Bridge with Other MQTT Services
MQTT Broker data integration provides EMQX with functionality to connect to another EMQX cluster or another MQTT service for message bridge, enabling cross-network, cross-service data interaction and communication. This page introduces the working principle of the MQTT message bridge in EMQX Cloud and offers practical guidance on creating and verifying message bridges.
How It Works
During bridging, EMQX Cloud establishes an MQTT connection with the target service as a client, achieving bidirectional message transmission through the publish-subscribe model:
- Outgoing messages: Publishes messages from local topics to specified topics on the remote MQTT service.
- Incoming messages: Subscribes to the topics of the remote MQTT service and forwards their messages to the current deployment.
EMQX Cloud supports configuring multiple bridging rules on the same connection, each with different topic mappings and message transformation rules, implementing a function similar to message routing. During bridging, you can also process messages through the Rule Engine to filter, enrich, and transform messages before forwarding.
The diagram below shows a typical architecture of data integration between EMQX Cloud and other MQTT services:
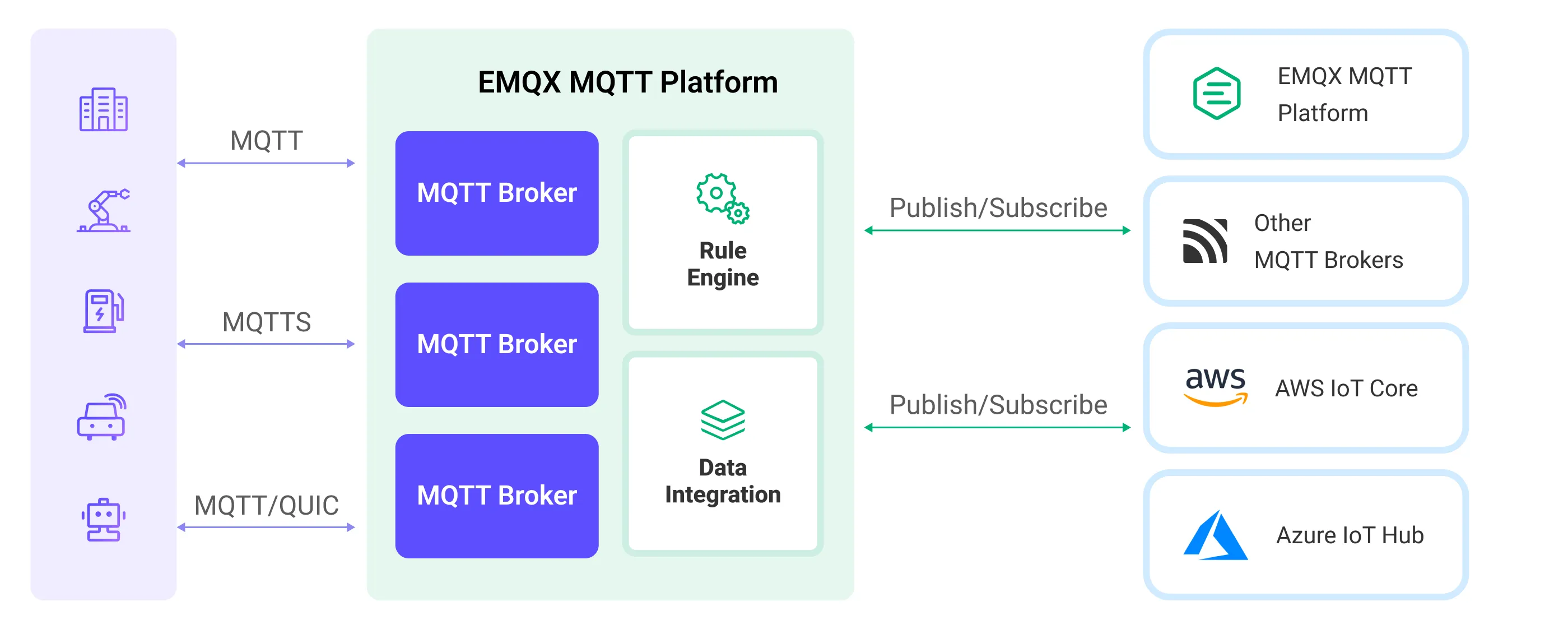
Features and Benefits
The MQTT Broker data integration has the following features and benefits:
- Extensive Compatibility: Uses the standard MQTT protocol to integrate with major IoT platforms such as AWS IoT Core and Azure IoT Hubs, as well as open-source and industry MQTT brokers.
- Flexible Topic Mapping: Supports adding prefixes to topics and dynamically constructing topics using the client's contextual information (such as client ID, username, etc.) to enable customized message routing.
- High Performance: Improves throughput and reduces latency through optimizations such as connection pooling and shared subscriptions.
