Ingest MQTT Data into RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is a widely used open-source message broker that implements the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP). It provides a robust and scalable platform for messaging between distributed systems. EMQX Cloud supports integration with RabbitMQ, allowing you to forward MQTT messages and events to RabbitMQ. It also enables consuming data from the RabbitMQ Server and publishing it to specific topics in the EMQX Cloud, achieving message delivery from RabbitMQ to MQTT.
This page provides a detailed overview of the data integration between EMQX Cloud and RabbitMQ, with practical instructions on creating and validating the data integration.
How It Works
The RabbitMQ data integration is an out-of-the-box feature in EMQX Cloud designed to bridge the gap between MQTT-based IoT data and RabbitMQ's powerful message queue processing capabilities. With a built-in rule engine component, the integration simplifies the process of ingesting data from EMQX Cloud to RabbitMQ for storage and management, eliminating the need for complex coding.
The diagram below illustrates a typical architecture of data integration between EMQX Cloud and RabbitMQ:
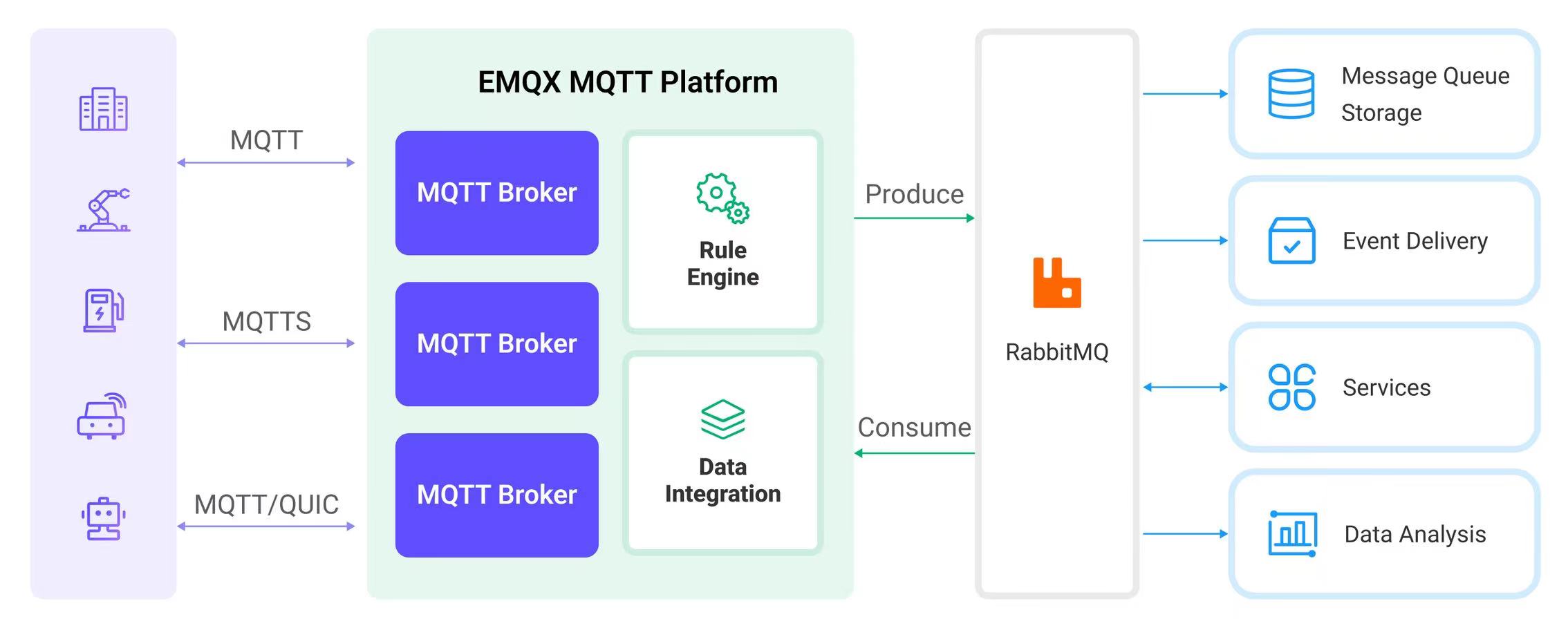
Ingesting MQTT data into RabbitMQ works as follows:
- Message publication and reception: Industrial IoT devices establish successful connections to EMQX Cloud through the MQTT protocol and publish real-time MQTT data to EMQX Cloud. When EMQX Cloud receives these messages, it initiates the matching process within its rules engine.
