Ingest MQTT Data into Amazon S3
Amazon S3 is an internet-based storage service known for its high reliability, stability, and security, allowing for rapid deployment and ease of use. EMQX Cloud is capable of efficiently storing MQTT messages into Amazon S3 buckets, enabling flexible Internet of Things (IoT) data storage functionalities.
This page provides a detailed introduction to the data integration between EMQX Cloud and Amazon S3 and offers practical guidance on the rule and Sink creation.
How It Works
Amazon S3 data integration in EMQX Cloud is a ready-to-use feature that can be easily configured for complex business development. In a typical IoT application, EMQX Cloud acts as the IoT platform responsible for device connectivity and message transmission, while Amazon S3 serves as the data storage platform, handling message data storage.
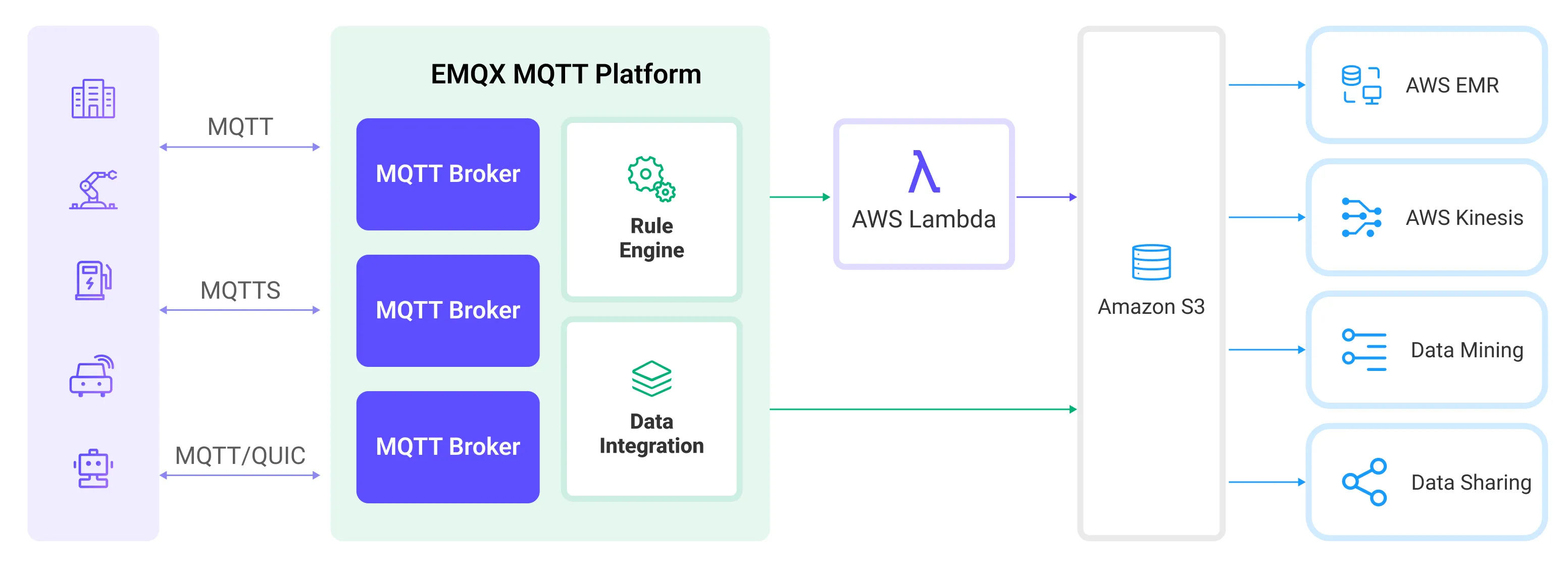
EMQX Cloud utilizes rules and Sinks to forward device events and data to Amazon S3. Applications can read data from Amazon S3 for further data applications. The specific workflow is as follows:
- Device Connection to EMQX Cloud: IoT devices trigger an online event upon successfully connecting via the MQTT protocol. The event includes device ID, source IP address, and other property information.
- Device Message Publishing and Receiving: Devices publish telemetry and status data through specific topics. EMQX Cloud receives the messages and compares them within the rules engine.