- Payload Transformation: Enables SQL-based processing of message payloads, including extraction, filtering, enrichment, and transformation before forwarding messages.
- Metrics Monitoring: Provides real-time metrics such as message counts, success and failure rates, and throughput to help monitor integration health and performance.
Before You Start
Prerequisites
- Knowledge about data integration
- Knowledge about data integration rules
Prepare MQTT Connection Information
Before creating an MQTT Broker data integration, you need to obtain the connection information for the remote MQTT service, including:
- MQTT Service Address: The address and port of the target MQTT service, for example,
broker.emqx.io:1883. - Username: The username required for the connection. If the target service does not require authentication, this can be left blank.
- Password: The password required for the connection. If the target service does not require authentication, this can also be left blank.
- Protocol Type: It is important to determine whether the target service has enabled TLS and whether it is using MQTT over TCP/TLS protocol. Note that the EMQX Cloud MQTT bridge currently does not support protocols like MQTT over WebSocket and MQTT over QUIC.
- Protocol Version: The protocol version used by the target MQTT service. EMQX Cloud supports MQTT 3.1, 3.1.1, and MQTT 5.0.
The data integration provides good compatibility and support for the EMQX Cloud or other standard MQTT servers. If you need to connect to other types of MQTT services, you can refer to their relevant documentation to obtain the connection information. Generally, most IoT platforms provide standard MQTT access methods, and you can convert device information into the aforementioned MQTT connection information based on their guidance.
Notice for Cluster Mode
When the EMQX Cloud is running in cluster mode or when a connection pool is enabled, using the same client ID to connect multiple nodes to the same MQTT service usually leads to device conflicts. Therefore, the MQTT message bridge currently does not support setting a fixed client ID.
Set up Network
Before configuring data integration, you must create an EMQX Cloud deployment and ensure network connectivity between EMQX Cloud and the target service.
For Dedicated Flex deployments:
Create a VPC Peering Connection between the EMQX Cloud VPC and the target service VPC. After the peering connection is established, EMQX Cloud can access the target service through its private IP address.
If access through a public IP is required, configure a NAT Gateway to enable outbound connectivity.
For BYOC (Bring Your Own Cloud) deployments:
Create a VPC peering connection between the VPC where the BYOC deployment is running and the VPC hosting the target service. Once peering is in place, the target service can be accessed via its private IP address.
If the target service must be accessed through a public IP, configure a NAT Gateway in the BYOC VPC using your cloud provider’s console.
Create a Connector
This section guides you on how to configure a connection with a remote MQTT server, using EMQX's online MQTT server as an example.
Before creating rules for data integration, you need to create an MQTT Broker connector to access the MQTT service. The connector can be used for both MQTT (Sink) and MQTT (Source).
Select Data Integration from the deployment menu, then select MQTT (Sink) under the Data Forward category. If you have already created connectors, select New Connector and then select MQTT (Sink) under the Data Forward category.
Connector Name: The system will automatically generate a connector name.
Configure the connection information:
MQTT Broker: Only supports MQTT over TCP/TLS. Set this to
broker.emqx.io:1883.ClientID Prefix: This can be left blank. In actual use, specifying a client ID prefix can facilitate client management. EMQX Cloud will automatically generate client IDs based on the client ID prefix and the size of the connection pool. For more information, see Connection Pool and Client ID Generation Rules.
Username and Password: These can be left blank, as authentication is not required for this server.
Keepalive: Specify the desired keepalive interval.
MQTT Version: Choose the appropriate version for the broker connection.
Static ClientId Entries: (Advanced) This section allows you to configure static client IDs for the connector to ensure stable connections, especially when connecting to services like Azure IoT Hubs. See the Configure Static Client IDs for more details on how to configure this.
TIP
If static client ID entries are defined, only the EMQX nodes that have been explicitly assigned static client IDs will start MQTT connections.
Leave other configurations as default.
Click the Test button. If the MQTT Broker is accessible, a prompt indicating connector available will be returned.
Click the New button to complete the creation.
Next, you can create data bridge rules based on this Connector.
Connection Pool and Client ID Generation Rules
EMQX Cloud enables multiple clients to simultaneously connect to the bridged MQTT service. When creating a Connector, you can set up an MQTT client connection pool and configure its size to indicate the number of client connections in the pool. The connection pool maximizes server resources for greater message throughput and better concurrent performance, which is crucial for handling high-load, high-concurrency scenarios.
As the MQTT protocol requires clients connected to an MQTT server to have a unique client ID, and since EMQX Cloud can be deployed in a cluster, each client in MQTT bridging is assigned a unique client ID. EMQX Cloud automatically generates client IDs according to the following pattern:
[Client ID Prefix]:{Connector Name}{8-digit Random String}:{Connection Sequence Number in the Pool}For example, if the client ID prefix is myprefix and the Connector name is foo, an actual client ID might be:
myprefix:foo2bd61c44:1Configure Static Client IDs
In some use cases, you only have a finite set of client IDs to use in an integration. In this case, it is possible to assign static client ID sets to individual nodes while configuring the connector. To configure static client IDs, provide a list of client IDs for each node in your EMQX cluster. For each client ID, you can specify the corresponding username and password. This is particularly useful for scenarios like connecting to Azure IoT Hubs, where each device (client ID) requires a unique set of credentials.