- Message data processing: When a message arrives, it passes through the rule engine and is then processed by the rule defined in EMQX Cloud. The rules, based on predefined criteria, determine which messages need to be routed to RabbitMQ. If any rules specify payload transformations, those transformations are applied, such as converting data formats, filtering out specific information, or enriching the payload with additional context.
- Message ingestion into RabbitMQ: When the rule has finished processing the message, it triggers an action of forwarding the messages to RabbitMQ. Processed messages will be seamlessly written into RabbitMQ.
- Data persistence and Utilization: RabbitMQ stores the messages in queues and delivers them to the appropriate consumers. The messages can be consumed by other applications or services for further processing, such as data analysis, visualization, and storage.
Features and Benefits
The data integration with RabbitMQ brings the following features and advantages to your business:
- Reliable IoT Data Message Delivery: EMQX Cloud ensures reliable connections and message delivery from devices to the cloud, while RabbitMQ handles message persistence and reliable delivery across different services, ensuring data reliability throughout various processes.
- MQTT Message Transformation: Using the rule engine, EMQX Cloud can filter and transform MQTT messages. Messages can undergo data extraction, filtering, enrichment, and transformation before being sent to RabbitMQ.
- Flexible Message Mapping: RabbitMQ data integration supports flexible mapping of MQTT topics to RabbitMQ Routing Key and Exchange, allowing seamless integration between MQTT and RabbitMQ.
- High Availability and Cluster Support: EMQX Cloud and RabbitMQ both support the construction of highly available message broker clusters, ensuring that the system can continue to provide services even in the event of node failures. Leveraging the cluster capabilities also provides excellent scalability.
- Processing Capabilities in High-Throughput Scenarios: RabbitMQ data integration supports both synchronous and asynchronous write modes, allowing for a flexible balance between latency and throughput according to different scenarios.
Before You Start
This section describes the preparations you need to complete before you start to create the RabbitMQ data integration, including how to create a RabbitMQ server and create RabbitMQ test exchange and queue.
Prerequisites
- Knowledge about data integration
- Knowledge about EMQX Cloud data integration rules
- Basic knowledge of UNIX terminal and commands
Set up Network
Before configuring data integration, you must create an EMQX Cloud deployment and ensure network connectivity between EMQX Cloud and the target service.
For Dedicated Flex deployments:
Create a VPC Peering Connection between the EMQX Cloud VPC and the target service VPC. After the peering connection is established, EMQX Cloud can access the target service through its private IP address.
If access through a public IP is required, configure a NAT Gateway to enable outbound connectivity.
For BYOC (Bring Your Own Cloud) deployments:
Create a VPC peering connection between the VPC where the BYOC deployment is running and the VPC hosting the target service. Once peering is in place, the target service can be accessed via its private IP address.
If the target service must be accessed through a public IP, configure a NAT Gateway in the BYOC VPC using your cloud provider’s console.
Start a RabbitMQ Server
This section introduces how to start a RabbitMQ server using Docker.
Run the following command to start a RabbitMQ server with the management plugin enabled. The management plugin allows you to inspect RabbitMQ with a web interface.
docker run -it --rm --name rabbitmq -p 5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 rabbitmq:3.11-managementYou can find more information about running RabbitMQ in Docker on Docker Hub.
Create an Exchange and Queue for Message Receiving
After the RabbitMQ server is started, you can use the RabbitMQ Management Web Interface to create a test exchange and a queue for receiving messages forwarded from EMQX Cloud. You can skip this section if you already have an exchange and queue to test with.
Open your web browser and navigate to http://{ip address}:15672/ to access the RabbitMQ Management Web Interface. On the login page, enter the default credentials and click Login.
- Username:
guest - Password:
guest
- Username:
Click the Exchanges tab in the top menu. Unfold Add a new exchange, and input the following information:
- Name: Type
test_exchange - Type: Select
directfrom the drop-down list - Durability: Select
Durableto make the exchange persistent, that is the queue exists after the RabbitMQ server is restarted. - Auto delete:
No - Internal:
No - Arguments: Leave empty
- Name: Type
Click the Add exchange button to create the test exchange.