- Rules Engine Processing Messages: The built-in rules engine processes messages and events from specific sources based on topic matching. It matches corresponding rules and processes messages and events, such as data format transformation, filtering specific information, or enriching messages with context information.
- Writing to Amazon S3: The rule triggers an action to write the message to S3. Using the Amazon S3 Sink, users can extract data from processing results and send it to S3. Messages can be stored in text or binary format, or multiple lines of structured data can be aggregated into a single CSV file, depending on the message content and the Sink configuration.
After events and message data are written to Amazon S3, you can connect to Amazon S3 to read the data for flexible application development, such as:
- Data archiving: Store device messages as objects in Amazon S3 for long-term preservation to meet compliance requirements or business needs.
- Data analysis: Import data from S3 into analytics services like Snowflake for predictive maintenance, device efficiency evaluation, and other data analysis services.
Features and Advantages
Using Amazon S3 data integration in EMQX Cloud can bring the following features and advantages to your business:
- Message Transformation: Messages can undergo extensive processing and transformation in EMQX Cloud rules before being written to Amazon S3, facilitating subsequent storage and use.
- Flexible Data Operations: With the S3 Sink, specific fields of data can be conveniently written into Amazon S3 buckets, supporting the dynamic setting of bucket and object keys for flexible data storage.
- Integrated Business Processes: The S3 Sink allows device data to be combined with the rich ecosystem applications of Amazon S3, enabling more business scenarios like data analysis and archiving.
- Low-Cost Long-Term Storage: Compared to databases, Amazon S3 offers a highly available, reliable, and cost-effective object storage service, suitable for long-term storage needs.
These features enable you to build efficient, reliable, and scalable IoT applications and benefit from business decisions and optimizations.
Before You Start
This section introduces the preparations required before creating an Amazon S3 Sink in EMQX Cloud.
Prerequisites
- Understand rules.
- Understand data integration.
Network Settings
Since EMQX accesses Amazon S3 through public network, you need to enable NAT Gateway in your deployment. Click VAS from the top menu bar and select the NAT Gateway card, or you can select Enable NAT Gateway service in the bottom tab bar of the Deployment Overview page.
Prepare an S3 Bucket
EMQX Cloud supports Amazon S3 and other S3-compatible storage services. Here you can use AWS cloud services to create an S3 bucket.
In the AWS S3 Console, click the Create bucket button. Follow the instructions to enter the relevant information, such as bucket name and region, to create an S3 bucket. For detailed operations, refer to the AWS Documentation.
Set bucket permissions. After the bucket is created successfully, select the bucket and click the Permissions tab. Based on your needs, you can set the bucket to public read/write, private, or other permissions.Setting bucket access can be referenced in the following JSON:
json{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "Stmt1ListBucket", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": ["s3:ListBucket"], "Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::emqx-cloud-s3-connector-test"] }, { "Sid": "Stmt2GetAndPutObject", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": ["s3:GetObject", "s3:PutObject"], "Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::emqx-cloud-s3-connector-test/*"] }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "s3:ListAllMyBuckets", "Resource": "*" } ] }Obtain access keys. In the AWS Console, search for and select the IAM service. Create a new user for S3 and obtain the Access Key and Secret Key.
With the Amazon S3 bucket created and configured, you are now ready to create an Amazon S3 Sink in EMQX Cloud.
Create a Amazon S3 Connector
Before creating data integration rules, you need to create the corresponding connector.
- If it is the first time for you to create a connector, select Amazon S3 under the Data Persistence category. If you have already created connectors, select New Connector and then select Amazon S3 under the Data Persistence category.
- Connector Name: The system will automatically generate a connector name.
- Enter the connection information:
- Host: The host varies by region and is formatted as
s3.{region}.amazonaws.com. - Port: Enter
443. - Access Key ID and Secret Access Key: Enter the access keys created in AWS.
- You need to click Enable TLS and turn off TLS Verify.
- Host: The host varies by region and is formatted as
- Click the Test button. If the Amazon S3 service is accessible, a success prompt will be returned.
- Click the New button to complete the creation.