To configure static client IDs, follow these steps:
Click Advanced Settings when creating the Connector.
In the Static ClientId Entries section, click the Add button to add a new static client ID entry. You can add multiple entries for different nodes as needed.
For each entry, fill in the following fields:
- Node Name: Specify the node where the client ID will be assigned. For example,
emqx@10.0.0.1. You need to submit a ticket to obtain the EMQX node name for the current deployment. - Client ID: Enter the static client ID. For example,
device1. You can add multiple client IDs for a node as needed by clicking Add.- Username: (optional) Provide the username associated with this client ID for authentication.
- Password: (optional) Enter the password associated with this client ID. This is the credential used to authenticate the device or client, which may be a device-specific key, secret, or certificate, depending on the platform (e.g., an authentication key in Azure IoT Hubs).
Configuration Example:
Node Client ID Username (optional) Password (optional) emqx@10.0.0.1clientid1username1secret1clientid3emqx@10.0.0.2clientid2username2emqx@10.0.0.3clientid4clientid5- Node Name: Specify the node where the client ID will be assigned. For example,
If static client IDs are configured, only MQTT connections using these client IDs will be started. Any configurations for dynamic client IDs, such as pool_size or clientid_prefix, will not take effect.
Create a Rule with MQTT (Sink)
This section demonstrates how to create a rule for specifying data to be forwarded to a remote MQTT service.
Click New Rule in the Rules area or click the New Rule icon in the Actions column of the connector you just created.
Set the rules in the SQL Editor based on the feature to use, Our goal is to trigger the engine when the client sends a temperature and humidity message to the
temp_hum/emqxtopic. Here you need a certain process of SQL:sqlSELECT topic, payload FROM "temp_hum/emqx"TIP
If you are a beginner user, click SQL Examples and Try It Out to learn and test the SQL rule.
Click Next to add an action.
Select the connector you just created from the Connector dropdown box.
Configure the information for publishing messages from EMQX Cloud to the external MQTT service:
- Topic: The topic to publish to the external MQTT service, supporting
${var}placeholders. Enterpub/${topic}here, meaning the original topic will be prefixed withpub/for forwarding. For example, if the original message topic ist/1, the topic forwarded to the external MQTT service will bepub/t/1. - QoS: The QoS for message publishing. Select from the dropdown options:
0,1,2, or${qos}, or enter a placeholder to set QoS from another field. Here, select${qos}to follow the QoS of the original message. - Retain: Select
true,false, or${falgs.retain}to decide whether to publish the message as retained, or enter a placeholder to set the retain flag from other fields. Here, select${falgs.retain}to follow the retain flag of the original message. - Payload: The template used to generate the payload for the forwarded message. Leave blank by default, which means forwarding the rule output result. Here, you can enter
${payload}to forward only the payload.
- Topic: The topic to publish to the external MQTT service, supporting
Use default values for other configurations and click the Confirm button to complete the rule creation.
In the Successful new rule pop-up, click Back to Rules, thus completing the entire data integration configuration chain.
After successful creation, you will return to the rule creation page. In the Rules list, you can see the newly created rule. In the Actions list, the Action (Sink) will show the list of data import actions.
Test the Rule
You are recommended to use MQTTX to simulate temperature and humidity data reporting, but you can also use any other client.
Subscribe to the pub/# topic in the external MQTT Service:
bashmqttx sub -t pub/# -q 1 -h broker.emqx.io -vUse MQTTX to connect to the deployment and send messages to the following Topic.
topic:
temp_hum/emqxclient id:
test_clientpayload:
json{ "temp": "27.5", "hum": "41.8" }
You can subscribe to the
pub/temp_hum/emqxtopic in MQTTX to receive the message, indicating that the message has been successfully forwarded from EMQX Cloud to the external MQTT service:bash[2024-3-21] [10:43:13] › topic: pub/temp_hum/emqx payload: { "temp": "27.5", "hum": "41.8"}
Create a Rule with MQTT (Source)
This section demonstrates how to create a rule to forward data from a remote MQTT service to the current deployment. You need to create both an MQTT (Source) and a Message Republishing action to facilitate the subscription from the remote MQTT service to EMQX, as well as the forwarding of the subscribed data.
The creation methods for MQTT (Source) connectors and MQTT (Sink) connectors are the same, refer to Create a Connector.
Click the new rule icon under the Actions column in the connector list, or click New Rule in the rule list to enter the New Rule step page.
