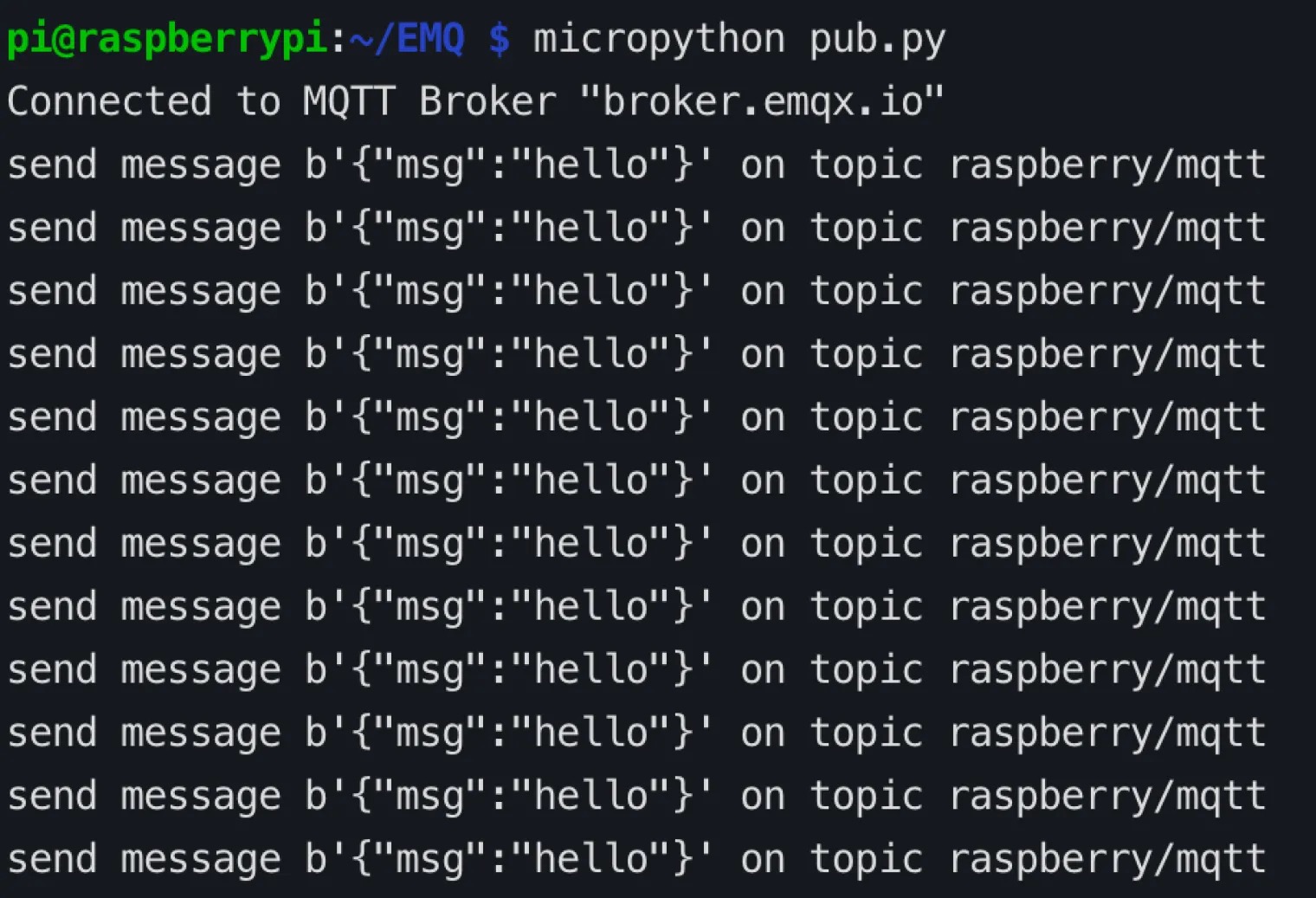
In the MQTTX client, view the messages sent by the Raspberry Pi.
More
To sum up, we have created an MQTT connection in the MicroPython project and simulated the scenario of using the client to connect, subscribe, and send and receive messages to the MQTT server. You can download the source code of the example at here, and you can also download it at GitHub to find more demo examples in other languages.