Click the Queues tab in the top menu. Unfold Add a new queue, and input the following information:
- Type:
Default for virtual host - Name: Type
test_queue - Durability: Select
Durableto make the queue persistent, - Arguments: Leave empty
- Type:
Click the Add queue button to create the test queue. The new
test_queueshould appear in All queues section.Click the queue name test_queue to open its details page. Unfold Bindings. In the Add binding to this queue section, input the following information:
- From exchange: Type
test_exchange - Routing key: Type
test_routing_key - Arguments: Leave empty
- From exchange: Type
Click the Bind button to bind the
test_queueto thetest_exchangewith the specified routing key.
Create a Connector
Before creating data integration rules, you need to first create a RabbitMQ connector to access the RabbitMQ server.
Go to your deployment. Click Data Integration from the left-navigation menu. If it is the first time for you to create a connector, select RabbitMQ under the Data Forward category. If you have already created connectors, select New Connector and then select RabbitMQ under the Data Forward category.
Connector Name: The system will automatically generate a connector name.
Enter the connection information:
- Server: Enter
localhostor the actual hostname/IP if the RabbitMQ server is running remotely. - Port: Enter
5672or the actual port if different. - Username: Enter
guest. - Password: Enter
guest. - Virtual Host: Enter RabbitMQ virtual host;
/by default. - Enable TLS: If you want to establish an encrypted connection, click the toggle switch.
- Configure advanced settings according to your business needs (optional).
- Server: Enter
Click the Test button. If the Pulsar service is accessible, a prompt indicating connector available will be returned.
Click the New button to complete the creation.
Create a Producer Rule
This section demonstrates how to create a RabbitMQ Producer Rule and add an action to the rule via the EMQX Cloud Console.
Click New Rule in the Rules area or click the New Rule icon in the Actions column of the connector you just created.
Set the rules in the SQL Editor based on the feature to use, Our goal is to trigger the engine when the client sends a temperature and humidity message to the
temp_hum/emqxtopic. Here you need a certain process of SQL:sqlSELECT timestamp, clientid, payload FROM "temp_hum/emqx"TIP
If you are a beginner user, click SQL Examples and Try It Out to learn and test the SQL rule.
Click Next to add an action.
Select the connector you just created from the Connector dropdown box.
Configure the information for publishing messages from the EMQX Cloud to the RabbitMQ service:
Exchange: Enter
test_exchangecreated before, which means messages will be published to this exchange.Routing Key: Enter
test_routing_keycreated before, which is the RabbitMQ routing key to be used when publishing messages.In the Message Delivery Mode dropdown, select between
non_persistentandpersistent:non_persistent(default): Messages are not persisted to disk and may be lost if RabbitMQ restarts or crashes.persistent: Messages are persisted to disk, providing durability in case RabbitMQ restarts or crashes.
TIP
You may also need to set the queue and exchange as durable to prevent messages from being lost in case RabbitMQ is restarted. See the RabbitMQ documentation for more information.
Payload Template: The default value is an empty string, meaning the message payload will be forwarded as JSON-formatted text to RabbitMQ without modification.
You can also define a custom message payload format using placeholders within the template to dynamically include data from the incoming MQTT messages. For example, if you want to include the MQTT message payload and its timestamp in the RabbitMQ message, you can use the following template:
json{"payload": "${payload}", "timestamp": ${timestamp}}This template will produce a JSON-formatted message containing the payload and timestamp of the incoming MQTT message.
${payload}and${timestamp}are placeholders and will be replaced by the actual values from the message when it is forwarded to the RabbitMQ server.Wait for Publish Confirmations: Enabled by default to ensure that messages are successfully published to RabbitMQ.
TIP
With this option enabled RabbitMQ broker acknowledges the receipt of a published message before considering it successfully published, which improves the reliability of your message delivery.
Expand Advanced Settings to configure Sync/Async mode, queue and batch, and other parameters as appropriate Advanced Settings Options (optional)
Click the Confirm button to complete the rule creation.
In the Successful new rule pop-up, click Back to Rules, thus completing the entire data integration configuration chain.
Test the Producer Rule
You are recommended to use MQTTX to simulate temperature and humidity data reporting, but you can also use any other client.
Use MQTTX to connect to the deployment and send messages to the following Topic.
topic:
temp_hum/emqxclient id:
test_clientpayload:
json{ "temp": "27.5", "hum": "41.8" }
If the action and rule are created successfully, a message should have been published to the specified exchange in the RabbitMQ server with the specified routing key. Visit the RabbitMQ Management Console at http://{ip address}:15672 and navigate to the Queues section.