You have now completed the connector creation and will proceed to create a rule and Sink for specifying the data to be written into the S3 service.
Create a Rule
This section demonstrates how to create a rule in EMQX Cloud to process messages from the source MQTT topic t/# and write the processed results to the emqx-cloud-s3-connector-test bucket in S3 through the configured Sink.
Click New Rule in Rules area or click the New Rule icon in the Actions column of the connector you just created.
Enter the rule matching SQL statement in the SQL editor.
sqlSELECT * FROM "t/#"TIP
If you are new to SQL, you can click SQL Examples and Enable Debug to learn and test the rule SQL results.
Click Next to add an action that contains the Amazon S3 Sink.
Select the connector you just created from the Connector dropdown box.
Set the Bucket by entering
emqx-cloud-s3-connector-test. This field also supports${var}format placeholders, but ensure the corresponding name bucket is created in S3 in advance.Select ACL as needed, specifying the access permission for the uploaded object.
Select the Upload Method. The differences between the two methods are as follows:
- Direct Upload: Each time the rule is triggered, data is uploaded directly to S3 according to the preset object key and content. This method is suitable for storing binary or large text data. However, it may generate a large number of files.
- Aggregated Upload: This method packages the results of multiple rule triggers into a single file (such as a CSV file) and uploads it to S3, making it suitable for storing structured data. It can reduce the number of files and improve write efficiency.
The configuration parameters differ for each method. Please configure according to the selected method:
Expand Advanced Settings and configure the advanced setting options as needed (optional). For more details, refer to Advanced Settings.
Click the Confirm button to complete the rule creation.
In the Successful new rule pop-up, click Back to Rules, thus completing the entire data integration configuration chain.
Test the Rule
This section shows how to test the rule configured with the direct upload method.
Use MQTTX to publish a message to the topic t/1:
mqttx pub -i EMQX Platform_c -t t/1 -m '{ "msg": "hello S3" }'After sending a few messages, access the MinIO console or Amazon S3 console to see the result.
Log in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon S3 console: https://console.aws.amazon.com/s3/.
In the bucket list, select the bucket emqx-cloud-s3-connector-test to enter the bucket. You can see in the object list that the message just published has been successfully written into the msg object. Select the checkbox next to the object, then choose Download to download the object to your local machine for viewing.
Advanced Settings
This section delves into the advanced configuration options available for the S3 Sink. In the Dashboard, when configuring the Sink, you can expand Advanced Settings to adjust the following parameters based on your specific needs.
| Field Name | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| Buffer Pool Size | Specifies the number of buffer worker processes, which are allocated to manage the data flow between EMQX Cloud and S3. These workers temporarily store and process data before sending it to the target service, crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring smooth data transmission. | 16 |
| Request TTL | The "Request TTL" (Time To Live) configuration setting specifies the maximum duration, in seconds, that a request is considered valid once it enters the buffer. This timer starts ticking from the moment the request is buffered. If the request stays in the buffer for a period exceeding this TTL setting or if it is sent but does not receive a timely response or acknowledgment from S3, the request is deemed to have expired. | |
| Health Check Interval | Specifies the time interval (in seconds) for the Sink to perform automatic health checks on its connection with S3. | 15 |
| Max Buffer Queue Size | Specifies the maximum number of bytes that can be buffered by each buffer worker process in the S3 Sink. The buffer workers temporarily store data before sending it to S3, acting as intermediaries to handle the data stream more efficiently. Adjust this value based on system performance and data transmission requirements. | 256 |
| Query Mode | Allows you to choose between synchronous or asynchronous request modes to optimize message transmission according to different requirements. In asynchronous mode, writing to S3 does not block the MQTT message publishing process. However, this may lead to clients receiving messages before they arrive at S3. | Asynchronous |
| In-flight Window | "In-flight queue requests" refer to requests that have been initiated but have not yet received a response or acknowledgment. This setting controls the maximum number of in-flight queue requests that can exist simultaneously during Sink communication with S3. When Request Mode is set to asynchronous, the "Request In-flight Queue Window" parameter becomes particularly important. If strict sequential processing of messages from the same MQTT client is crucial, then this value should be set to 1. | 100 |