For the source data rule, you first need to configure the input action. The rule editing page will automatically pop up the input action configuration, or select Actions (Source) -> New Action on the right side of the panel, select MQTT (Source), and click Next to enter the configuration.
- Select the connector created before.
- Topic: Enter the topic to subscribe to from the remote MQTT, such as the topic
temp_hum/emqxsubscribed from the remote end. - QoS: Choose the message QoS.
Click the Confirm button to complete the configuration.
The SQL Editor will update the data source field:
sqlSELECT * FROM "$bridges/mqtt:source-d1f51e81"Click Next to start creating the output action.
In the new output action, select Republish.
Configure the output action information:
- Topic: The MQTT topic to forward to, supports
${var}format placeholders. Here, entersub/${topic}, indicating that asub/prefix is added to the original topic for forwarding. For example, when the original message topic ist/1, the forwarded topic would besub/t/1. - QoS: Message publish QoS, choose from
0,1,2, or${qos}. You can also enter placeholders to set QoS from other fields, here choosing${qos}indicates following the original message's QoS. - Retain: Choose
true,false, or${flags.retain}, to confirm whether to publish messages as retain messages, also can enter placeholders to set retain message flags from other fields. Here, choosing${flags.retain}indicates following the original message's retain message flag. - Message Template: Template for generating the forwarded message Payload, default is blank to forward the rule output results. Here, entering
${payload}means only forwarding the Payload.
- Topic: The MQTT topic to forward to, supports
Use default settings for other configurations, and click the Confirm button to complete the creation of the output action.
After successful creation, you will return to the rule creation page. The Republish action is currently not displayed in the Actions (Source). If needed, click the rule edit button, and you can see the Republish output action at the bottom of the rule settings.
Test the Rule
The rule created is configured to bridge messages from the external MQTT service's temp_hum/emqx topic to the current deployment's sub/${topic} topic. Therefore, when you publish messages to the external MQTT service's temp_hum/emqx topic, the messages will be forwarded to the deployed sub/temp_hum/emqx topic.
The following steps demonstrate how to use MQTTX to send messages to the external MQTT service and subscribe to the forwarded topic to receive messages.
Use MQTTX to subscribe to the current deployment's topic
sub/#.Use MQTTX to publish messages to the external MQTT service's
temp_hum/emqxtopic:json{ "temp": 55, "hum": 32 }MQTTX receives messages within the current deployment's
sub/temp_hum/emqxtopic:json{ "temp": 55, "hum": 32 }
Troubleshooting
This section provides solutions to common issues you may encounter when using the MQTT Connector in the MQTT broker data integration.
“Inconsistent for Nodes in the Cluster” Appears in the MQTT Connector Interface
Description
This issue occurs when the cluster nodes display inconsistent status for the MQTT broker Connector.
Possible Causes
Remote MQTT Broker Connection Limits
The remote MQTT broker may have reached its connection limit or imposed restrictions, preventing EMQX cluster nodes from establishing a proper connection.
VPC Peering Connection Restrictions
When using a VPC peering connection, security group rules may restrict access to the remote broker by the EMQX node.
Solution
For remote broker limits:
Reduce the connection pool size to half of its current value in the MQTT connector configuration, and then retry.
For VPC restrictions:
Verify that the security group rules allow access from the VPC subnet where EMQX is deployed (typically
10.x.x.0/24) to the remote broker.If the issue persists, submit a support ticket to EMQ support.
“Axios Error: timeout” When Updating or Saving MQTT Connector Configuration
Description
A timeout error occurs when updating or saving an MQTT connector configuration that uses shared subscriptions.
Possible Cause
When the source connector includes multiple connection pools and subscription topics, EMQX must re-establish all shared subscription connections during updates.
If the configuration is large (for example, 16 pools across 2 nodes with multiple topics per client), the remote broker processes subscription acknowledgments (SUBACK) sequentially during re-establishment.
Because of performance latency in shared subscriptions, the initialization process can take longer to complete, causing the console or API request to exceed the 30-second timeout and result in a timeout error.
Solution
- Create separate connectors for different data sources, for example, each connector handling 2–4 sources.
- Set the connection pool size in each connector to
2to improve reinitialization performance.
MQTT Action Data Not Forwarded and Messages Dropped Due to Expiration
Description
Some MQTT action data may not be forwarded successfully, and monitoring may show messages being dropped because they expired before processing.
Possible Cause
If the remote broker cannot handle the current throughput or the connection pool size is insufficient, messages accumulate in the buffer queue. By default, messages in this queue have a time-to-live (TTL) of 45 seconds. Once expired, they are discarded.
Solution
- Verify that the remote broker can handle the current transactions per second (TPS).
- Increase the connection pool size according to throughput requirements.
- Adjust the request timeout value in the Actions configuration to prevent premature message expiration.