Verify that the message has been routed to the appropriate queue(s). Click the queue to see details and then click the Get Message(s) button to see the detailed message contents.
payload:
json{"payload": "{ "temp": "27.5", "hum": "41.8" }", "timestamp": 1711333401673 }
Create a RabbitMQ Source Rule
This section demonstrates how to create a RabbitMQ Source rule and add a republish action to the rule for forwarding the message consumed from the RabbitMQ source to the EMQX Cloud and publishing to the topic t/1.
Click New Rule in the Rules area or click the New Rule icon in the Actions column of the connector you just created.
Enter the rule ID
my_rule_source.Configure the source (Data Inputs) that triggers the rule. Click the Actions (Source) tab on the right side of the page, and click New Action (Source) to create a RabbitMQ Source.
In the slided pane, select RabbitMQ (Source) for the source type and click Next to enter the configuration step.
Select the previously created
my-rabbitmqconnector from the Connector dropdown box. You can also click the create button next to the dropdown box to quickly create a new connector in the popup, with required configuration parameters referring to Create a Connector.Configure the Source information to complete the setup for consuming messages from RabbitMQ to EMQX Cloud:
- Queue: Fill in the queue name
message-sendpreviously created in RabbitMQ. - No Ack: Select according to the situation, whether to consume messages from RabbitMQ using the
no_ackmode. Enablingno_ackmode means RabbitMQ does not wait for a message to be acknowledged after delivering it to a consumer, so it is removed from the queue immediately, even if the consumer has not processed it successfully. - Wait for Publish Confirmations: Specify whether to wait for RabbitMQ to confirm messages when using message publisher acknowledgments.
- Queue: Fill in the queue name
Advanced settings (optional): Use the default values.
Click the Confirm button to complete the creation of the Source, adding it to the rule data inputs. At the same time, you can see the rule SQL has changed to:
sql
sqlSELECT * FROM "$bridges/rabbitmq:my-rabbitmq-source"The rule SQL can access the following fields from the RabbitMQ Source, and you can adjust the SQL for data processing operations. The default SQL can be used here.
Field Name Description payload The content of the RabbitMQ message event The event topic, formatted as $bridges/rabbitmq:<source name>metadata Rule ID information timestamp The timestamp when the message arrives at EMQX node The name of the EMQX node where the message arrives queue The name of the queue from which the message was consumed exchange The exchange through which the message was routed routing_key The routing key used to route the message from the exchange to the queue Click Next, and create the output action.
In the new output action, select Republish.
Fill in the message republish configuration:
- Topic: The topic to publish to MQTT, enter
t/1here. - QoS: Select
0,1,2, or${qos}, or enter a placeholder to set QoS from other fields. Selecting${qos}here means to follow the original message's QoS. - Retain: Select
trueorfalse. Determine whether to publish the message as a retained message, placeholders can also be entered to set the retain message flag from other fields. In this example, selectfalse. - Payload: Set a template for generating the forwarded message payload. Leaving it blank by default means forwarding the rule output result. Here you can enter
${payload}to indicate forwarding Payload only. - MQTT 5.0 Message Properties: Disabled by default. For detailed settings, see Add Republish Action.
- Topic: The topic to publish to MQTT, enter
Use default settings for other configurations, and click the Confirm button to complete the creation of the output action.
After successful creation, you will return to the New Rule page. In the Rules list, you can see the newly created rule. Republish actions are currently not displayed in the Actions (Source). If needed, click the rule edit button, and you can see the republish output action at the bottom of the rule settings.
Test the RabbitMQ Source Rule
Use MQTTX CLI to subscribe to the topic
t/1:bash
mqttx sub -t t/1You can produce a message in RabbitMQ using the following command:
bash
rabbitmqadmin --username=guest --password=guest \ publish routing_key=message-send \ payload="{ \"msg\": \"Hello EMQX\"}"publishis the command used to publish a message.routing_key=message-sendoption is used to set the message's routing key. In this example, the queue's name is used as the routing key.payload="{ \"msg\": \"Hello EMQX\"}"option is used to set the content of the message.
Alternatively, you can also publish a message from the RabbitMQ management interface:
- Click the Queues tab in the top menu bar.
- Click message-send in the Name column to open its details page.
- Expand Publish message, enter
"Hello EMQX"in the Payload box, and then click the Publish message button.
You will see the output in MQTTX:
bash[2024-2-23] [16:59:28] › payload: {"payload":{"msg":"Hello EMQX"},"event":"$bridges/rabbitmq:my-rabbitmq-source","metadata":{"rule_id":"rule_0ly1"},"timestamp":1708678768449,"node":"emqx@127.0.0.1"}